Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trigonometry SOHCAHTOA Guide
Uploaded by
Franca OkechukwuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trigonometry SOHCAHTOA Guide
Uploaded by
Franca OkechukwuCopyright:
Available Formats
Trigonometry
Finding Missing Sides and Angles using
SOHCAHTOA
Ms. Franca 9/19/22
Learning Objectives
To be able to use the trigonometric functions (sine, cosine and tangent)
to find the missing sides in a right-angled triangle
To be able to use the trigonometric functions (sine, cosine and tangent)
to find the missing angles in a right-angled triangle
Ms Franca Okechukwu 9/19/22
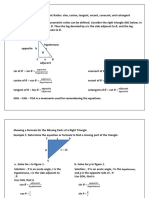
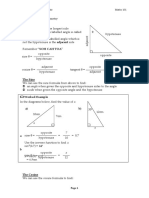
Recap- SOHCAHTOA
hy
po
sin θ = ten
opposite
us
e
cos θ =
tan θ = θ
adjacent
sin θ = cos θ = tan θ =
Ms Franca Okechukwu 9/19/22
Summarily, SOHCAHTOA…
hy
po
If we let O be the opposite, A be the adjacent, and t en
opposite
us
H be the hypotenuse, then these are shortened to: e
θ
adjacent
Ms Franca Okechukwu 9/19/22
Summarily, Special Angles are…
B A
45o 30o 30o
√2 2 2
1
√3
45o 60o 60o
A C B C
1 1 D 1
sin cos tan
30o
45o 1
60o √3
90o 1 0 ∞
Ms Franca Okechukwu 9/19/22
Let’s find a missing side…
First of all, we need to find which
equation we need to use.
The working angle is 30o.
We have the hypotenuse; H = 8 cm 8 cm
We are to find the adjacent; O = b b
Hence, we’ll use the SOH formula
30o
sin θ =
Substituting, we have; Find the length of the side marked b to 1 d.p.
sin 30 =
b = 8 × sin 30
b=8×
b = 4 cm
Ms Franca Okechukwu 9/19/22
Let’s find another missing side…
The working angle, θ is 45o.
And we have the opposite; O=4m
To find w, weare
areto
tofind
findthe
theadjacent;
hypotenuse; 45o
z, we
H
A = zw w
z
Hence, we’ll use the SOH
TOA formula
sin
tan θ =
Substituting, we have; 4m
sin
tan 45 = Find the length of the sides marked w and z.
w
z == ==
w = 4 × = 4√2 m
z=4m
Ms Franca Okechukwu 9/19/22
Extension
The working angle, θ is 38o.
And we have the hypotenuse; H = 12 cm
We are to find the adjacent; A = y
Hence, we’ll use the CAH formula
cos θ =
Substituting, we have;
cos 38 =
y = 12 × cos (38)
Using the calculator, we have; Find the length of the side marked y to 1 d.p.
y = 9.4561... = 9.5 cm (to 1 d.p.)
Ms Franca Okechukwu 9/19/22
Let’s find a missing angle…
We have the adjacent, A = 3”
We have the hypotenuse, H = 6”
θ
We need to find the working angle = θ
6”
So, if we have A and H, then we use CAH 3”
cos (x) = becomes cos (θ) =
cos (θ) = ½
Find the size of the angle θ.
To find θ, you need to cancel out the cos
function using its inverse function (cos–1).
Thus, we’ll have;
θ = cos–1 (½)
From the table,
θ = 60o
Ms Franca Okechukwu 9/19/22
Let’s find another missing angle…
We have the opposite, O = 6 cm
We have the adjacent, H = 12 cm
We need to find the working angle = θ
So, if we have O and H, then we use SOH
12 cm
sin (x) = becomes sin (v) = 6 cm
sin (v) = ½
v
To find v, you need to cancel out the sin
Find the size of the angle v.
function using its inverse function (sin–1).
Thus, we’ll have;
v = sin–1 (½)
From the table,
v = 30o
Ms Franca Okechukwu 9/19/22
Extension
We have the opposite length = 5 mm
We have the adjacent length = 8 mm
We need to find the working angle = θ Find the size of angle z to 2 s.f.
So, if we have O and A, then we use TOA
tan (x) = becomes tan (z) =
tan (z) = 0.625
To find z, you need to cancel out the tan function
using its inverse function (tan–1). Thus, we’ll have;
z = tan–1 (0.625)
To get tan–1 using your calculator, enter shift tan
(0.625)
z = 32.0053 = 32.0o
Ms Franca Okechukwu 9/19/22
Now, it’s “Your Turn”!
Find the length of the side marked p to 2 s.f. Find the size of angle q to 1 d.p.
Find the size of angle x to 1 d.p.
Find the length of the side /CB/.
Find the size of
angle w to 1 d.p.
Ms Franca Okechukwu 9/19/22
Success Criteria
I can use the trigonometric functions (sine, cosine and tangent) to find
the missing sides in a right-angled triangle
I can use the trigonometric functions (sine, cosine and tangent) to find
the missing angles in a right-angled triangle
Ms Franca Okechukwu 9/19/22
9/19/22
You might also like
- 95 Suzuki Sidekick Wiring DiagramDocument46 pages95 Suzuki Sidekick Wiring DiagramDominic Bufton88% (8)
- Use trigonometry to find unknown sides and angles (40Document28 pagesUse trigonometry to find unknown sides and angles (40OO O OONo ratings yet
- Trigonometry IDocument13 pagesTrigonometry IAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Trigonometric RatiosDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Trigonometric RatiosBenster Andrew AlcaideNo ratings yet
- TM 5-2430-200-10Document196 pagesTM 5-2430-200-10Advocate100% (1)
- D1653Document5 pagesD1653manox007No ratings yet
- Defining Special Angles Using SOHCAHTOADocument10 pagesDefining Special Angles Using SOHCAHTOAFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Summary Notes and Worked ExamplesDocument17 pagesTrigonometry Summary Notes and Worked ExamplesArdit ZotajNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios PresentationDocument15 pagesTrigonometric Ratios PresentationArchie ConagNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Part 1Document28 pagesTrigonometry Part 1Maria Mae100% (1)
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Mathematics: The Six Trigonometric Ratios: Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosecant, and TangentDocument3 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Mathematics: The Six Trigonometric Ratios: Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosecant, and TangentHazel LiwanagNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Triangle TrigonometryDocument9 pagesModule 7 Triangle TrigonometryKatherine Joy CruzNo ratings yet
- Triangle TrigonometryDocument22 pagesTriangle TrigonometryDikano MorareNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Part 1Document28 pagesTrigonometry Part 1Annisa IstiqomahNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 03-01-24Document4 pagesGrade 9 03-01-24Stephanie Grace SitonNo ratings yet
- Triangle TrigonometryDocument22 pagesTriangle Trigonometryerika sampanNo ratings yet
- Presentation Trigonometry (Wecompress - Com) 1535913988 354634Document49 pagesPresentation Trigonometry (Wecompress - Com) 1535913988 354634monikaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry RatiosDocument30 pagesTrigonometry RatiosNathaniel WhyteNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios GuideDocument16 pagesTrigonometric Ratios GuideFlaaffyNo ratings yet
- Session 1: MA.1.01 - Create, Interpret and Analyze Trigonometric Ratios That Model Real-World SituationsDocument19 pagesSession 1: MA.1.01 - Create, Interpret and Analyze Trigonometric Ratios That Model Real-World SituationsAbo Alphotoh GamingNo ratings yet
- A-Level Preparation - Right Angled TrigonometryDocument6 pagesA-Level Preparation - Right Angled TrigonometrymhacunaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Finding Angles and Sides in Right-Angled TrianglesDocument7 pagesTrigonometry: Finding Angles and Sides in Right-Angled TrianglesBorhan Nordin DaudNo ratings yet
- 10.lesson Plan in Trigonometric RatiosDocument7 pages10.lesson Plan in Trigonometric RatiosAeron TamaniNo ratings yet
- Maths In Focus Mathematics Extension 1 Preliminary TrigonometryDocument2 pagesMaths In Focus Mathematics Extension 1 Preliminary TrigonometrysNo ratings yet
- The Basics: Trigonometry Study Guide Maths 101Document7 pagesThe Basics: Trigonometry Study Guide Maths 101nooree hossenbuxNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Trigonometry FunctionsDocument9 pagesIntroduction to Trigonometry FunctionsYogesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Q4 Math 9 Week 2Document4 pagesQ4 Math 9 Week 2Jiles M. MasalungaNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras' and Trigonometry Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPythagoras' and Trigonometry Cheat SheetThalia CooleyNo ratings yet
- Pythagroas and SOHCAHTOADocument8 pagesPythagroas and SOHCAHTOA姚凤娇No ratings yet
- 4 - Mathematical Language and Symbols (Part 2)Document31 pages4 - Mathematical Language and Symbols (Part 2)Bevelyn Layosa AbellonNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry 101Document6 pagesTrigonometry 101Nightcrawler KurtNo ratings yet
- Illustrates The 6 Trigonometric RatiosDocument31 pagesIllustrates The 6 Trigonometric RatiosAngelica Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: 4 QuarterDocument21 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: 4 QuarterSelena ThaliaNo ratings yet
- Q4 MATH 9-WEEK 3-Solving Right Triangle Using Trigonometric RatiosDocument39 pagesQ4 MATH 9-WEEK 3-Solving Right Triangle Using Trigonometric RatiosAngela Camille PaynanteNo ratings yet
- ParabolDocument13 pagesParabolEDM musicNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Las q4 Melc 1.1Document4 pagesMath 9 Las q4 Melc 1.1Maria Sophia PradoNo ratings yet
- Math in Focus Year 11 2 Unit CH 6 Trigonometry PDFDocument78 pagesMath in Focus Year 11 2 Unit CH 6 Trigonometry PDFPaul TurnerNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Trigonometry Applications of Trigonometry Cbse Class X ProjectDocument12 pagesDokumen - Tips - Trigonometry Applications of Trigonometry Cbse Class X ProjectRajput gamersNo ratings yet
- Q4 W1Six Trigonometric RatiosDocument29 pagesQ4 W1Six Trigonometric RatiosDaywalker PedragozaNo ratings yet
- TrigReviewNotesDocument7 pagesTrigReviewNotesjieseljoyceoliliNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument2 pagesTrigonometryMCHNo ratings yet
- G9 Math Q4 - Week 1 - 2-Six Trigonometric RatioDocument25 pagesG9 Math Q4 - Week 1 - 2-Six Trigonometric RatioEloisa Grace AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets in Mathematics 9Document4 pagesActivity Sheets in Mathematics 9Ella AltNo ratings yet
- VBJKDocument8 pagesVBJKiyd70712No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 TrigonometryDocument41 pagesChapter 2 TrigonometryAish CherryNo ratings yet
- The Six Trigonometric RatiosDocument28 pagesThe Six Trigonometric RatiosMary Joy Bagolantoy Morada80% (5)
- Lesson 1 Trigonometric RatiosDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Trigonometric RatiosBenster Andrew AlcaideNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Equations and Identities Solved ExamplesDocument16 pagesTrigonometric Equations and Identities Solved Examplesmazhar10325No ratings yet
- Sin, Cos and Tan: ExampleDocument4 pagesSin, Cos and Tan: ExampleMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesLesson PlanIrish Ga-aNo ratings yet
- Sir Gian Trigonometry 102Document14 pagesSir Gian Trigonometry 102jennifferpabuayaNo ratings yet
- EngineeringDocument11 pagesEngineeringElysa DilalilyNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Ratios in Right TriangleDocument19 pagesTrigonometry Ratios in Right Trianglemicaela Jomil TizonNo ratings yet
- A2 12-1 Study Guide and Intervention AnswersDocument2 pagesA2 12-1 Study Guide and Intervention Answersjta86183No ratings yet
- Trigonometry RatiosDocument27 pagesTrigonometry RatiosElla de la Cruz Gulanes100% (1)
- A Hypotenuse Opposite side Adjacent side: θ Reference AngleDocument4 pagesA Hypotenuse Opposite side Adjacent side: θ Reference AngleJulius BayagaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Math 9 Week 1 8combinedDocument29 pagesQ4 Math 9 Week 1 8combinedjewel baglinaNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Topics in First Year Mathematics: WwlchenandxtduongDocument17 pagesMiscellaneous Topics in First Year Mathematics: WwlchenandxtduongEhab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Pre-Calculus 11Document18 pagesReviewer in Pre-Calculus 11RJ Seva IIINo ratings yet
- Triangle Trigonometry: What This Module Is AboutDocument26 pagesTriangle Trigonometry: What This Module Is AboutisayblankNo ratings yet
- Module 1 in MfeDocument9 pagesModule 1 in Mfevantae SmithNo ratings yet
- Atomic Number and Mass Number: Date/PeriodDocument1 pageAtomic Number and Mass Number: Date/PeriodFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- 0620 w18 Ms 41Document9 pages0620 w18 Ms 41Arhaan SawhneyNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of Matter (Multiple Choice) QPDocument11 pagesThe Particulate Nature of Matter (Multiple Choice) QPSumathi Ganasen50% (2)
- Teacher Intro - HSDocument1 pageTeacher Intro - HSFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Atomic Number and Mass Number: Date/PeriodDocument1 pageAtomic Number and Mass Number: Date/PeriodFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- A GUIDE TO PHYTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS Ijariie9430Document10 pagesA GUIDE TO PHYTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS Ijariie9430Franca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Drawing and Interpreting Cummulative Frequency DiagramsDocument27 pagesDrawing and Interpreting Cummulative Frequency DiagramsFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Science Fair ProjectDocument3 pagesScience Fair ProjectFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Drawing A Pie ChartDocument13 pagesDrawing A Pie ChartFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Test For IonsDocument1 pageTest For IonsFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Linear ProgrammingDocument25 pagesLinear ProgrammingFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium BWDocument54 pagesEquilibrium BWFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Listing OutcomesDocument8 pagesListing OutcomesFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- GatmosppsDocument66 pagesGatmosppsFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Cps 5Document4 pagesCps 5Franca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper IiDocument2 pagesChemistry Paper IiFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Coal Derivatives: Coke, Tar, GasDocument3 pagesCoal Derivatives: Coke, Tar, GasFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Term 1 Continuous AssessmentDocument3 pagesTerm 1 Continuous AssessmentFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Acids and Alkalis Test Yourself 3Document2 pagesAcids and Alkalis Test Yourself 3Franca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- 21 - 0620Document3 pages21 - 0620Franca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Term 1 Continuous AssessmentDocument3 pagesTerm 1 Continuous AssessmentFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Analysis Physics Educators-ProspectsDocument1 pageAnalysis Physics Educators-ProspectsFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- The Diffusion of Ammonia and Hydrogen Chloride - Technician NotesDocument2 pagesThe Diffusion of Ammonia and Hydrogen Chloride - Technician NotesFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- 8B Destructive Distillation of Coal 2.pngDocument1 page8B Destructive Distillation of Coal 2.pngFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- BRAINTEASER QUESTION FOR JSS 1-3 1st TermDocument12 pagesBRAINTEASER QUESTION FOR JSS 1-3 1st TermFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Atomic Electron Configurations Instructor's Guide: Noble GasesDocument1 pageAtomic Electron Configurations Instructor's Guide: Noble GasesFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistry Paper 1 Multiple Choice May/June 2005 45 MinutesDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistry Paper 1 Multiple Choice May/June 2005 45 MinutesFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- REFRESHER EXAM REVIEWDocument4 pagesREFRESHER EXAM REVIEWGiemhel GeleraNo ratings yet
- JBMO ShortLists-2001Document2 pagesJBMO ShortLists-2001OklaNo ratings yet
- Food Groups Intake in Relation To Stunting Among Exceptional ChildrenDocument8 pagesFood Groups Intake in Relation To Stunting Among Exceptional ChildrenAriqah GinaNo ratings yet
- Spin SellingDocument12 pagesSpin SellingKarthik SiddabatthulaNo ratings yet
- Revamping Ammonia ConverterDocument5 pagesRevamping Ammonia ConverterHsein WangNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine Design PrinciplesDocument16 pagesElectrical Machine Design PrinciplesAamir Ahmed Ali SalihNo ratings yet
- MS2680-2017 Energy Efficiency and Use of Renewable Energy For Residential BuildingsDocument61 pagesMS2680-2017 Energy Efficiency and Use of Renewable Energy For Residential BuildingsChern Yue EweNo ratings yet
- C 78 - 94 QZC4LTK0Document3 pagesC 78 - 94 QZC4LTK0Rufo CascoNo ratings yet
- Ms7820 ManualDocument64 pagesMs7820 ManualJesus Velazquez AriasNo ratings yet
- Download Risc V Assembly Language Programming Stephen Smith all chapterDocument67 pagesDownload Risc V Assembly Language Programming Stephen Smith all chapteralec.powell515100% (4)
- Sivision DigitalDocument12 pagesSivision Digitalbogdan_h2000No ratings yet
- Types of Faults 3Document3 pagesTypes of Faults 3blood lustNo ratings yet
- Gen Math11 - Q1 - Mod1 - Functions - v2Document28 pagesGen Math11 - Q1 - Mod1 - Functions - v2Anonymous 6gthRen100% (1)
- Marine Engine-6170 Series: General SpecificationsDocument3 pagesMarine Engine-6170 Series: General SpecificationsTrần Hoài VinhNo ratings yet
- Math8 - q1 - Mod5a - Multiplying and Dividing Rational Algebraic Expressions - 08092020Document34 pagesMath8 - q1 - Mod5a - Multiplying and Dividing Rational Algebraic Expressions - 08092020JaylanGalasi100% (4)
- Manual Del Usuario MCI-WIR-00787 (ENG)Document23 pagesManual Del Usuario MCI-WIR-00787 (ENG)Helio CoragemNo ratings yet
- DPR TemplateDocument74 pagesDPR TemplateAnupamPanja0% (1)
- Definitions: - : I) Soft PalateDocument30 pagesDefinitions: - : I) Soft PalateNikita AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Base Design - SecondaryDocument20 pagesBase Design - SecondaryFarah Diba Pos-PosNo ratings yet
- 522 ZhouDocument6 pages522 ZhouLimbert Edwin BustillosNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Review Physics 11Document2 pagesKinematics Review Physics 11Raymond NguyenNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Characterization of HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesPreparation and Characterization of HydrocarbonspaoloNo ratings yet
- JavaScript Factorial CalculatorDocument13 pagesJavaScript Factorial CalculatorSandipa ShindeNo ratings yet
- Applying Geophysics Methods for Geothermal ExplorationDocument24 pagesApplying Geophysics Methods for Geothermal ExplorationNabilla AzizahNo ratings yet
- Inf311 01 42016022Document12 pagesInf311 01 42016022Hazem QaedNo ratings yet
- JUST GIVE ME A REASONDocument1 pageJUST GIVE ME A REASONS fu fuNo ratings yet
- The Van Der Pauw Method of Measurements in High-TcDocument12 pagesThe Van Der Pauw Method of Measurements in High-TcNolbert Renzo Umpire IncaNo ratings yet