Professional Documents
Culture Documents
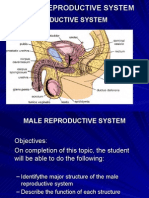
Reproductive System Table of Functions
Uploaded by
eborangez5Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reproductive System Table of Functions
Uploaded by
eborangez5Copyright:
Available Formats
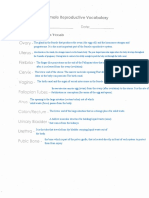
Complete the following table:
Structure: Function:
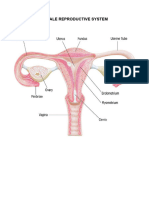
Vagina Provides a passageway for blood and mucosal tissue from the
uterus during a woman's monthly period. receives the penis during
sexual intercourse and holds the sperm until they pass into the
uterus. provides a passageway for childbirth.
Cervix allows fluids to flow inside and out of your uterus. It's also a
powerful gatekeeper that can open and close in ways that make
pregnancy and childbirth possible
Ovary They produce and store your eggs (also called ovum) and make
hormones that control your menstrual cycle and pregnancy
Uterus where a fertilised egg implants during pregnancy and where your
baby develops until birth
Fallopian tube channels for oocyte transport and fertilisation
Uterus lining preparation for implantation, maintenance of pregnancy if
implantation occurs, and menstruation in the absence of
pregnancy
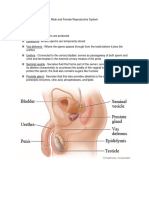
Testes making sperm and are also involved in producing a hormone called
testosterone
Penis urination and sexual intercourse
Urethra allows urine to pass outside the body
Vas deferens transports mature sperm to the urethra in preparation for
ejaculation
Epididymis store the sperms for maturation and transport it to vas deferens
Prostate produce the fluid that nourishes and transports sperm (seminal
fluid).
Seminal vesicle store and produce the majority of the fluid that makes up semen.
You might also like
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesMale Reproductive SystemLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemHye JinNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemYsthanamhire TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - Bio 2 - 12 Stem - l11Document4 pagesReproductive System - Bio 2 - 12 Stem - l11Lyka Lobido CabeltesNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageMale Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemEunimae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Bahan UASDocument4 pagesBahan UASislamiah sybNo ratings yet
- Ovaries: The Female Gonads, The Ovaries Produce Ova. When One Matures, It Is Released Down Into A Fallopian TubeDocument2 pagesOvaries: The Female Gonads, The Ovaries Produce Ova. When One Matures, It Is Released Down Into A Fallopian TubeCyril AlngogNo ratings yet
- Science 5Document26 pagesScience 5barangay89zone9No ratings yet
- Health 8 - Q1 W6Document5 pagesHealth 8 - Q1 W6Lanibelle TanteoNo ratings yet
- 07 05 Reproductive SystemDocument6 pages07 05 Reproductive SystemOkoye ClappinNo ratings yet
- SXSXDocument27 pagesSXSXJoevany E. BigorniaNo ratings yet
- Concept Block - NamocoDocument4 pagesConcept Block - NamocoGladys NamocoNo ratings yet
- Science Presentation: By: Beam BorachoDocument33 pagesScience Presentation: By: Beam BorachoPEMAR ACOSTANo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesReproductive SystemLeah Beth CañedoNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument20 pagesThe Reproductive SystemeamlezahNo ratings yet
- Fantiyao Reproductive System Group 2Document4 pagesFantiyao Reproductive System Group 2Jushelle Anne Tigoy PilareNo ratings yet
- Biomedical PerpectiveDocument22 pagesBiomedical Perpectiveedmaration 2002No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemreignda774No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemTa NhetNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document2 pagesQuiz 3sitti marwa baraNo ratings yet
- Y11 Hum - Rep1 20 3 17Document8 pagesY11 Hum - Rep1 20 3 17Rabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- 1.the Reproductive SystemDocument47 pages1.the Reproductive SystemAkai ShuichiNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2ericasinamagNo ratings yet
- Task 4Document20 pagesTask 4maryamshahzad489No ratings yet
- Reproductive Systems in HumansDocument3 pagesReproductive Systems in Humansvishalajagmohan3No ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesMale and Female Reproductive Systemchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Female ReproducDocument2 pagesFemale ReproducKrystel charess PangalayNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System ChartDocument2 pagesReproductive System ChartValeria Guadalupe Ramírez MoctezumaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesReproductive SystemHayley Doreen GarcesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systempt09651934948No ratings yet
- Kuliah Sem4 2008-2Document16 pagesKuliah Sem4 2008-2cathencloxNo ratings yet
- The Path Sperm-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageThe Path Sperm-WPS OfficeBryan Reufrir CortezanoNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewDocument3 pagesScience ReviewAinieNo ratings yet
- Euthenics ModuleDocument4 pagesEuthenics ModuleHanna AsmadNo ratings yet
- Gender & Society Lo4Document6 pagesGender & Society Lo4Mark Eugene DeocampoNo ratings yet
- Fallopian TubesDocument1 pageFallopian TubesCrisandra ErinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument27 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ReproductionÆRO YT CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Reproduction 2Document5 pagesReproduction 2CeliaGCNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction WJECDocument12 pagesHuman Reproduction WJECTharanga HewabuhageNo ratings yet
- Bio Female Reproduction System FunctionsDocument2 pagesBio Female Reproduction System FunctionsBenteNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Male Reproductive Organ1!31!24Document11 pagesParts and Functions of Male Reproductive Organ1!31!24enriquemargalbanNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesThe Reproductive SystemffingNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document4 pagesScience 10Dawn April sanoyNo ratings yet
- S10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREDocument35 pagesS10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREREGLOS, Marie Nhelle K.No ratings yet
- Female Voc DiagramDocument3 pagesFemale Voc DiagramAngie Sanchez-GalvezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemJune PinedaNo ratings yet
- Female and Male Reproductive SystemsDocument5 pagesFemale and Male Reproductive SystemsPol HuelarNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document3 pagesScience 10Andrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemCharice RamosNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemMary Grace NovidaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System of MammalsDocument21 pagesReproductive System of MammalsMarc Jay L. SolidumNo ratings yet
- Notes For HSB ExamDocument3 pagesNotes For HSB Examdanielle napierNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)Document40 pagesSexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)puspita8967628No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemaynNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument4 pagesSCIENCEMa. Isabel AtanesNo ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive System FinalDocument16 pagesThe Human Reproductive System FinalIlac Tristan BernardoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System of CowDocument3 pagesReproductive System of Cowshreya bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemKrishnan Nicolai MiguelNo ratings yet