Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reproductive System
Uploaded by
Arvin Villanueva0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views18 pagesThis document summarizes the male and female reproductive systems. It explains that the male system produces sperm in the testes and transports it through the vas deferens. The female system produces eggs in the ovaries and transports them through the fallopian tubes where fertilization can occur if sperm enters the egg. Fertilization results in a zygote that implants in the uterus and is protected by an amnion sac filled with fluid.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes the male and female reproductive systems. It explains that the male system produces sperm in the testes and transports it through the vas deferens. The female system produces eggs in the ovaries and transports them through the fallopian tubes where fertilization can occur if sperm enters the egg. Fertilization results in a zygote that implants in the uterus and is protected by an amnion sac filled with fluid.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views18 pagesReproductive System
Uploaded by
Arvin VillanuevaThis document summarizes the male and female reproductive systems. It explains that the male system produces sperm in the testes and transports it through the vas deferens. The female system produces eggs in the ovaries and transports them through the fallopian tubes where fertilization can occur if sperm enters the egg. Fertilization results in a zygote that implants in the uterus and is protected by an amnion sac filled with fluid.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
Reproductive System
Why do we need to reproduce?
• To ensure survival of the species
• To produce egg and sperm cells
• To transport and sustain these cells
• To nurture the developing offspring
• To produce hormones
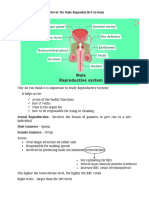
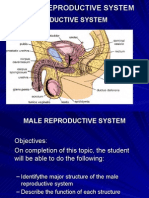
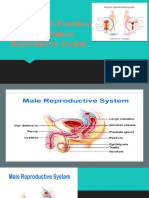
Male Reproductive System
Male Testes – produce sperm
• Also known as testicles and gonads
• Male Duct System Vas Deferens – transports mature sperm to the
urethra Epididymis – sperm mature in epididymis
• Male Seminal vesicles – attached to vas deferens – produce a sugar-
rich fluid that provides energy to sperm
• Male Prostate Gland – makes fluid
• Male Urethra – tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside of the body – also carries sperm out of
the body
Male
The Journey of the Sperm
Female Reproductive System
Female
• Female Vagina – canal that joins the cervix to the outside of the body – also is known as the birth canal
• Female Uterus – hollow organ that is the home to a developing fetus
• Female Ovaries – produce eggs and hormones – oval-shaped glands
that are located on either side of the uterus
• Female Fallopian Tubes – tunnels for the egg cell to travel from the
ovaries to the uterus – where fertilization happens
The Journey of the Egg Cell
• Male + Female = Fertilization The Magic of Life
• Male + Female = Fertilization Sperm enters the egg cell
• Male + Female = Fertilization – fertilization of an egg by a sperm,
normally occurs in the fallopian tubes – fertilized egg cell is called a
zygote – the zygote then moves to the uterus, where it implants into
the lining of the uterine wall
• Amnion – transparent sac that protects the baby inside – filled with
amniotic fluid
You might also like
- Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemMary Grace NovidaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument14 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemapi-327037403No ratings yet
- Our Body SystemsDocument26 pagesOur Body Systemsclay adrianNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Lecture WebsiteDocument35 pagesReproductive System Lecture Websiteapi-295110496No ratings yet
- SCIENCE10Document19 pagesSCIENCE10Jowelyn MaderalNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesThe Reproductive SystemKem Marian MauricioNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesScience 10 - Reproductive SystemHanabi Scarlet ShadowNo ratings yet
- Animal Reproduction and GeneticsDocument74 pagesAnimal Reproduction and GeneticsdassureshkumarNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesBiology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemRYLE IBANEZNo ratings yet
- G5 Science Week 11Document30 pagesG5 Science Week 11Park Vincent PrinceNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageFemale Reproductive SystemMaura FecakNo ratings yet
- Animal Reproduction and GeneticsDocument73 pagesAnimal Reproduction and GeneticsZhedriex EspirituNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument21 pagesReproductive SystemAshley RañesesNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument20 pagesReproductive SystemGodfrey MuchaiNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesMale and Female Reproductive Systemchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SysytemDocument21 pagesMale Reproductive SysytemJacquelyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System - 1Document62 pagesFemale Reproductive System - 1Reendelle JamiatreNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document3 pagesScience 10Andrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction WJECDocument12 pagesHuman Reproduction WJECTharanga HewabuhageNo ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive SytemDocument23 pagesThe Human Reproductive SytemAbegail Bugayong ViceraNo ratings yet
- 16.4 Sexual Reproduction in HumansDocument63 pages16.4 Sexual Reproduction in Humansnie20060301No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesSexual Reproductive Systemred JimNo ratings yet
- MF009 6B Human Reproduction System James LDocument26 pagesMF009 6B Human Reproduction System James LPikuNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson 1 G5 1Document31 pagesScience Lesson 1 G5 1Sarah JumalonNo ratings yet
- Reproduction From Anatomy Class 2009Document28 pagesReproduction From Anatomy Class 2009api-209542414No ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument24 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproduceShubhada WarakeNo ratings yet
- Rhsi, LSDocument56 pagesRhsi, LSMary AkellaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ReproDocument4 pagesReviewer Repromelody111mendozaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument81 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Male Reproductive SystemMj BrionesNo ratings yet
- Y11 Hum - Rep1 20 3 17Document8 pagesY11 Hum - Rep1 20 3 17Rabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumansDocument14 pagesReproduction in HumansarnoldnsondojrNo ratings yet
- Reproduction SystemDocument81 pagesReproduction SystemGabrielle GreyNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument26 pagesReproductive SystemViscount MalamiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 101 Reproductive SystemDocument52 pagesLesson 101 Reproductive SystemtheacielaNo ratings yet
- Safe Environment ContractDocument37 pagesSafe Environment Contractdipanjang panjanginNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 1Document19 pagesThe Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 1valjulene monteNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Sem4 2008-2Document16 pagesKuliah Sem4 2008-2cathencloxNo ratings yet
- 02 Overview of The Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument30 pages02 Overview of The Male and Female Reproductive SystemsOsman Saidu SesayNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Document19 pagesThe Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1lourd nabNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumansDocument24 pagesReproduction in Humanssnoops moopsNo ratings yet
- 3Q Module 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systems 1Document29 pages3Q Module 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systems 1Pau BluzaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SysytemDocument32 pagesMale Reproductive SysytemJacquelyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systempt09651934948No ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive System and MenstruationDocument11 pagesMale and Female Reproductive System and MenstruationSav LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Q4 Lesson 4 Plant and Animal ReproductionDocument38 pagesQ4 Lesson 4 Plant and Animal ReproductionPhan MhiveNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System: by Malak, Nancy, AminaDocument10 pagesHuman Reproductive System: by Malak, Nancy, Aminakhadija farahNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System: by Malak, Nancy, AminaDocument10 pagesHuman Reproductive System: by Malak, Nancy, Aminakhadija farahNo ratings yet
- Principles of Reproduction and BreedingDocument65 pagesPrinciples of Reproduction and BreedingRovie Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction Part 1Document20 pagesSexual Reproduction Part 1Jurez N. EvansNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemJune PinedaNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System AutosavedDocument49 pagesThe Female Reproductive System AutosavedVenice izza Venancio100% (1)
- The Reproductive System: Creating New Life ReproductionDocument29 pagesThe Reproductive System: Creating New Life ReproductionHildaAmaliaNo ratings yet
- 15 - Swine Reproductive SystemDocument23 pages15 - Swine Reproductive SystemElijahNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument14 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemShiena marie Ma-alatNo ratings yet
- Malereproductivesystem BriefDocument30 pagesMalereproductivesystem Briefanju kumawatNo ratings yet
- LTO in ScienceDocument1 pageLTO in ScienceNorman M.No ratings yet
- L3 Teachsci Human ReproductionDocument72 pagesL3 Teachsci Human ReproductionMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- The Principles of ArtzzzDocument62 pagesThe Principles of ArtzzzArvin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Cost of Good SaleDocument6 pagesCost of Good SaleArvin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Cost of Good SaleDocument6 pagesCost of Good SaleArvin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Direction: Trace The Given Letters, and Fill The Missing Alphabets in The BoxDocument2 pagesDirection: Trace The Given Letters, and Fill The Missing Alphabets in The BoxArvin VillanuevaNo ratings yet