Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lewis Pancreatitis PP
Uploaded by
Jose Bernel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views69 pagesPancreatitis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPancreatitis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views69 pagesLewis Pancreatitis PP
Uploaded by
Jose BernelPancreatitis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 69
Pancreatitis
Chapter 44
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
• An acute inflammatory process of
the pancreas
• Varies from mild edema to severe
necrosis
• Most common in middle-aged
persons and African Americans
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• A.J. is a 48-year-old woman who
comes to the ED.
• She has nausea, vomiting, and
epigastric and left upper quadrant
pain.
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• She describes the pain as severe,
sharp, and radiating through to her
midback.
• She states the pain started 24 hours
ago.
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• A.J. admits to smoking a half-pack
of cigarettes/day but denies drinking
alcohol or using any illegal drugs.
• Her past medical history is positive
for gallstones and hypothyroidism.
• She is 5 feet 4 inches tall and weighs
160 lb.
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• A.J.’s vital signs:
• Blood pressure 100/70
• Heart rate 97
• Respiratory rate 30
• Temperature 100.2°F
• Health care provider suspects acute
pancreatitis and admits A.J. to the
medical-surgical unit.
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• What are the possible causes of
A.J.’s pancreatitis?
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Etiology
• Gallbladder disease (women)
• Chronic alcohol intake (men)
• Smoking
• Hypertriglyceridemia
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Etiology
• Less common causes
• Drugs
• Metabolic disorders
• Vascular diseases
• Surgery and endoscopic procedures
• Idiopathic causes
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Etiology
• Less common causes
• Trauma (postsurgical, abdominal)
• Viral infections
• Penetrating duodenal ulcer
• Cysts
• Abscesses
• Cystic fibrosis
• Kaposi sarcoma
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• A.J. asks you what pancreatitis is.
• How would you explain the
pathophysiology of this disease
process to her?
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
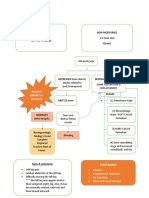
Acute Pancreatitis
Pathophysiology
• Caused by autodigestion of pancreas
• Injury to pancreatic cells
• Activation of pancreatic enzymes
• Activation of trypsinogen to trypsin
within the pancreas leads to
bleeding
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Pathophysiology
• Mild pancreatitis
• Edematous or interstitial
• Severe pancreatitis
• Necrotizing
• Endocrine and exocrine dysfunction
• Necrosis, organ failure, sepsis
• Rate of mortality: 25%
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Clinical Manifestations
• Abdominal pain predominant
• Left upper quadrant or midepigastrium
• Radiates to the back
• Sudden onset
• Deep, piercing, continuous or steady
• Aggravated by eating
• Starts when recumbent
• Not relieved with vomiting
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• As you admit A.J. to the medical-
surgical unit, for what other clinical
manifestations of pancreatitis would
you assess her?
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Clinical Manifestations
• Flushing
• Cyanosis
• Dyspnea
• Nausea/vomiting
• Low-grade fever
• Leukocytosis
• Hypotension, tachycardia
• Jaundice
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Clinical Manifestations
• Abdominal tenderness with guarding
• Decreased or absent bowel sounds
• Crackles
• Abdominal skin discoloration
• Grey Turner’s spots or sign
• Cullen’s sign
• Shock
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• For what potential complications of
acute pancreatitis will you monitor
A.J.?
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Complications
• Pseudocyst
• Fluid, enzyme, debris, and exudates
surrounded by wall
• Abdominal pain, palpable mass,
nausea/vomiting, anorexia
• Detected with imaging
• Resolves spontaneously or may
perforate and cause peritonitis
• Surgical or endoscopic drainage
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Complications
• Pancreatic abscess
• Collection of pus
• Results from extensive necrosis
• May perforate
• Upper abdominal pain, mass, high
fever, leukocytosis
• Surgical drainage
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Complications
• Systemic complications
• Pleural effusion
• Atelectasis
• Pneumonia
• ARDS
• Hypotension
• Hypocalcemia: tetany
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• What diagnostic studies would you
expect the health care provider to
order for A.J.?
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Diagnostic Studies
• Laboratory tests
• Serum amylase level
• Serum lipase level
• Liver enzyme levels
• Triglyceride levels
• Glucose level
• Bilirubin level
• Serum calcium level
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Diagnostic Studies
• Abdominal ultrasonography
• X-ray
• Contrast-enhanced CT scan
• Endoscopic retrograde
cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Diagnostic Studies
• Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS)
• Magnetic resonance
cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
• Angiography
• Chest x-ray
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Collaborative Care
• Objectives include
• Relief of pain
• Prevention or alleviation of shock
• ↓ Pancreatic secretions
• Correction of fluid/electrolyte
imbalance
• Prevention/treatment of infection
• Removal of the precipitating cause
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Collaborative Care
• Conservative therapy
• Supportive care
• Aggressive hydration
• Pain management
• IV morphine, antispasmodic agent
• Management of metabolic complications
• Oxygen, glucose levels
• Minimizing pancreatic stimulation
• NPO status, NG suction, decreased acid
secretion, enteral nutrition if needed
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Collaborative Care
• Conservative therapy
• Shock
• Plasma or plasma volume expanders
(dextran or albumin)
• Fluid/electrolyte imbalance
• Lactated Ringer’s solution
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Collaborative Care
• Conservative therapy
• Ongoing hypotension
• Vasoactive drugs: dopamine (Intropin)
• Prevent infection
• Enteral nutrition
• Antibiotics
• Endoscopically or CT-guided
percutaneous aspiration
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Collaborative Care
• Surgical therapy
• For gallstones
• ERCP
• Cholecystectomy
• Uncertain diagnosis
• Not responding to conservative therapy
• Drainage of necrotic fluid collections
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Collaborative Care
• Drug therapy
• IV morphine
• Antispasmodics
• Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
• Antacids
• Proton pump inhibitors
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Collaborative Care
• Nutritional therapy
• NPO status initially
• Enteral versus parenteral nutrition
• Monitor triglycerides if IV lipids given
• Small, frequent feedings when able
• High-carbohydrate
• No alcohol
• Supplemental fat-soluble vitamins
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Assessment
• Subjective data
• Health history
• Biliary tract disease
• Alcohol use
• Abdominal trauma
• Duodenal ulcers
• Infection
• Metabolic disorders
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Assessment
• Subjective data
• Medications
• Thiazides
• NSAIDs
• Surgery or other treatments
• Pancreas, stomach, duodenum, biliary
tract
• ERCP
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Assessment
• Subjective data: functional health
patterns
• Alcohol abuse
• Fatigue
• Nausea, vomiting, anorexia
• Dyspnea
• Pain
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Assessment
• Objective data
• Restlessness, anxiety, low-grade fever
• Flushing, diaphoresis
• Discoloration of abdomen/flank
• Cyanosis
• Jaundice
• Decreased skin turgor
• Dry mucous membranes
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Assessment
• Objective data
• Tachypnea
• Basilar crackles
• Tachycardia
• Hypotension
• Abdominal distention/tenderness
• Diminished bowel sounds
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Assessment
• Abnormal laboratory findings
• ↑ Serum amylase/lipase levels
• Leukocytosis
• Hyperglycemia
• Hypocalcemia
• Abnormal findings on
ultrasonography/CT scans
• Abnormal findings on ERCP
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• A.J.’s laboratory results
demonstrate
• Elevated serum amylase and lipase
levels
• Mild leukocytosis
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• She undergoes an ERCP, which
revealed the presence of gallstones
blocking the common bile duct.
• She is currently on NPO status and
receiving IV morphine for pain
control.
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• When you plan care for A.J., what
priority nursing diagnoses would
you identify for her?
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Diagnoses
• Acute pain
• Deficient fluid volume
• Imbalanced nutrition: less than body
requirements
• Ineffective self-health management
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Planning
• Patient will have
• Relief of pain
• Normal fluid and electrolyte balance
• Minimal to no complications
• No recurrent attacks
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Implementation
• Health promotion
• Assessment and early treatment of
predisposing/etiologic factors
• Early diagnosis/treatment of biliary
tract disease
• Elimination of alcohol intake
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Implementation
• Acute intervention
• Monitoring vital signs
• Assess respiratory function
• Monitor IV fluids
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• For what electrolyte imbalances
would you monitor A.J.?
• Explain the rationale for your
answer.
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Implementation
• Acute intervention
• Monitor fluid and electrolyte balance
• Chloride, sodium, and potassium
• Hypocalcemia
• Tetany
• Calcium gluconate to treat
• Hypomagnesemia
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Monitoring for Tetany
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Implementation
• Acute intervention
• Pain assessment and management
• Morphine
• Position of comfort with frequent position
changes
• Flex trunk and draw knees to abdomen
• Side-lying with head of bed elevated 45
degrees
• Frequent oral/nasal care
• Proper administration of antacids
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Implementation
• Acute intervention
• Observation for signs of infection
• TCDB, semi-Fowler’s position
• Wound care
• Observation for paralytic ileus, renal
failure, mental changes
• Monitor serum glucose
• Post-op wound care
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Audience Response Question
The nurse explains to a patient with an episode of
acute pancreatitis that the most effective means
of relieving pain by suppressing pancreatic
secretions is the use of:
a. Antibiotics.
b. NPO status.
c. Antispasmodics.
d. Proton pump inhibitors.
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Case Study
Fuse/Thinkstock
• A.J. is recuperating from her acute
pancreatitis without difficulty.
• Her health care provider writes an
order for her to be discharged home.
• What would be your priority
teaching to be completed prior to
her leaving?
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Implementation
• Ambulatory and home care
• Physical therapy
• Assessment of narcotic addiction
• Counseling regarding abstinence from
alcohol and smoking
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Implementation
• Ambulatory and home care
• Dietary teaching
• Low-fat, high-carbohydrate
• No crash diets
• Patient/family teaching
• Signs of infection, diabetes mellitus,
steatorrhea
• Medications/diet
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Acute Pancreatitis
Nursing Implementation
• Expected outcomes
• Have adequate pain control
• Maintain adequate fluid volume
• Be knowledgeable about treatment
regimen
• Get help for alcohol dependence ( if
appropriate)
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Chronic Pancreatitis
• Continuous, prolonged inflammatory,
and fibrosing process of the pancreas
• Etiology
• Alcohol, gallstones, tumor,
pseudocysts, trauma, systemic disease
• Acute pancreatitis
• Idiopathic
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Pathophysiology
• Two major types
• Chronic obstructive pancreatitis
• Gallstones cause inflammation of
sphincter of Oddi
• Chronic nonobstructive pancreatitis
• Inflammation and sclerosis in head of
pancreas and around duct
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Clinical Manifestations
• Abdominal pain
• Located in the same areas as in acute
pancreatitis
• Heavy, gnawing feeling; burning and
cramplike
• Malabsorption with weight loss
• Constipation, jaundice, icteric urine,
steatorrhea, diabetes mellitus
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Clinical Manifestations
• Complications include
• Pseudocyst formation
• Bile duct or duodenal obstruction
• Pancreatic ascites
• Pleural effusion
• Splenic vein thrombosis
• Pseudoaneurysm
• Pancreatic cancer
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Diagnostic Studies
• Confirming diagnosis can be
challenging
• Based on signs/symptoms,
laboratory studies, and imaging
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Diagnostic Studies
• Laboratory tests
• Serum amylase/lipase levels
• May be ↑ slightly or not at all
• ↑ Serum bilirubin level
• ↑ Alkaline phosphatase level
• Mild leukocytosis
• ↑ Sedimentation rate
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Diagnostic Studies
• ERCP
• CT, MRI, MRCP, abdominal and/or
endoscopic ultrasonography
• Stool samples for fat content
• ↓ Fat-soluble vitamin and cobalamin
levels
• Glucose intolerance/diabetes
• Secretin stimulation test
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Collaborative Care
• Analgesics for pain relief (morphine
or fentanyl transdermal patch
[Duragesic])
• Diet
• Bland, low-fat
• Small, frequent meals
• No smoking
• No alcohol or caffeine
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Collaborative Care
• Pancreatic enzyme replacement
• Bile salts
• Insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents
• Acid-neutralizing and acid-inhibiting
drugs
• Antidepressants
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Collaborative Care
• Surgery
• Indicated when biliary disease is
present or if obstruction or pseudocyst
develops
• Diverts bile flow or relieves ductal
obstruction
• Choledochojejunostomy
• Roux-en-Y pancreatojejunostomy
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Collaborative Care
• Pancreatic drainage
• ERCP with spincterotomy and/or
stent placement
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Nursing Management
• Focus is on chronic care and health
promotion
• Patient and family teaching
• Dietary control
• Pancreatic enzyme with meals/snack
• Observe for steatorrhea
• Monitor glucose levels
• Antacids after meals and at bedtime
• No alcohol
Copyright © 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
You might also like
- CH 42 GastritisDocument24 pagesCH 42 GastritisNina Patricia OrbeNo ratings yet
- The Ideal Dialysis Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Managing Kidney Problems And Soothing Dialysis With Nutritious Low Sodium Low Potassium RecipesFrom EverandThe Ideal Dialysis Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Managing Kidney Problems And Soothing Dialysis With Nutritious Low Sodium Low Potassium RecipesNo ratings yet
- AFEM Approach To Abdominal Pain in AdultsDocument53 pagesAFEM Approach To Abdominal Pain in AdultsSaktai DiyamiNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Disorders: Prepared by Captain: Jumana AL-Momani RN - MSNDocument72 pagesHepatic Disorders: Prepared by Captain: Jumana AL-Momani RN - MSNJanuaryNo ratings yet
- 7 - Acute AbdomenDocument31 pages7 - Acute Abdomenwayel2013No ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis: Roy Phitayakorn, M.D. Christopher Brandt, M.DDocument41 pagesAcute Appendicitis: Roy Phitayakorn, M.D. Christopher Brandt, M.DLavasa SharmaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Dyspepsia: Dr. Ghalia Abu MohsenDocument60 pagesApproach To Dyspepsia: Dr. Ghalia Abu MohsenMohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 52 Urinary Tract Bladder AgentsDocument40 pagesChapter 52 Urinary Tract Bladder Agentsjanmishelle208No ratings yet
- Esophageal CancerDocument40 pagesEsophageal Cancerapi-282115150No ratings yet
- Tetanus by NeurologDocument41 pagesTetanus by NeurologIrfan AchmadNo ratings yet
- Inflammation of Gastric Mucosa One of Most Common Problems Affecting The StomachDocument24 pagesInflammation of Gastric Mucosa One of Most Common Problems Affecting The StomachMuhajir AbbasNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument53 pagesAcute AbdomenMahdi DiabNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument39 pagesHepatitisDocRN50% (2)
- Acute Appendicitis: Roy Phitayakorn, M.D. Christopher Brandt, M.DDocument41 pagesAcute Appendicitis: Roy Phitayakorn, M.D. Christopher Brandt, M.DOrinda ElvanandaNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis PpsDocument41 pagesAppendicitis PpsOrinda ElvanandaNo ratings yet
- Patho SlidesDocument46 pagesPatho Slidesapi-400411160No ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument21 pagesAcute AbdomenMillicent AwuzieNo ratings yet
- Disorder of BladderDocument27 pagesDisorder of BladderAshraf QotmoshNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients With Cancer of The LiverDocument20 pagesCare of Patients With Cancer of The LiverJumar Vallo ValdezNo ratings yet
- The AppendixDocument5 pagesThe AppendixAmik, Aila H.No ratings yet
- Abdomen Akut Nyeri Abdomen Akut Gawat Abdomen: DR Agung Ary Wibowo SPB (K) BDDocument64 pagesAbdomen Akut Nyeri Abdomen Akut Gawat Abdomen: DR Agung Ary Wibowo SPB (K) BDharisNo ratings yet
- GI Board ReviewDocument176 pagesGI Board Reviewjosh hagsNo ratings yet
- PYELONEPHRITISDocument16 pagesPYELONEPHRITISshenecajean carajayNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument35 pagesAcute AbdomenRonit ChandNo ratings yet
- Selected-Handbook-Case ArimgsasDocument62 pagesSelected-Handbook-Case ArimgsasGabriela ChristianNo ratings yet
- OBSTETRICS HISTORY TAKING DR. ELIOBADocument30 pagesOBSTETRICS HISTORY TAKING DR. ELIOBAmarvinlevanteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Urinary EliminationDocument22 pagesChapter 21 Urinary EliminationMalak JawabrehNo ratings yet
- Early Diagnosis & Prompt Treatment of Acute Abdominal PainDocument69 pagesEarly Diagnosis & Prompt Treatment of Acute Abdominal PainRani Silmi ZulafaNo ratings yet
- Morning Report - PyelonephritisDocument54 pagesMorning Report - PyelonephritisjonNo ratings yet
- The Acute Abdomen: MR P Vaughan-Shaw December 2010Document37 pagesThe Acute Abdomen: MR P Vaughan-Shaw December 2010Sutapa PawarNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument24 pagesAcute AbdomenGrace SimmonsNo ratings yet
- Abdominal PainDocument18 pagesAbdominal PainDwi indah KusumaNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting PDFDocument8 pagesNausea and Vomiting PDFRoosita Arbaane SafitriNo ratings yet
- Oncological Emeergancy 5Document19 pagesOncological Emeergancy 5222041No ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Group 4: Surya Patricya Serikat Niscaya Theresia Yuni Venggy Reylandhie Yustina NayDocument15 pagesDiarrhea: Group 4: Surya Patricya Serikat Niscaya Theresia Yuni Venggy Reylandhie Yustina NayvenggyNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdominal Emergencies GuideDocument126 pagesAcute Abdominal Emergencies GuidekityamuwesiNo ratings yet
- Nephro Nursing - Urinary and Renal Dysfunctions (Part 2)Document53 pagesNephro Nursing - Urinary and Renal Dysfunctions (Part 2)ALLAINE MARIE TANNo ratings yet
- Approach To Abdominal Pain in EDDocument29 pagesApproach To Abdominal Pain in EDAneeq Nayer KhanNo ratings yet
- Signs, Symptoms and Investigations in Acute Abdominal PainDocument40 pagesSigns, Symptoms and Investigations in Acute Abdominal PainPoh TseNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of GIT Dr. Bereket Molla TigabuDocument44 pagesEvaluation of GIT Dr. Bereket Molla Tigabuphoto copyhemnNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Biliary DisordersDocument26 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Biliary DisordersBav VAansoqnuaetz100% (1)
- Approach To Abdominal PainDocument22 pagesApproach To Abdominal PainOmar AbdillahiNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Pain Jan 2023Document64 pagesPelvic Pain Jan 2023Giuliana GuarnaNo ratings yet
- Urinary RetentionDocument28 pagesUrinary RetentionSchoeb MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Female Physiologic Processes - Management of Patients With Female Reproductive DisordersDocument59 pagesAssessment and Management of Female Physiologic Processes - Management of Patients With Female Reproductive DisordersMaruf100% (1)
- Acute appendicitis diagnosis and managementDocument6 pagesAcute appendicitis diagnosis and managementPraktek Dokter Umum drjosefdrelsyNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersDocument32 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersJills JohnyNo ratings yet
- Patients With Noninflammatory Intestinal Disorders: UPNS 232 Adult Health and IllnessDocument41 pagesPatients With Noninflammatory Intestinal Disorders: UPNS 232 Adult Health and Illnesslucas dibenedettoNo ratings yet
- Basic Medical Terminology: Presented By: Penny Osmon, BA, CPCDocument256 pagesBasic Medical Terminology: Presented By: Penny Osmon, BA, CPCdmsa100% (8)
- Alterations in Fluid and Electrolyte and AcidDocument11 pagesAlterations in Fluid and Electrolyte and Acidlaurie.charlynjaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 52Document40 pagesChapter 52kdayeon018No ratings yet
- Chapter 47Document30 pagesChapter 47Jessica GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdomen - DR Raya Batubara, SP.BDocument39 pagesAcute Abdomen - DR Raya Batubara, SP.BGJMasterNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A, B & C VirusesDocument47 pagesHepatitis A, B & C VirusesChristone “Zuluzulu” ZuluNo ratings yet
- UCD School of Medicine Surgical HandbookDocument429 pagesUCD School of Medicine Surgical HandbookLouise FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Cauti105 508Document42 pagesCauti105 508Yahia HassaanNo ratings yet
- CELLULAR ABERRATIONS DETECTION GUIDEDocument36 pagesCELLULAR ABERRATIONS DETECTION GUIDEmidoNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Intestinal and Rectal DisordersDocument54 pagesManagement of Patients With Intestinal and Rectal DisordersJills JohnyNo ratings yet
- Bowel Elimination SW STDocument36 pagesBowel Elimination SW STIvan TranconNo ratings yet
- Modified Aldrete ScoringDocument1 pageModified Aldrete ScoringJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Past HistoryDocument2 pagesPast HistoryJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Medical treatment record templateDocument2 pagesMedical treatment record templateJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument50 pagesEctopic PregnancyJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Malabon Hospital Admission GuideDocument2 pagesMalabon Hospital Admission GuideJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2Jose BernelNo ratings yet
- AMBULATORY SURGICAL CLINICwpsDocument3 pagesAMBULATORY SURGICAL CLINICwpsJose Bernel100% (1)
- Or FormsDocument7 pagesOr FormsJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Towards A General Systems Theory of Nursing: A Literature Review David GlennisterDocument19 pagesTowards A General Systems Theory of Nursing: A Literature Review David GlennisterJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Consent Form For Stress TestDocument1 pageConsent Form For Stress TestJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Core Competencies, 2012 NNCCSDocument23 pagesCore Competencies, 2012 NNCCSJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices During The Covid-19 Pandemic Among Filipino Jeepney DriversDocument2 pagesKnowledge, Attitudes, and Practices During The Covid-19 Pandemic Among Filipino Jeepney DriversJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Nurse Practitioners, Medical Negligence and Crime: A Case StudyDocument8 pagesNurse Practitioners, Medical Negligence and Crime: A Case StudyJose BernelNo ratings yet
- PPH ReportDocument22 pagesPPH ReportJose Bernel100% (1)
- Operation Record For Chole + AP - Insert WatermarkDocument2 pagesOperation Record For Chole + AP - Insert WatermarkJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Criteria An DpointsDocument1 pageCriteria An DpointsJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Human and Animal Health Collaboration in Rabies Control in The PhilipinesDocument25 pagesHuman and Animal Health Collaboration in Rabies Control in The PhilipinesJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices During The Covid-19 Pandemic Among Filipino Jeepney DriversDocument2 pagesKnowledge, Attitudes, and Practices During The Covid-19 Pandemic Among Filipino Jeepney DriversJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Modifiable: Trauma (Impact or Pressure)Document1 pageNon-Modifiable Modifiable: Trauma (Impact or Pressure)Jose BernelNo ratings yet
- M4 Albores (31) UpdatedDocument5 pagesM4 Albores (31) UpdatedJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Profile of RespondentsDocument9 pagesChapter 4 Profile of RespondentsJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices During The Covid-19 Pandemic Among Filipino Jeepney DriversDocument7 pagesKnowledge, Attitudes, and Practices During The Covid-19 Pandemic Among Filipino Jeepney DriversJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Instructional Material Javier Et AlDocument3 pagesInstructional Material Javier Et AlJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Juris Clown AssignmentDocument4 pagesJuris Clown AssignmentJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Research Design, Sampling, and Instrumentation for a Study on COVID-19 Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Jeepney DriversDocument3 pagesResearch Design, Sampling, and Instrumentation for a Study on COVID-19 Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Jeepney DriversJose BernelNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER IV (Knowledge) Javier Et Al.Document20 pagesCHAPTER IV (Knowledge) Javier Et Al.Jose BernelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Javier Et Al. Final ..Document19 pagesChapter 4 Javier Et Al. Final ..Jose BernelNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iv ReferencesDocument2 pagesChapter Iv ReferencesJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Javier Et Al. SCRIPTDocument2 pagesJavier Et Al. SCRIPTJose BernelNo ratings yet
- Gastric Function Test.... RohitDocument28 pagesGastric Function Test.... RohitJr Jc Rohit SahNo ratings yet
- Bio FrogDocument9 pagesBio FrogMARK JIRON ROTONINo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Review QuestionsDocument10 pagesGastrointestinal System Review QuestionsSiena PlacinoNo ratings yet
- 4Document3 pages4Milton Chin100% (1)
- AbdomenDocument23 pagesAbdomenjnyamusiNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes: Digestion (IB HL 6.1)Document6 pagesBio Notes: Digestion (IB HL 6.1)BekNo ratings yet
- Definition.: The Human Digestive SystemDocument32 pagesDefinition.: The Human Digestive SystemEmma Joel OtaiNo ratings yet
- Endodermal Derivatives, Formation of The Gut and Its Subsequent RotationDocument14 pagesEndodermal Derivatives, Formation of The Gut and Its Subsequent RotationmikeNo ratings yet
- Acute CholecystitisDocument18 pagesAcute CholecystitisOktavia PutriNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesDigestive SystemReginaNo ratings yet
- Bhagatwala Et Al 2015, Indications and ContraindicationsDocument27 pagesBhagatwala Et Al 2015, Indications and Contraindicationsedo adimastaNo ratings yet
- Care of Adults 27 Gastrointestinal ManagementDocument33 pagesCare of Adults 27 Gastrointestinal ManagementGaras AnnaBerniceNo ratings yet
- Gastric Analysis: Printable Version Download PDF Cite This PageDocument4 pagesGastric Analysis: Printable Version Download PDF Cite This PageFranz Mercader100% (1)
- Enteral Nutrition: Sana Inam Lecturer College of Pharmacy, GCUFDocument18 pagesEnteral Nutrition: Sana Inam Lecturer College of Pharmacy, GCUFAnum AzamNo ratings yet
- Digestive System of Silkworm LarvaDocument17 pagesDigestive System of Silkworm LarvaRaghvendra NiranjanNo ratings yet
- Medical and Nutritional Management of Cholestasis in Infants and ChildrenDocument29 pagesMedical and Nutritional Management of Cholestasis in Infants and ChildrenYi Teng SohNo ratings yet
- Bio4 4Document14 pagesBio4 4HarmonyChuiNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung's Disease in Africa: Challenges of Late PresentationDocument27 pagesHirschsprung's Disease in Africa: Challenges of Late PresentationVita MadmoNo ratings yet
- Case Study of AmoebiasisDocument19 pagesCase Study of Amoebiasisstar7707No ratings yet
- Gastrectomy. (N.D.) - Retrieved From Encycopedia of Surgery:: Why Is A Partial Gastrectomy Performed?Document7 pagesGastrectomy. (N.D.) - Retrieved From Encycopedia of Surgery:: Why Is A Partial Gastrectomy Performed?Angel Joy CATALAN (SHS)No ratings yet
- Plabable-Gems-6. Gastroenterology Plabable GemsDocument39 pagesPlabable-Gems-6. Gastroenterology Plabable GemsHabo Habo100% (1)
- Growing Poultry Industry Meets Need for Alternative FeedsDocument47 pagesGrowing Poultry Industry Meets Need for Alternative FeedsJakin Aia TapanganNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System ExplainedDocument40 pagesThe Digestive System ExplainedIrma Julyanti PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- 296 1179 1 PBDocument2 pages296 1179 1 PBKriti KumariNo ratings yet
- CT EnterographyDocument8 pagesCT EnterographyAbin VlNo ratings yet
- The Small Intestine: Anatomy and RelationsDocument5 pagesThe Small Intestine: Anatomy and RelationsaoifeoxNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder Adenomyomatosis Imaging FindingsDocument9 pagesGallbladder Adenomyomatosis Imaging FindingsSamuel WidjajaNo ratings yet
- The Esophagus Anatomy and Swallowing ProcessDocument3 pagesThe Esophagus Anatomy and Swallowing ProcessjosetelhadoNo ratings yet
- Nicolás Alberto Cely Aldana Interno Fujnc Agosto-2020Document62 pagesNicolás Alberto Cely Aldana Interno Fujnc Agosto-2020nicolasNo ratings yet
- Acute CholangitisDocument9 pagesAcute CholangitisMike GNo ratings yet