100% found this document useful (1 vote)
458 views36 pagesOverview of Male and Female Reproductive Systems
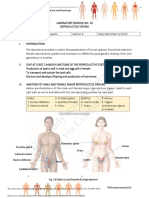
The document summarizes the key structures and functions of the male and female reproductive systems. It describes that the reproductive system allows for sexual reproduction through the production of gametes and offspring with genetic characteristics from both parents. It then outlines the major external and internal sex organs of the female system including the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and others. Similarly, it details the main parts of the male system such as the testes, penis, seminal vesicles, and others. The purpose of the reproductive system is to facilitate reproduction through sexual intercourse and development of offspring.
Uploaded by
Kem Marian MauricioCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
458 views36 pagesOverview of Male and Female Reproductive Systems
The document summarizes the key structures and functions of the male and female reproductive systems. It describes that the reproductive system allows for sexual reproduction through the production of gametes and offspring with genetic characteristics from both parents. It then outlines the major external and internal sex organs of the female system including the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and others. Similarly, it details the main parts of the male system such as the testes, penis, seminal vesicles, and others. The purpose of the reproductive system is to facilitate reproduction through sexual intercourse and development of offspring.
Uploaded by
Kem Marian MauricioCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to the Reproductive System: Explains the importance and functions of the reproductive system and its role in the continuation of life.
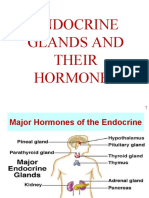
- Hormones and Their Role: Discusses the hormones involved in the reproductive system and their specific functions.
- Female Reproductive System: Describes the anatomy and function of the female reproductive system, including the role of each part.
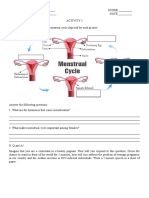
- Menstrual Cycle Phases: Details the stages of the menstrual cycle, including hormonal changes and physiological effects.
- Male Reproductive System: Provides information on the anatomy and function of the male reproductive system and its components.
- Reproductive System Quiz: Offers a quiz to test knowledge on topics covered in the reproductive system study.