0% found this document useful (0 votes)
125 views65 pages2 - Design Essentials of The Structure
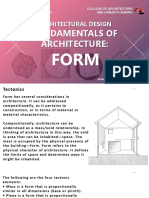
The document discusses the fundamentals of architectural design and structure. It describes the invisible structure as the building plan and arrangement of rooms. The visible structure is composed of the mass or volume and surface. Mass is three-dimensional and can take various shapes, directions, and forms. Surface has two dimensions and is defined by its texture, tone, light and shade, and color. Form deals with the three-dimensional shape and mass of a structure.
Uploaded by
Jaelaurence DiosanaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
125 views65 pages2 - Design Essentials of The Structure
The document discusses the fundamentals of architectural design and structure. It describes the invisible structure as the building plan and arrangement of rooms. The visible structure is composed of the mass or volume and surface. Mass is three-dimensional and can take various shapes, directions, and forms. Surface has two dimensions and is defined by its texture, tone, light and shade, and color. Form deals with the three-dimensional shape and mass of a structure.
Uploaded by
Jaelaurence DiosanaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd