Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Male and Female Reproductive System
Uploaded by
christopher daniolco0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesMale and Female Reproductive System
Uploaded by
christopher daniolcoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
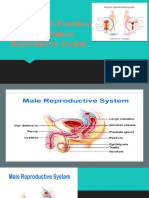
Male and Female Reproductive System
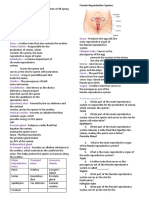
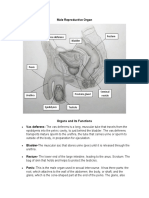
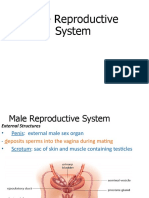
Male Reproductive System
Testis- Where sperms are produced
Epididymis- Where sperms are temporarily stored
Vas deferens - Where the sperm passes through from the testis before it joins the
urethra
Urethra - Connected to the urinary bladder; serves as passageway of both sperm and
urine and terminates in the external urinary meatus of the penis
Seminal vesicle - Secretes fluid that forms part of the semen; secretion gives the semen
its alkaline characteristic to counteract the acidity of the vaginal tract and therefore
protect the sperm; the fluid also contains sugars like fructose
Prostate gland - Secretes fluid that also provides alkalinity to the semen; it also contains
proteolytic enzymes, citric acid, phosphatases, and lipids
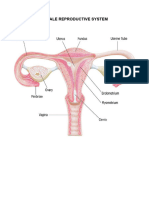
Female Reproductive System
Vagina- Main entrance to the female reproductive tract; receives the penis during sexual
intercourse
Cervix- Where the vagina ends; projection of the uterus into the vagina; leads to the
uterus
Uterus- Also known as the womb; where the embryo develops; with thick muscular walls,
blood vessels; and the endometrial lining
Endometrium- Innermost lining of the uterus where the embryo implants and develop
Fallopian tubes- Also known as oviducts; paired tubes that are connected to the uterus
and terminate near the ovaries; this is where fertilization takes place
Ovaries- Female gonads that release the oocytes during ovulation, which are then
caught by the fimbrae of the fallopian tubes in order for the oocytes to pass on to the
fallopian tubes
You might also like
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesMale Reproductive SystemRaisashimi M.S.100% (1)
- Science 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesScience 10 - Reproductive SystemHanabi Scarlet ShadowNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageMale Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemEunimae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System:: Summary QuestionDocument4 pagesMale Reproductive System:: Summary QuestionwagkangtangaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive ReviewerDocument1 pageReproductive ReviewerMaricel BalagsoNo ratings yet
- SXSXDocument27 pagesSXSXJoevany E. BigorniaNo ratings yet
- S10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREDocument35 pagesS10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREREGLOS, Marie Nhelle K.No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument18 pagesReproductive SystemArvin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Summary QuestionDocument4 pagesSummary QuestionwagkangtangaNo ratings yet
- Notes For HSB ExamDocument3 pagesNotes For HSB Examdanielle napierNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System: Alyssa Ashley R. DiegoDocument46 pagesThe Reproductive System: Alyssa Ashley R. DiegoteacherashleyNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewDocument3 pagesScience ReviewAinieNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document2 pagesQuiz 3sitti marwa baraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systempt09651934948No ratings yet
- Reproductive System Table of FunctionsDocument1 pageReproductive System Table of Functionseborangez5No ratings yet
- Y11 Hum - Rep1 20 3 17Document8 pagesY11 Hum - Rep1 20 3 17Rabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesReproductive SystemMatt MasilonganNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument75 pagesReproductive SystemErnie SyarinaNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesThe Reproductive SystemKem Marian MauricioNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument26 pagesScience Notespiecreamy51No ratings yet
- Human Male and Female Reproductive System (Reviewer)Document8 pagesHuman Male and Female Reproductive System (Reviewer)Justine Yuan DoradoNo ratings yet
- 1a. Reproductive OrgansDocument60 pages1a. Reproductive OrgansJerrald Meyer L. BayaniNo ratings yet
- MATERNAL-AND-CHILD-NURSING Notes For BoardsDocument10 pagesMATERNAL-AND-CHILD-NURSING Notes For BoardsJill Margarett BongatoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System 1Document56 pagesReproductive System 1zekesergmanuedenina08No ratings yet
- BIO 282 Male Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesBIO 282 Male Reproductive SystemLira Pagara100% (1)
- Male Reproductive System ReviewerDocument3 pagesMale Reproductive System ReviewerNors SulaboNo ratings yet
- Ovaries: The Female Gonads, The Ovaries Produce Ova. When One Matures, It Is Released Down Into A Fallopian TubeDocument2 pagesOvaries: The Female Gonads, The Ovaries Produce Ova. When One Matures, It Is Released Down Into A Fallopian TubeCyril AlngogNo ratings yet
- Science QUARTER 2 WEEK 1Document2 pagesScience QUARTER 2 WEEK 1Hadi DaquisNo ratings yet
- PSGUNP279020221123075249578Unit 2 - Lesson 3 - Human Reproductive System - OrgansDocument11 pagesPSGUNP279020221123075249578Unit 2 - Lesson 3 - Human Reproductive System - OrgansAshneel ChakravortyNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document3 pagesScience 10Andrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- 1.the Reproductive SystemDocument47 pages1.the Reproductive SystemAkai ShuichiNo ratings yet
- Science 5Document26 pagesScience 5barangay89zone9No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction WJECDocument12 pagesHuman Reproduction WJECTharanga HewabuhageNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument20 pagesReproductive SystemGodfrey MuchaiNo ratings yet
- G10 3RD Quarter ScienceDocument15 pagesG10 3RD Quarter ScienceRaven MayoNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Sem4 2008-2Document16 pagesKuliah Sem4 2008-2cathencloxNo ratings yet
- Ana ReproDocument4 pagesAna ReproFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- 3rd Monthly Test ReviewerDocument5 pages3rd Monthly Test ReviewerLaxen JunioNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive OrganDocument4 pagesMale and Female Reproductive OrganLawren Ira LanonNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson 1 G5 1Document31 pagesScience Lesson 1 G5 1Sarah JumalonNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument68 pagesThe Reproductive SystemStef FieNo ratings yet
- Cmca 1Document5 pagesCmca 1Erika Mae Sta. MariaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - Bio 2 - 12 Stem - l11Document4 pagesReproductive System - Bio 2 - 12 Stem - l11Lyka Lobido CabeltesNo ratings yet
- Malereproductivesystem BriefDocument30 pagesMalereproductivesystem Briefanju kumawatNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemCharice RamosNo ratings yet
- 2 The Reproductive SystemDocument122 pages2 The Reproductive SystemBryan Lloyd Ballestar RayatNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemKrishnan Nicolai MiguelNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Power Point AckroydDocument7 pagesMale Reproductive System Power Point AckroydSham JoanNo ratings yet
- SISTEM REPRODUKSI PADA MANUSIA - Power PDocument38 pagesSISTEM REPRODUKSI PADA MANUSIA - Power PWike RevanalizaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemMary Grace NovidaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 - The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesSCIENCE 10 - The Reproductive SystemJyña Khura TanoNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument14 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemShiena marie Ma-alatNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 10 ICSEDocument5 pagesPhysics Class 10 ICSEmohammedumar7864521No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument81 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Male Reproductive SystemMj BrionesNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemsDocument9 pagesReproductive Systemsapi-376200062No ratings yet
- Rhsi, LSDocument56 pagesRhsi, LSMary AkellaNo ratings yet
- The Path Sperm-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageThe Path Sperm-WPS OfficeBryan Reufrir CortezanoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument21 pagesReproductive SystemAshley RañesesNo ratings yet
- BIO 282 Male Reproductive System - FINALDocument46 pagesBIO 282 Male Reproductive System - FINALLira PagaraNo ratings yet
- Earth HistoryDocument7 pagesEarth Historychristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Biology Animal NutritionDocument6 pagesBiology Animal Nutritionchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Biology - Gas ExchangeDocument5 pagesBiology - Gas Exchangechristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Development of Evolutionary ThoughtDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Evolutionary Thoughtchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Relation and Function ReviewDocument7 pagesCalculus - Relation and Function Reviewchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Limit ConceptDocument14 pagesCalculus - Limit Conceptchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Differentiation FormulasDocument4 pagesCalculus - Differentiation Formulaschristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Derivative of The Algebraic FunctionsDocument9 pagesCalculus - Derivative of The Algebraic Functionschristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Increment, DerivativeDocument6 pagesCalculus - Increment, Derivativechristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Research - Inquiry and ResearchDocument4 pagesResearch - Inquiry and Researchchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Research - Designing The MethodologyDocument4 pagesResearch - Designing The Methodologychristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Research - Content of Scope and LimitationDocument3 pagesResearch - Content of Scope and Limitationchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Research - Conclusion, Recommendation and ReferencesDocument2 pagesResearch - Conclusion, Recommendation and Referenceschristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet