Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.1 Grammar PowerPoint
Uploaded by
Juan Pablo MoliciaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.1 Grammar PowerPoint
Uploaded by
Juan Pablo MoliciaCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
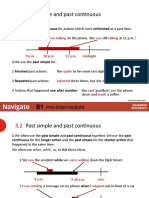
1 Narrative forms
1 A narrative is a story or a description of past events.
2 We usually use three different verbs forms when we tell stories: the past simple,
the past continuous and the past perfect. Which verb forms can you see?
past simple past perfect
I said ‘goodnight’ to the children and switched off their light. We needed to get up
early the next day, so we had packed our bags and had prepared everything ready to
leave at 6 a.m. I woke up suddenly in the middle of the night. The wind was howling
and something was banging outside. I went downstairs quietly to see what was
making the noise. I was sure I had locked the back door before I had gone to bed
that night.
past continuous
© Oxford University Press
2.1 Narrative forms
1 We use the past simple to describe the main events in a narrative.
1 She picked up the phone and called an ambulance.
2 They watched the robber outside the bank, and then they arrested him.
2 Most past simple verb forms add -ed, but many common verbs are irregular.
take took sleep slept wake woke put put have had
3 We form the negative and questions in the past simple with did and the infinitive.
1 I didn’t see him. NOT I didn’t saw him.
2 Did you wait? NOT You waited?
© Oxford University Press
2.1 Narrative forms
1 We use the past continuous to describe background events and situations. We
also use the past continuous to contrast longer actions with shorter ones.
2 We form the past continuous with was/were and the -ing form of the main verb.
1 We were walking in the park while the children were playing.
2 The sun was shining and the birds were singing.
3 They were watching the match when the phone rang.
3 We form the negative past continuous with was/were not. We form questions by
changing the order of the subject and was/were.
1 He wasn’t looking when he stepped into the road. What was he thinking?
2 Where were you going when I saw you last night?
3 We weren’t having dinner; we were only having a drink when you saw us.
© Oxford University Press
2.1 Narrative forms
1 We use the past perfect to describe things that happened before the main events
in the story or before the time of the story.
1 I had never been to Africa before, so I was excited when the plane landed.
2 She hadn’t met him before the party.
3 We’d spoken on the phone that morning.
2 We form the past perfect with had + past participle. We make the negative form
with had + not. We often use contractions ’d and hadn’t.
3 We form questions by changing the order of the subject and had.
1 Had you ever seen that man before?
2 Had they left before you arrived?
© Oxford University Press
2.1 Narrative forms
1 Choose the correct options to complete the sentences.
1 They had never seen/never saw such a big hotel.
2 The boat had hit/hit a rock, there was/had been a rush of water and it had sunk/sank.
3 Snow was falling/fell and people were hurrying/hurried home as quickly as possible.
4 We had realized/realized our mistake five minutes after we had arrived/arrived.
5 Just as we were driving/drove back home, we saw/were seeing the fire engine
outside our house.
© Oxford University Press
You might also like
- Biber, Conrad, Leech - Student Grammar of Spoken and Written EnglishDocument497 pagesBiber, Conrad, Leech - Student Grammar of Spoken and Written EnglishIva Basar100% (10)
- Different Question Types: 1 We Often Form Questions by Putting An Auxiliary Verb Before The SubjectDocument101 pagesDifferent Question Types: 1 We Often Form Questions by Putting An Auxiliary Verb Before The SubjectMonica MotNo ratings yet
- GRPPT B1+Document93 pagesGRPPT B1+Monica MotNo ratings yet
- Completed Pt3 ModuleDocument160 pagesCompleted Pt3 ModuleAnonymous 1Y3FIHJNo ratings yet
- Past PerfectDocument13 pagesPast PerfectacroaliNo ratings yet
- Coordinator (DDE) 484-2-103010BA2001IIEnglishIIStudyMaterialDocument84 pagesCoordinator (DDE) 484-2-103010BA2001IIEnglishIIStudyMaterialPUBG GAMERNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous and Past SimpleDocument6 pagesPast Continuous and Past SimplesayudeviNo ratings yet
- Noun Phrases: A Noun Phrase Is A Group of Words Before, And/or After A NounDocument29 pagesNoun Phrases: A Noun Phrase Is A Group of Words Before, And/or After A NounSofia WeirNo ratings yet
- Plan Lectie Cls II AlphabetDocument4 pagesPlan Lectie Cls II AlphabetDaniela Matei Şora100% (1)
- Rubric in Poem RecitationDocument2 pagesRubric in Poem RecitationVanessa Baniaw100% (1)
- Week 9: Unit 3: Grammar SummaryDocument3 pagesWeek 9: Unit 3: Grammar SummaryDang Duy QuachNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses ALLDocument4 pagesPast Tenses ALLVanina SivoriNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and ContinuousDocument4 pagesPast Simple and ContinuousVanina SivoriNo ratings yet
- Narrative Tenses: Past Simple and Present Perfect 1 The Past Simple Refers To Finished PastDocument7 pagesNarrative Tenses: Past Simple and Present Perfect 1 The Past Simple Refers To Finished PastNevena BajicNo ratings yet
- Grammar Review c1-2 PDFDocument7 pagesGrammar Review c1-2 PDFEduardo RuizNo ratings yet
- Grammar FocusDocument35 pagesGrammar FocusTrabajos AcadémicosNo ratings yet
- English 7 Week 4: Learning Activity Sheets First QuarterDocument7 pagesEnglish 7 Week 4: Learning Activity Sheets First QuarterAC BonbonNo ratings yet
- HDW - UpperInt - Grammar - 1.2 - English Tense UsageDocument8 pagesHDW - UpperInt - Grammar - 1.2 - English Tense UsageNevena BajicNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Perfect TenseDocument7 pagesPast Simple Perfect TensejeanNo ratings yet
- Past Simple: 1 We Often Use The Past Simple To Talk About Finished Actions in The Past, and To Tell StoriesDocument4 pagesPast Simple: 1 We Often Use The Past Simple To Talk About Finished Actions in The Past, and To Tell StoriesMauro Rene GIMENEZNo ratings yet
- In English There Is Two Types of Verbs, Dyanmic and StativeDocument21 pagesIn English There Is Two Types of Verbs, Dyanmic and StativetriplelouNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8. Narrative TensesDocument18 pagesLesson 8. Narrative Tensesmerzarbe tizkorNo ratings yet
- Module Pt3docxDocument84 pagesModule Pt3docxNik Razin Azim IsmailNo ratings yet
- Num2libro InglesDocument127 pagesNum2libro InglesJose SandovalNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses Handout Mark SchemeDocument12 pagesPast Tenses Handout Mark SchemeWarissaNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and Past Continuous: 1 We Use The Past Continuous For Actions Which Were Unfinished at A Past TimeDocument4 pagesPast Simple and Past Continuous: 1 We Use The Past Continuous For Actions Which Were Unfinished at A Past TimeMauro Rene GIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Syntax and Teaching Grammar - AssignmentDocument6 pagesSyntax and Teaching Grammar - AssignmentAlex RiveraNo ratings yet
- 1st Bach Final Review - With AnswersDocument11 pages1st Bach Final Review - With AnswersviktorsevillaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Discussion Report (Right)Document4 pagesLesson 7 Discussion Report (Right)adlynaANo ratings yet
- Adverbial Clauses: Type of Adverbial Clauses Free Adjuncts Linking AdverbsDocument35 pagesAdverbial Clauses: Type of Adverbial Clauses Free Adjuncts Linking AdverbsTú Nguyễn Hoàng NhậtNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Tarea de Ingles.. ReynaldoDocument5 pagesVerb Tenses Tarea de Ingles.. ReynaldoreynaldoNo ratings yet
- I Think There'd Be A Lot of Children Who'd Love To Have A Climbing Wall in SchoolDocument11 pagesI Think There'd Be A Lot of Children Who'd Love To Have A Climbing Wall in SchoolEmil FejzagićNo ratings yet
- Past Tense: NAMA: Ahmad Supianor Kelas: X Mipa 2Document8 pagesPast Tense: NAMA: Ahmad Supianor Kelas: X Mipa 2Rani RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Past PerfectDocument2 pagesPast Perfectnagdee.bNo ratings yet
- Types of Preposition: Time Prepositions: Place Prepositions: Direction PrepositionsDocument13 pagesTypes of Preposition: Time Prepositions: Place Prepositions: Direction PrepositionsYasmin KhanNo ratings yet
- Nef Upper Int SB 134 145Document12 pagesNef Upper Int SB 134 145LaraURNo ratings yet
- IT1 Lecture 3 - Technical English-IIDocument14 pagesIT1 Lecture 3 - Technical English-II오뚜기No ratings yet
- Unit 2.2pptxDocument11 pagesUnit 2.2pptxwlaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: Ashley Del Socorro Mejía GámezDocument34 pagesEnglish Grammar: Ashley Del Socorro Mejía Gámezjordan montenegroNo ratings yet
- GR9 Unit 3 EnglishDocument21 pagesGR9 Unit 3 EnglishTipa JacoNo ratings yet
- Tenses ReviewDocument7 pagesTenses Reviewtahafartouti0No ratings yet
- Ling Chin Chuan Low Ying Yee Amir Akmal Lee Seo Lin Mohd IdrisDocument10 pagesLing Chin Chuan Low Ying Yee Amir Akmal Lee Seo Lin Mohd IdrisLisa WongNo ratings yet
- English 5 Unit 5Document52 pagesEnglish 5 Unit 5ArjayNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous - 2C2Document6 pagesPast Continuous - 2C2Trang Choi ChoiNo ratings yet
- ArticlesDocument3 pagesArticlesMaria DíazNo ratings yet
- Tema 01Document47 pagesTema 01Felix Pinedo QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Narrative TensesDocument3 pagesNarrative TenseszamotehNo ratings yet
- Definition of The Simple Past TenseDocument7 pagesDefinition of The Simple Past TenseJhonatan MendozaNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument47 pagesPast SimplemiaNo ratings yet
- Revision of Verb TensesDocument4 pagesRevision of Verb Tensesmarcela noemiNo ratings yet
- NP C4 CD4.1 P2.1 SlideDocument14 pagesNP C4 CD4.1 P2.1 SlideGinko KuinNo ratings yet
- Modul English - Active Voice (1-14)Document14 pagesModul English - Active Voice (1-14)Amanda Fatma NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Theory Simple ContinuousDocument2 pagesTheory Simple Continuousflower powerNo ratings yet
- Basic Verb TensesDocument5 pagesBasic Verb TensesJochelle Mae SucuanoNo ratings yet
- New PP StructureDocument31 pagesNew PP Structuregalih febriandryNo ratings yet
- Simple TensesDocument12 pagesSimple TensesHienNo ratings yet
- 1 Home and Away: Language FocusDocument120 pages1 Home and Away: Language FocusMounir Angad100% (2)
- DOSSIERDocument7 pagesDOSSIERElena GarciaNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice FormsDocument6 pagesPassive Voice FormsNilai100% (1)
- Oblique Moods in EnglishDocument53 pagesOblique Moods in EnglishОлесеа Амброс50% (2)
- Past Tense by Erik Subandi MaulanaDocument7 pagesPast Tense by Erik Subandi MaulanaHaan AilaNo ratings yet
- Today'S Objective: - Reading Comprehension - Grammar: The Past Perfect - ExercisesDocument31 pagesToday'S Objective: - Reading Comprehension - Grammar: The Past Perfect - ExercisesExcelsior SchoolNo ratings yet
- Good Morning!Document21 pagesGood Morning!Mike Edrian BantingNo ratings yet
- The Working Day British English TeacherDocument9 pagesThe Working Day British English TeacherCinthia MurilloNo ratings yet
- Lets Save Our EnvironmentDocument3 pagesLets Save Our EnvironmentSalma BazziNo ratings yet
- English Review Gen-Ed: Prepared By: Niki Mia A. GustiloDocument127 pagesEnglish Review Gen-Ed: Prepared By: Niki Mia A. GustiloDominic DizonNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous ClassDocument7 pagesPresent Continuous ClassWilmar SuarezNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Pointers For PT 1Document5 pagesGrade 3 Pointers For PT 1Fretchiel Mae SusanNo ratings yet
- Pronunciation Level 1Document23 pagesPronunciation Level 1resky marantinanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English Grade 7Document15 pagesLesson Plan in English Grade 7guia bullecerNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech PDFDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech PDFBianca ZobNo ratings yet
- ABC Poem - Capa ModelDocument4 pagesABC Poem - Capa ModelRishamjot KNo ratings yet
- G95 FilipinoDocument18 pagesG95 FilipinoMelody KillaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Warm-Up: Aim: To Create A Pleasant Atmosphere and To Relax TimingDocument3 pagesActivity 1 Warm-Up: Aim: To Create A Pleasant Atmosphere and To Relax Timingmaria nicolaeNo ratings yet
- Speaking Assessment Criteria C1Document1 pageSpeaking Assessment Criteria C1GERESNo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis: Mr. Trương Văn ÁnhDocument13 pagesDiscourse Analysis: Mr. Trương Văn ÁnhBich Huyen PhamNo ratings yet
- Soal UAS Bahasa InggrisDocument1 pageSoal UAS Bahasa InggrisAnnisahNo ratings yet
- Relationships Friends ForeverDocument2 pagesRelationships Friends ForeverYarenNo ratings yet
- David CRYSTAL-EMERGING - ENGLISHES - NEWDocument5 pagesDavid CRYSTAL-EMERGING - ENGLISHES - NEWTeresaNo ratings yet
- A Pragmatic Study of Speech Acts of Warning in English and ArabicDocument21 pagesA Pragmatic Study of Speech Acts of Warning in English and Arabickm944950No ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument8 pagesFigures of SpeechKrista LorNo ratings yet
- Key Stage 2: Easter Revision Booklet Timed Daily Activities in Arithmetic, Reasoning and Grammar For 10 DaysDocument41 pagesKey Stage 2: Easter Revision Booklet Timed Daily Activities in Arithmetic, Reasoning and Grammar For 10 DaysAyman GaffoorNo ratings yet
- PSI Syllabus GujaratDocument4 pagesPSI Syllabus GujaratTechnical JeeNo ratings yet
- How To Hail Satan in Proper Latin - Latin For SatanistsDocument8 pagesHow To Hail Satan in Proper Latin - Latin For SatanistsRockyNo ratings yet
- Function Words KobrinaDocument14 pagesFunction Words KobrinaВлада ГуменюкNo ratings yet
- Direct and Reported SpeechDocument40 pagesDirect and Reported SpeechJeneros PartosNo ratings yet
- Guia de Trabajo Autonomo (4) Plural Se Sustantivos SaDocument14 pagesGuia de Trabajo Autonomo (4) Plural Se Sustantivos SaPaulita MejiaNo ratings yet
- Tips For SPM Speaking TestDocument13 pagesTips For SPM Speaking Testseehong620No ratings yet