Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chromatography Lesson Note
Uploaded by
Amy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views20 pagesChromatography can be used to separate mixtures like ink dyes. Pure substances will produce only one spot, while mixtures will separate into multiple spots on the chromatogram. Paper chromatography is used to separate mixtures because it allows calculation of Rf values, which can be used to identify unknown substances by comparing to known reference values under the same solvent conditions. The Rf value represents how much a substance is retained on the paper versus being carried by the solvent.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChromatography can be used to separate mixtures like ink dyes. Pure substances will produce only one spot, while mixtures will separate into multiple spots on the chromatogram. Paper chromatography is used to separate mixtures because it allows calculation of Rf values, which can be used to identify unknown substances by comparing to known reference values under the same solvent conditions. The Rf value represents how much a substance is retained on the paper versus being carried by the solvent.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views20 pagesChromatography Lesson Note
Uploaded by
AmyChromatography can be used to separate mixtures like ink dyes. Pure substances will produce only one spot, while mixtures will separate into multiple spots on the chromatogram. Paper chromatography is used to separate mixtures because it allows calculation of Rf values, which can be used to identify unknown substances by comparing to known reference values under the same solvent conditions. The Rf value represents how much a substance is retained on the paper versus being carried by the solvent.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
Chromatography
The elephant and mouse proverb...
Interpretation of Chromatography...
• Which is able to run more quickly through the forest?
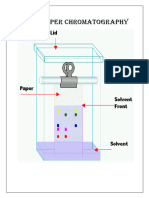
A mixture of substances can be separated by paper chromatography such as ink; the
mixture of different colored dye.
Note: Pure substance cannot be separated.
• Pure substances will produce only one spot on the chromatogram
• If two or more substances are the same, they will produce identical
chromatograms
• If the substance is a mixture, it will separate on the paper to show all
the different components as separate spots
• An impure substance therefore will produce a chromatogram with
more than one spot
Why do we use paper chromatography?
How chromatography works?
Rf Values………
• These values are used to identify the components of mixtures
• The Rf value of a particular compound is always the same but it is dependent,
however, on the solvent used
• If the solvent is changed then the value changes
• Calculating the Rf value allows chemists to identify unknown substances because
it can be compared with Rf values of known substances under the same conditions
• These values are known as reference values
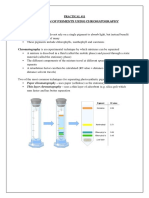
Calculating Retention factor (Rf) values
• How much a substance is held back by the paper is called the
Retention factor (Rf) Value.
• You can calculate this by:
Reminder…..
• The Rf value will always lie
between 0 and 1; the closer it
is to 1, the more soluble is that
component in the solvent
• The Rf value is a ratio and
therefore has no units
You might also like
- ChromatographyDocument10 pagesChromatographyKnk SeriesNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument9 pagesPaper Chromatographyantocapo2008No ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument4 pagesChromatographyDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument6 pagesChromatographyUmer AyazNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography Model and Practical LabDocument4 pagesPaper Chromatography Model and Practical Labdebbie bongNo ratings yet
- Separation and Purification in Chemistry Grade 9Document26 pagesSeparation and Purification in Chemistry Grade 9Fandy100% (2)
- Chromatography Student 2021-2022Document17 pagesChromatography Student 2021-2022Nickoye WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: Is A Technique Used To Separate and Identify The Components of A MixtureDocument72 pagesChromatography: Is A Technique Used To Separate and Identify The Components of A MixtureMustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- 2.2.1. Criteria of Purity PDFDocument3 pages2.2.1. Criteria of Purity PDFOttoNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: Chemical AnalysisDocument3 pagesChromatography: Chemical AnalysisafnaanqurreshiNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument5 pagesPaper ChromatographyMaria Elena PascualNo ratings yet
- PAPER+CHROMATOGRAPHY PpsDocument35 pagesPAPER+CHROMATOGRAPHY PpsjasyeelelooNo ratings yet
- F9 - Chromatography of InkDocument7 pagesF9 - Chromatography of InkRosaElizabethValentePereiraNo ratings yet
- EXP10 ChromatographyDocument27 pagesEXP10 ChromatographyKiara Sy0% (1)
- 3.6 (Lesson 2) Testing For Protein SNDocument13 pages3.6 (Lesson 2) Testing For Protein SNjnfjngsdjNo ratings yet
- Retention FactorDocument1 pageRetention Factorsirrah jonesNo ratings yet
- AlexDocument2 pagesAlexYasar Arafath SNo ratings yet
- Food Coloring ChromatographyDocument7 pagesFood Coloring ChromatographyHenry Lee100% (1)
- Paper Chromatography QuestionsDocument4 pagesPaper Chromatography QuestionsMuhammadJahangirAlam100% (1)
- Paper Chromatography - ChemguideDocument7 pagesPaper Chromatography - ChemguideNick NikeshNo ratings yet
- Ink ChromatographyDocument9 pagesInk Chromatographyapi-2639095050% (1)
- 2: Paper Chromatography of Gel Ink Pens (Experiment) : ObjectivesDocument3 pages2: Paper Chromatography of Gel Ink Pens (Experiment) : ObjectivesDivya TripathyNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument27 pagesPaper ChromatographyAlea PrillyNo ratings yet
- CHEMDocument13 pagesCHEMMohamed MusthapaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesBIOLOGY Investigatory ProjectShruti GarjeNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument19 pagesPaper Chromatographywidya sariNo ratings yet
- Chromatography Lab Report: Judy Faour 13DDocument5 pagesChromatography Lab Report: Judy Faour 13DJudy FaourNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument5 pagesPaper ChromatographyDr. P.S.SenguptaNo ratings yet
- CHROMATOGRAPHYDocument1 pageCHROMATOGRAPHYᴇᴜᴘʜᴏʀɪxNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography PDFDocument8 pagesPaper Chromatography PDFVenice Eurika RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Et ST 9 Mod-2Document14 pagesEt ST 9 Mod-2pdchemigcse1786No ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures: Inquiry Question: How Do The Properties of Substances Help Us To Classify and Separate Them?Document18 pagesSeparating Mixtures: Inquiry Question: How Do The Properties of Substances Help Us To Classify and Separate Them?Tashna LalNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Analytical TechniquesDocument12 pages1.6 Analytical TechniquesMûhd AïZām ÄhmâdNo ratings yet
- Seperation of Photosynthetic Pigment - ChromotographyDocument15 pagesSeperation of Photosynthetic Pigment - ChromotographyIyvd sdfshethNo ratings yet
- Lab Report No. XDocument5 pagesLab Report No. XJerome MosadaNo ratings yet
- Chromatography Planar: Taufik Turahman, M.Farm., AptDocument57 pagesChromatography Planar: Taufik Turahman, M.Farm., AptPutri BilaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Techniques (Chapter 2) : Presented By: Mrs. SaimaDocument16 pagesExperimental Techniques (Chapter 2) : Presented By: Mrs. SaimaMohamed MunirNo ratings yet
- Chem PD 2Document3 pagesChem PD 2aljaycolley2020No ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument7 pagesChromatographyPshtiwan RaheemNo ratings yet
- ORG LAB Paper Chromatography2009Document6 pagesORG LAB Paper Chromatography2009Caresse LisetteNo ratings yet
- M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.D Research ScholarDocument31 pagesM.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.D Research ScholarAlbert EinsteinNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Notes THDocument2 pagesGR 10 Notes THLisandra SantosNo ratings yet
- Ipchmclass12th Converted1 191208134113Document15 pagesIpchmclass12th Converted1 191208134113rathorepadamsingh698No ratings yet
- T5 Chromatography AQA KS3Document34 pagesT5 Chromatography AQA KS3Megan RyanNo ratings yet
- Analytical techniques-TLC, HPLC, GLCDocument27 pagesAnalytical techniques-TLC, HPLC, GLCKudzayi TusaumweNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument53 pagesChemistry NotesAbha RathoreNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument3 pagesChromatographyAashiNo ratings yet
- Chromotography Lab 2018Document2 pagesChromotography Lab 2018AndrewNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab #1Document3 pagesBio Lab #1Brianna MelbourneNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - ChromatographyDocument2 pagesLab 7 - ChromatographyChivonne AlsuranNo ratings yet
- Analytical Techniques Final Note NADocument121 pagesAnalytical Techniques Final Note NAyuvi78312No ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography 2Document4 pagesPaper Chromatography 2Emily MangraNo ratings yet
- 37 Analytical Techniques PDFDocument225 pages37 Analytical Techniques PDFKomal EhsanNo ratings yet
- Spinach Chromatography LabDocument6 pagesSpinach Chromatography LabGerson Antonio Echeverria VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Document 3Document5 pagesDocument 3SOLOMON RIANNANo ratings yet
- Notes 9 - Particulate Nature of MatterDocument3 pagesNotes 9 - Particulate Nature of MatterNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesisWinston Jake GerolagaNo ratings yet
- ChromotographyDocument36 pagesChromotographySanstubNo ratings yet
- PollutionDocument32 pagesPollutionAmyNo ratings yet
- MagneticsDocument22 pagesMagneticsAmyNo ratings yet
- What Is A TsunamisDocument4 pagesWhat Is A TsunamisAmyNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument33 pagesElectricityAmyNo ratings yet
- Earth's MovementDocument23 pagesEarth's MovementAmyNo ratings yet
- The Earth and The SunDocument14 pagesThe Earth and The SunAmyNo ratings yet
- The Solar SystemDocument27 pagesThe Solar SystemAmyNo ratings yet
- Today WeatherDocument30 pagesToday WeatherAmyNo ratings yet
- The Earth and The SunDocument6 pagesThe Earth and The SunAmyNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument8 pagesVolcanoesAmyNo ratings yet
- Mole CalculationsDocument27 pagesMole CalculationsAmyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Practice Part#1Document22 pagesChapter-1 Practice Part#1AmyNo ratings yet
- Element, Compound, Mixture NotesDocument38 pagesElement, Compound, Mixture NotesAmyNo ratings yet
- Balancing EquationsDocument11 pagesBalancing EquationsAmyNo ratings yet
- Balanced Diet G-8Document19 pagesBalanced Diet G-8AmyNo ratings yet
- Calculating Speed G-9Document19 pagesCalculating Speed G-9AmyNo ratings yet
- All About Roots and StemDocument14 pagesAll About Roots and StemAmyNo ratings yet