Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human reproductive system and development
Uploaded by
Ms.Muriel Morong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views72 pages Girls experience menstruation because it is part of the natural monthly cycle in a woman's body that allows her to become pregnant. During puberty, a girl's body begins producing hormones that prepare the uterus for a potential pregnancy each month. If pregnancy does not occur, the uterine lining sheds through the vagina as menstrual blood along with the unfertilized egg. This monthly cycle of changes allows the female body to be fertile and able to sustain a pregnancy.
Original Description:
REPRODUCTION
Original Title
L3 TEACHSCI HUMAN REPRODUCTION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document Girls experience menstruation because it is part of the natural monthly cycle in a woman's body that allows her to become pregnant. During puberty, a girl's body begins producing hormones that prepare the uterus for a potential pregnancy each month. If pregnancy does not occur, the uterine lining sheds through the vagina as menstrual blood along with the unfertilized egg. This monthly cycle of changes allows the female body to be fertile and able to sustain a pregnancy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views72 pagesHuman reproductive system and development
Uploaded by
Ms.Muriel Morong Girls experience menstruation because it is part of the natural monthly cycle in a woman's body that allows her to become pregnant. During puberty, a girl's body begins producing hormones that prepare the uterus for a potential pregnancy each month. If pregnancy does not occur, the uterine lining sheds through the vagina as menstrual blood along with the unfertilized egg. This monthly cycle of changes allows the female body to be fertile and able to sustain a pregnancy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 72
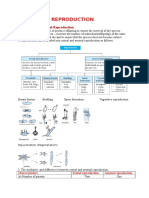
ACTIVITY NO.
3
• Make a family tree. In the boxes below, paste the
pictures of your mom and dad, then your picture and
your siblings. You may add boxes if needed. Label the
pictures. Illustration board 1/8. Coloring materials.
• Compare your face with your parents’ face. Do you
look like your dad? Do you look like your mom? What
features do you have that are similar to your dad? To
your mom?
UNSCRAMBLE THE WORD
OR GROUP OF WORDS
MYPIESIDID
Storage for inactive cells
EPIDYDIMIS
Storage for inactive cells
SPINE
External male organ
PENIS
External male organ
MEENS
Mixture of fluid and sperm
SEMEN
Mixture of fluid and sperm
EESSTT
Produce sperm cells
TESTES
Produce sperm cells
MUSTROC
Has lower temperature than
that of the body
SCROTUM
Has lower temperature than
that of the body
THERAUR
Passageway of both urine
and sperm
URETHRA
Passageway of both urine
and sperm
SLANG
Tip of the penis
GLANS
Tip of the penis
AVS NERDEFEES
Passageway of sperm cells
only
VAS DEFERENS
Passageway of sperm cells
only
TOASTERP ADLNG
Secretes fluid that is
mixed with sperm cells
PROSTATE GLAND
Secretes fluid that is
mixed with sperm cells
MAILSEN ESCLIVE
Temporary storage of sperms cells
because they are released in the
urethra
SEMINAL VESICLE
Temporary storage of sperms cells
because they are released in the
urethra
DIVOUCT
A tube that leads the egg
from the uterus
OVIDUCT
A tube that leads the egg
from the uterus
RETUSU
A place where the unborn
baby is developed
UTERUS
A place where the unborn
baby is developed
YOVRA
Produces egg cells and sex
hormones
OVARY
Produces egg cells and sex
hormones
XIVREC
Narrow opening between the
vagina and uterus
CERVIX
Narrow opening between the
vagina and uterus
GAANIV
Also called the birth canal
VAGINA
Also called the birth canal
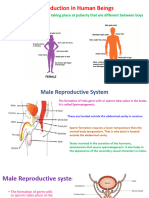
MALE REPRODUCTIVE ORGAN
Penis- external male organ with
a tip called glans. It is
covered with foreskin that may
be removed through circumcision.
Scrotum- a pair of pouch-like
sacs. It serves as the skin of
testes. It also controls its
temperature because the testes
must be slightly cooler than the
body to produce sperm cells.
Testes- the gland that produce
sperm cells, and male sex
hormone called testosterone. Scrotum
Epididymis- a narrow coiled tube
that stores immature sperm
cells.
Urethra- in males is the
passageway of both urine from
the urinary bladder and semen
from the glands
Seminal Vesicles- are sac-like
pouches attached to the vas
deferens. It produces a sugar-
rich fluid that provides energy
to sperm cells’ motility
Prostate gland- is a walnut-
sized gland located between the
bladder and the penis. It Scrotum
Scrotum
secretes fluid that nourishes
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE ORGAN
Uterus- also called the womb. Fallopian tube-
Where the unborn baby developed. also called
Has soft, smooth, inner lining of the oviduct, a tube
uterus called uterine lining or that leads the egg
endometrium. from the ovary to
the uterus. Usual
place where the egg
is fertilized by
the sperm cell.
Ovary- produces egg cells and
the sex hormones estrogen and
Cervix- narrow opening androgen
between the uterus and Mature egg cells are released
vagina. from the ovaries during
Enlarges to let the passage menstruation.
of a fetus during birth. Vagina- also called the birth canal. It expands
to let baby pass through during normal
DEVELOPMENT OF SECONDARY
SEX CHARACTERISTICS
• Puberty is the stage of human growth and
development in which a person becomes physically
mature. Puberty or adolescence usually happens
between 10 and 16 years old. These changes,
called secondary sex characteristics, are
brought by the sex hormones form the ovaries and
testes. In boys, the sex hormone is
testosterone. In girls, the sex hormones are
estrogen and progesterone.
MENSTRUAL CYCLE
• Menstruation is the monthly
discharge of blood from the
uterus through the vagina .
This is the first sign of
puberty for girls.
• Menstruation is part of the
menstrual cycle. The
average menstrual cycle for
a woman is 28 days.
ANIMATED VIDEO ABOUT MENSTRUATION
FERTILIZATION
When a sperm cell
unites with an egg
cell, fertilization
occurs. The egg cell
is usually fertilized
in the oviduct or
fallopian tube.
FERTILIZATION
When one sperm cell
enters the egg cell, the
eggs get fertilized and
is now called a zygote.
The zygote divides into
cells and develops into
an embryo. This embryo
travels for about five
days to reach the womb
or uterus.
IMPLANTATION
Implantation occurs
about seven days after
fertilization. It is
when the fertilized egg
becomes embedded on the
uterine lining.
IMPLANTATION
As the embryo continues to
develop, the placenta,
which is partly from the
uterine lining, also
develops. The umbilical
cord, which connects the
embryo and the placenta,
also grows and becomes the
passageway for nutrients
that the developing baby
needs as well as its waste.
IMPLANTATION
The amniotic sac is like a
bag filled with fluid that
encloses the embryo. This
fluid supports and protects
the unborn baby when the
mother slips or falls.
About 10-12 weeks after
fertilization, the embryo
is called a fetus.
FERTILIZATION AND IMPLANTATION
COMMON DISORDERS OF THE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) or
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) refer
to infectious diseases that are spread from
person to person through close contact. The
bacteria or viruses carried in the blood of
the infected person may be transmitted to
another person through semen or fluid in the
vagina.
COMMON DISORDERS OF THE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• The most widely- known transmitted disease
is the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
(AIDS). It is caused by a virus called Human
Immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV). Aside from
sexual intercourse, AIDS is also transmitted
through sharing of virus infected needles,
blood transfusion, and pregnancy. HIV
destroys the immune system of a person.
COMMON DISORDERS OF THE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• The immune system protects a person against
infection. Since the immune system of a
person with AIDS is destroyed, the person is
not protected from diseases. This is why
AIDS victims usually die young.
DISORDERS OF THE MALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• Inflammation of the Penis
This is the bacterial infection
affecting the penis with symptoms of
redness, itching, swelling, and pain.
Proper hygiene must be observed to
prevent this.
DISORDERS OF THE MALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• Inguinal Hernia
This is a condition wherein portion of the
intestines pushes through an abnormal
opening or weakening of the abdominal wall
and into the scrotum. It may look like a
bulge in the area of the scrotum. This can
be corrected with surgery.
Inguinal Hernia
DISORDERS OF THE MALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• Prostate Cancer
This is a form of cancer that develops
in the prostate gland. It causes pain
and difficulty in urinating.
Prostate Cancer
DISORDERS OF THE MALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• Testicular Injury
This usually occurs when the testicles
are struck, hit, kicked, or crushed,
usually during sports or due to other
trauma. It is advised to take care of
your external genital from bumps.
Testicular Injury
DISORDERS OF THE FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• Cervical Cancer
This is an abdominal build up of a mass
of tissue in the cervix, often causing
pain in the abdomen and severe bleeding.
Cervical Cancer
DISORDERS OF THE FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• Dysmenorrhea
This is characterized by pain in the
abdomen during menstruation. This is
mainly due to menstrual cramps and is
usually associated with the contraction
of the uterine muscles during ovulation
and menstruation.
Dysmenorrhea
DISORDERS OF THE FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• Ovarian Cysts
These cyst grow in the ovary. Normally, this is
not a problem unless they grow very large. Large
cysts may push on surrounding organs, causing
abdominal pain. In most cases, cysts will
disappear naturally and treatment is unnecessary.
If the cysts are painful, a doctor may prescribe
birth control pills to alter their growth, or
they may be removed by a surgeon.
Ovarian Cysts
DISORDERS OF THE FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• Vulvovaginitis
This is an inflammation of the vulva and the
vagina. It may be caused by irritating
substances such as laundry soaps or bubble
baths. Poor personal hygiene may also cause
this problem. Symptoms include redness and
itching of the vulva and sometimes vaginal
discharge.
Vulvovaginitis
QUIZ NO. 2
REPRODUCTION IN HUMAN BEINGS
Multiple choice---- dictation from the book 1-12
II. Write M if the disorder concerns the male reproductive
system and F if it concerns that of the female.
_____1. ovarian cyst _____5. inguinal hernia
_____2. testicular injury _____6. inflammation
of the penis
_____3. dysmenorrhea _____7. cervical
cancer
_____4. prostate cancer _____8. vulvovaginitis
III. Explain in three to five sentences why girls
experience an increase in the production of sex
hormones earlier than boys.
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
IV. List down five ways to take care of your
reproductive system.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
You might also like
- Ovum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandOvum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)Document40 pagesSexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)puspita8967628No ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument5 pagesHuman ReproductionKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument39 pagesReproductive SystemCenando Bodanio100% (1)
- SCIENCEDocument3 pagesSCIENCEjoannalyn gregorioNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Revision NotesDocument8 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 11 Revision NotesShayon BeraNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Document7 pagesHuman Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Zach ZaneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 101 Reproductive SystemDocument52 pagesLesson 101 Reproductive SystemtheacielaNo ratings yet
- (Unit 3) Human Reproductive SystemDocument14 pages(Unit 3) Human Reproductive SystemHanif AlfarizkiNo ratings yet
- Natural Science. Unit 3 Reproduction in HumansDocument19 pagesNatural Science. Unit 3 Reproduction in HumansmaryNo ratings yet
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDocument13 pages8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre KachigambaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesReproductive SystemSachin PatilNo ratings yet
- Peralta Robles, Nicole Palomino Ruiz, Jorge Montero Túpac, Alejandra Tataje, José Yanamango Salazar, Juan LuisDocument26 pagesPeralta Robles, Nicole Palomino Ruiz, Jorge Montero Túpac, Alejandra Tataje, José Yanamango Salazar, Juan LuisAlfredo Zavaleta GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument21 pagesReproductive SystemAshley RañesesNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Notes - 073143Document8 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Notes - 073143John Axel CosmodNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: A Concise Guide to the Male and Female AnatomyDocument58 pagesHuman Reproduction: A Concise Guide to the Male and Female AnatomyFelix HorseradaNo ratings yet
- 16.4 Sexual Reproduction in HumansDocument63 pages16.4 Sexual Reproduction in Humansnie20060301No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System: Anatomy, Function, and HealthDocument17 pagesMale Reproductive System: Anatomy, Function, and HealthN DrewNo ratings yet
- Term i - Chapter 15 CoreDocument37 pagesTerm i - Chapter 15 Core1005754antonioNo ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive SystemDocument53 pagesThe Human Reproductive Systemapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systempt09651934948No ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemERIC ASAMAMLEH KLEMEHNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument33 pagesReproductive Systemjheannegabriellea.ylaganNo ratings yet
- Science 3rd QuarterDocument22 pagesScience 3rd QuarterBethel AquinoNo ratings yet
- Human Sexuality Unit: Reproductive SystemsDocument38 pagesHuman Sexuality Unit: Reproductive SystemsMary Grace CacalNo ratings yet
- CXC BIOLOGY LECTURE SERIES COVERS KEY TOPICSDocument58 pagesCXC BIOLOGY LECTURE SERIES COVERS KEY TOPICSShantay BurtonNo ratings yet
- Puberty & AdoloscenceDocument59 pagesPuberty & Adoloscencekefz100% (1)
- Male and Female Reproductive System and MenstruationDocument11 pagesMale and Female Reproductive System and MenstruationSav LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemHye JinNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburDocument24 pagesReproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburOKTAVIANI HAPSARINo ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive System FinalDocument16 pagesThe Human Reproductive System FinalIlac Tristan BernardoNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: Anatomy and ProcessesDocument47 pagesFemale Reproductive System: Anatomy and ProcessesСухоставець Наталія ПетрівнаNo ratings yet
- 3Q Module 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systems 1Document29 pages3Q Module 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systems 1Pau BluzaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE10Document19 pagesSCIENCE10Jowelyn MaderalNo ratings yet
- Echidnas (/ɪ Kɪdnəz/), Sometimes Known As Spiny Anteaters. The FourDocument7 pagesEchidnas (/ɪ Kɪdnəz/), Sometimes Known As Spiny Anteaters. The FourHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Part-II.pptxDocument16 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce Part-II.pptxraghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument42 pagesHuman ReproductionangelynNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System AnatomyDocument30 pagesReproductive System AnatomyJune PinedaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction ExplainedDocument8 pagesHuman Reproduction ExplainedRabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Nurs 5351 Advanced Reproductive HealthDocument91 pagesNurs 5351 Advanced Reproductive HealthRachel BiokoNo ratings yet
- 4 Male and Female Reproductive Organs PPTDocument71 pages4 Male and Female Reproductive Organs PPTDanica Marie Sibay100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument53 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ReproductionPrincess Diane M. RagusNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument96 pagesHuman Reproductionsanya razaNo ratings yet
- Human Growth and Development: 5th Grade FemaleDocument28 pagesHuman Growth and Development: 5th Grade FemalemarigenNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System: Chapter 16: Lesson 3Document17 pagesThe Female Reproductive System: Chapter 16: Lesson 3NARDITO TUMAMPILNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & FertilizationDocument27 pagesAnatomy & FertilizationBAGAVATHI RNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumansDocument4 pagesReproduction in HumansIsra OmerNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTION L2 (Prashant Kirad)Document32 pagesREPRODUCTION L2 (Prashant Kirad)superherosunny13No ratings yet
- Sexual EducationDocument14 pagesSexual EducationLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System of MammalsDocument21 pagesReproductive System of MammalsMarc Jay L. SolidumNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System: Creating New Life ReproductionDocument29 pagesThe Reproductive System: Creating New Life ReproductionHildaAmaliaNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document3 pagesScience 10Andrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction OrgansDocument34 pagesHuman Reproduction OrgansJaeshelle FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemAhmie MarcosNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 - The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesSCIENCE 10 - The Reproductive SystemJyña Khura TanoNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemKrishnan Nicolai MiguelNo ratings yet
- Department of Zoology Govt Hss Mylachal: PresentsDocument69 pagesDepartment of Zoology Govt Hss Mylachal: PresentsBiju MylachalNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Science 10Document22 pagesReproductive Science 10palicpicbea50No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - Reproduction 1.2Document15 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Reproduction 1.2Halizah RamthanNo ratings yet
- DRRR Q2 M2 Fire HazardsDocument4 pagesDRRR Q2 M2 Fire HazardsMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- DRRR Q2 M4 Government Profile of Disaster Risk in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDRRR Q2 M4 Government Profile of Disaster Risk in The PhilippinesMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- DRRR Q1 M4 Volcanic HazardsDocument4 pagesDRRR Q1 M4 Volcanic HazardsMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- DRRR Q2 M3 Disaster Risk Reduc ManagementDocument4 pagesDRRR Q2 M3 Disaster Risk Reduc ManagementMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- DRRR Q2 M1 Hydrometerological HazardsDocument6 pagesDRRR Q2 M1 Hydrometerological HazardsMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety Tips to Prevent HazardsDocument26 pagesFire Safety Tips to Prevent HazardsMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- 11 Concept of DisasterDocument15 pages11 Concept of DisasterMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- 11 Concept of VulnerabilityDocument14 pages11 Concept of VulnerabilityMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- 11 Concept of VulnerabilityDocument14 pages11 Concept of VulnerabilityMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: Ideology DefinedDocument5 pagesI. Objectives: Ideology DefinedMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- 11 Concept of ExposureDocument8 pages11 Concept of ExposureMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- 11 Earthquake HazardsDocument22 pages11 Earthquake HazardsMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- Effective Lesson PlanningDocument16 pagesEffective Lesson PlanningMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics - Module 3 - 3rd QuarterDocument4 pagesApplied Economics - Module 3 - 3rd QuarterMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- Community Engagement1 DLLDocument10 pagesCommunity Engagement1 DLLMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Chemical Reaction RatesDocument6 pagesFactors Affecting Chemical Reaction RatesAriane Ignao Lagatic100% (2)
- Applied Economics - Module 1 - 3rd QuarterDocument4 pagesApplied Economics - Module 1 - 3rd QuarterMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- Classroom Observation ReportDocument3 pagesClassroom Observation ReportMs.Muriel Morong100% (1)
- Detailed LP Format - ScienceDocument1 pageDetailed LP Format - ScienceMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- Detailed LP Format - EppDocument2 pagesDetailed LP Format - EppMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- L1 - Teachsci - Science Curriculum FrameworkDocument13 pagesL1 - Teachsci - Science Curriculum FrameworkMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- L3 - Teachsci - Human Body Parts and FunctionsDocument12 pagesL3 - Teachsci - Human Body Parts and FunctionsMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- How Animals ReproduceDocument11 pagesHow Animals ReproduceMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- L4 - Teachtle Agrifishery ArtsDocument22 pagesL4 - Teachtle Agrifishery ArtsMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Human Reproduction - Grade 12Document27 pagesWorksheet On Human Reproduction - Grade 12Palani G Pazhani GNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet Grade 10 Science: Feedback Mechanisms: Key To HomeostasisDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Grade 10 Science: Feedback Mechanisms: Key To HomeostasisKeisha Janelle ZetazateNo ratings yet
- Infographics - Male CondomDocument1 pageInfographics - Male CondompastidiokatherineNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Concept MapDocument16 pagesReproductive System Concept MapQK CLARONo ratings yet
- Important Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 - Human ReproductionDocument17 pagesImportant Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 - Human ReproductionYuvraj MehtaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 5 - Q2 - Mod1Document13 pagesSCIENCE 5 - Q2 - Mod13tj internetNo ratings yet
- 12 TH Study MaterialDocument63 pages12 TH Study MaterialAkash VigneshwarNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of the OvaryDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of the OvaryJay PaulNo ratings yet
- CAMCA QUIZ ReviewDocument3 pagesCAMCA QUIZ ReviewShyla mayNo ratings yet
- LPM 602 Bits..Document4 pagesLPM 602 Bits..Vijaya lakshmiNo ratings yet
- CP Vs BE en La IATFDocument7 pagesCP Vs BE en La IATFSterlin MorenoNo ratings yet
- DepEdClub human reproductive system lessonDocument33 pagesDepEdClub human reproductive system lessonMylene DiazNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesASSESSMENT Reproductive SystemJossie Allen PradoNo ratings yet
- Indus Universal School worksheet on reaching adolescenceDocument2 pagesIndus Universal School worksheet on reaching adolescenceAshwika AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For How Humans Evolved 8th by BoydDocument15 pagesTest Bank For How Humans Evolved 8th by Boydjordanmeyersszkrywqfog100% (24)
- Free MartinismDocument16 pagesFree MartinismMuhammad Farrukh Hafeez100% (1)
- ME Sci 10 Q3 1001 PSDocument17 pagesME Sci 10 Q3 1001 PSsino56601No ratings yet
- Hormones and the Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesHormones and the Reproductive SystemMARITESS COLLADONo ratings yet
- Common Breeding Systems For Livestock ProductionDocument4 pagesCommon Breeding Systems For Livestock ProductionRica Mae EnvergaNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document23 pagesWeek 2Za Natividad MarzanNo ratings yet
- G5 Q2W2 DLL SCIENCE MELCsDocument9 pagesG5 Q2W2 DLL SCIENCE MELCsFloriza MangiselNo ratings yet
- Anderson and Vitt, 1990.sexual Selection Versus Alternative Causes of Sexual Dimorphism in Teiid LizardsDocument14 pagesAnderson and Vitt, 1990.sexual Selection Versus Alternative Causes of Sexual Dimorphism in Teiid LizardsFred LimaNo ratings yet
- VGO Course Outline-1Document7 pagesVGO Course Outline-1nitvetdrNo ratings yet
- Afa Apswine Shs q1 Las2 FinalDocument12 pagesAfa Apswine Shs q1 Las2 FinalGrace Roloma ReboldadNo ratings yet
- Vagina:: Female Reproductive System (Human), Details ..Document8 pagesVagina:: Female Reproductive System (Human), Details ..Giovanni CeneriniNo ratings yet
- MenstruationDocument3 pagesMenstruationcoco yomieNo ratings yet
- UT Human Reproduction System Grade 9 TestDocument8 pagesUT Human Reproduction System Grade 9 Test24kxrooNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesLesson 3 Reproduction and DevelopmentroiveryepesNo ratings yet
- Natural Method To Control BirthDocument8 pagesNatural Method To Control BirthManish OliNo ratings yet
- Sperm Wars - Robin Baker: Chapter 1: The Generation GameDocument6 pagesSperm Wars - Robin Baker: Chapter 1: The Generation GameGustavo PernaNo ratings yet