Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Tissue
Uploaded by
Mary Grace Navarro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views36 pagesThis document provides an overview of the basic structures and functions of animal cells, known as organelles. It describes 15 major cell organelles, including their roles in processes like protein synthesis, cellular respiration, waste digestion, and cell division. The cell membrane, microtubules, centrosomes, microfilaments, lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, secretory vesicles, peroxisomes, vacuoles, Golgi apparatus, chromatin, nucleus, ribosomes, intermediate filaments, and mitochondria are all explained in terms of their contributions to cell structure and activity.
Original Description:
Original Title
Ppt Cell Tissue
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of the basic structures and functions of animal cells, known as organelles. It describes 15 major cell organelles, including their roles in processes like protein synthesis, cellular respiration, waste digestion, and cell division. The cell membrane, microtubules, centrosomes, microfilaments, lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, secretory vesicles, peroxisomes, vacuoles, Golgi apparatus, chromatin, nucleus, ribosomes, intermediate filaments, and mitochondria are all explained in terms of their contributions to cell structure and activity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views36 pagesCell Tissue
Uploaded by
Mary Grace NavarroThis document provides an overview of the basic structures and functions of animal cells, known as organelles. It describes 15 major cell organelles, including their roles in processes like protein synthesis, cellular respiration, waste digestion, and cell division. The cell membrane, microtubules, centrosomes, microfilaments, lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, secretory vesicles, peroxisomes, vacuoles, Golgi apparatus, chromatin, nucleus, ribosomes, intermediate filaments, and mitochondria are all explained in terms of their contributions to cell structure and activity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 36
CEBU CITY MEDICAL CENTER
COLLEGE OF NURSING
CELL AND TISSUES
(Anatomy and Physiology)
By: Maria Wellinda A. Cabuenas
Cells The cell (with
trillions in the body)
is the basic unit of
any living organ and
it is the organ that
replicate on its own
determining growth.
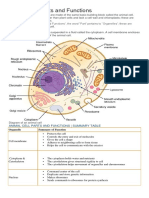
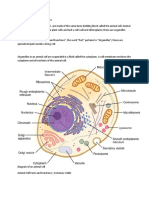
The Cell and Its Function
1. Cell Membrane (outer
semi-solid covering of the
cell)
Facilitate movement of
cell organs to other
places and gives protection
to the cell
Regulates exchange
of substances from
the cell to outside
atmosphere.
2.Microtubules (moving
chromosomes)
Play a vital role in cell
division by pairing
with chromosomes
allowing it to split and
attaching to each new
daughter cell.
3. Centrosome
Is the microtubule
organizing center.
Regulates the cell
cycle via assembly
of microtubules.
4.Microfilaments are thin
protein structure
Hold & give shape of the
cell like the microtubules
and facilitates
movement.
5. Lysosome
Digest excess or worn
out organelles, food
particles, and engulfed
viruses or bacteria.
6.Smooth Endoplasmic
Reticulum
It synthesizes lipids,
phospholipids as in
plasma membranes,
and steroids.
Present in cells of
the testes, ovaries,
and skin oil glands.
7. Secretory Vesicle
(small cell organelles)
• Store and transport
substances to and from
• one cell to another and
from one part of a cell
to another.
8. Peroxisome
Responsible for
oxidation reactions
that break down
fatty acids and
amino acids.
Neutralize free radicals,
which cause cellular
damage and cell death.
9. Vacoule
• Store nutrients (NaCl,
water, CHON and
CHO) for the cell for
survival and store
waste products so the
rest of the cells are
protected from
contamination.
10. Cytoplasm or
Protoplasm(filling
Fluid of the cell)
It is the place where
cell organs like golgi
bodies, endoplasmic
reticulum and
mitochondria is
freely floating for
protection
10. Golgi vesicles and Golgi
Apparatus
Golgi vesicles are pinched
off the membranes and
float through the cell.
Golgi apparatus is a
series of membranes
shaped like pancakes.
Responsible for
modifying, sorting
and packaging of
proteins for secretion.
Also involved in lipid
cell transport and the
creation of lysosomes.
11. Chromatin
Compress the DNA into
a compact unit that will
be less voluminous and
can fir within the
nucleous
12. Nucleus and Nucleolus
Controls/regulates the cell activities Helps in protein synthesis and
& carries the genes, structure that production of the ribosome in the
contain the hereditary information. cells.
13. Rough Endoplasmic
Reticulum
Involved with the
production, folding,
quality control and
dispatch of some
proteins. SER is for
lipid (fat) manufacture
and metabolism.
14. Ribosomes
Are protein builders
or the protein
synthesizers of the
cell.
Builds and connects
one amino acid at
a time and build
long chains.
15. Intermediate Filament
Provide mechanical
support for the
plasma membrane
but do not participate
in cell motility
16. Mitochondria
The powerhouse of
the cell since they are
always bundling or
collecting energy to be
able to supply
continuous energy to
the cell.
The continuous
supply of
mitochondria by
the breaking down
of nutrients and
supplying nutrients
to all parts of the
body is called
cellular respiration.
The end!!!
You might also like
- Unit II. Cells, Tissues, Glands and MembranesDocument23 pagesUnit II. Cells, Tissues, Glands and MembranesLexi LoreNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Genetics 101Document4 pagesGenetics 101Jhon Ric BajeNo ratings yet
- Bio Exam ReviewerDocument10 pagesBio Exam ReviewerMarlon JonasNo ratings yet
- Edible Plant CellDocument4 pagesEdible Plant CellgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYeshua Dan BigasaNo ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- Vacuoles and Vesicles Peroxisomes Centrosomes Cytoskeleton Nucleoid Nucleus Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle Interphase 1Document14 pagesVacuoles and Vesicles Peroxisomes Centrosomes Cytoskeleton Nucleoid Nucleus Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle Interphase 1cfhsmjmdqnNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life 1Document22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life 1Matt Andrei AmorosoNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM (Exercise 1)Document4 pagesBIOCHEM (Exercise 1)KATHLEEN MAE HERMONo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell BIOLOGYDocument43 pagesParts of A Cell BIOLOGYSam Ferbyn LomotanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The CellDocument4 pagesExercise 1 The CellKATHLEEN MAE HERMONo ratings yet
- Marquez 3d CellDocument5 pagesMarquez 3d CellSatori TendōNo ratings yet
- What Is Cytology? What Is Cell?Document3 pagesWhat Is Cytology? What Is Cell?Elcee QuindozaNo ratings yet
- Cells OrganellesDocument3 pagesCells OrganellesLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- Cells OrganellesDocument3 pagesCells OrganellesLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - OrganellesDocument34 pagesLesson 2 - OrganellesArvin Jay Lamberte100% (1)
- Cell and Tissue: Mathew Jeffrey MikeDocument33 pagesCell and Tissue: Mathew Jeffrey MikeKristine JoyNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument23 pagesThe CellAUBREY LISAYENNo ratings yet
- General Biology Modules 1 3Document36 pagesGeneral Biology Modules 1 3Glen MillarNo ratings yet
- Importance of MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesImportance of MicrobiologyynaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Cell PlantDocument7 pagesCell PlantEbiz MarkNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument18 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsAleia Trixie100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Cell OrganellesAly FayeNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCell PhysiologyReslie Joy Serrano100% (1)
- CellDocument11 pagesCellNicole ArangurenNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 2 Cell NotesDocument10 pagesHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 2 Cell NotesS PaulNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: The CellDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: The Celllourd nabNo ratings yet
- JetDocument14 pagesJetAnnie Lyn VillamorNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableDocument16 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableAnnie Lyn Villamor100% (1)
- Cell and TissuesDocument18 pagesCell and Tissuesalvin jr ayugatNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Function and PropertiesDocument10 pagesCell Structure Function and PropertiesWanda JohnNo ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument17 pagesCell AnalogyJianne CabildoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Theory: Heba Abd El Fattah May 2011 Biology SL CellsDocument8 pages2.1 Cell Theory: Heba Abd El Fattah May 2011 Biology SL Cellsansarish94No ratings yet
- Draw A Neat and Clean Diagram of Eukaryotic Cell. Write Down An Exhaustive Note On The Functions of CellDocument3 pagesDraw A Neat and Clean Diagram of Eukaryotic Cell. Write Down An Exhaustive Note On The Functions of CellPratik SagarNo ratings yet
- Acad Fall08 ThecellDocument13 pagesAcad Fall08 Thecellhassanmusahassan81No ratings yet
- What Are CellsHS PDFDocument12 pagesWhat Are CellsHS PDFIbrahim SiddigNo ratings yet
- Bio Assignment 1Document6 pagesBio Assignment 1ditucalan.ha2003No ratings yet
- Animal Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and FunctionsKarren Ferrer-Mora Handayan100% (1)
- Virly CellstructureDocument23 pagesVirly CellstructureVirly vcNo ratings yet
- Membrane-Bound Organelles Which Are Found in Animal Cells. Enzymes Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesMembrane-Bound Organelles Which Are Found in Animal Cells. Enzymes Digestive SystemFarah Jaye Verde CayayanNo ratings yet
- The Big Picture:: Eukaryotes Have A Much More Complex Cell Structure Than ProkaryotesDocument5 pagesThe Big Picture:: Eukaryotes Have A Much More Complex Cell Structure Than ProkaryotesNicolas Gomez CombellasNo ratings yet
- Inte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Document11 pagesInte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- Gen Zoology ReviewerDocument19 pagesGen Zoology ReviewerDarey ApostolNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- The Basis of LifeDocument17 pagesThe Basis of LifeKhalil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3Document55 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 3Yasin Putra EsbeyeNo ratings yet
- Function BIODocument3 pagesFunction BIOChi RosNo ratings yet
- Cell 2 Grading in Science ViiDocument6 pagesCell 2 Grading in Science ViiJerez De PaduaNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- Biology Prelim NotesDocument47 pagesBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell DefinitionDocument10 pagesAnimal Cell DefinitionAngelique VeteNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology BasicsDocument23 pagesCell Biology BasicsAbume DougyNo ratings yet
- Diagram of Plant CellDocument4 pagesDiagram of Plant CellekongNo ratings yet
- Bio1 Lesson 1 NotesDocument7 pagesBio1 Lesson 1 Notesykanemoto81No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDocument7 pagesCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm and OrganellesDocument22 pagesCytoplasm and OrganellesKrishiaDeVeraNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Biology Foundation Bharati BhawanDocument175 pagesClass 9 Biology Foundation Bharati Bhawans88% (8)
- CELL-THE UNIT OF LIFE-Ribosomes, CytoskeletonDocument19 pagesCELL-THE UNIT OF LIFE-Ribosomes, CytoskeletonHridyanshu Singh RoyNo ratings yet
- BIOL 220 SyllabusDocument6 pagesBIOL 220 SyllabusarvinbhamNo ratings yet
- Cell BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesCell BIOLOGYAria Moon100% (1)
- Biochem Hw1 CellDocument5 pagesBiochem Hw1 Celljazzmin ivy evaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument30 pagesCell Biology Cell Structures and Their FunctionsMing Shahir SalehNo ratings yet
- 12 Lecture Presentation ShortDocument84 pages12 Lecture Presentation ShortnohaNo ratings yet
- Cell City ProjectDocument8 pagesCell City ProjectDaisy beNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 8th Edition Patton Test BankDocument25 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 8th Edition Patton Test BankJacquelineFranklinaxej100% (57)
- MitochondriaDocument10 pagesMitochondriaAshima GoelNo ratings yet
- Cell-The Unit of Life - Shobhit NirwanDocument23 pagesCell-The Unit of Life - Shobhit NirwanVraj M Barot70% (10)
- Biology Midterms 2021Document13 pagesBiology Midterms 2021Keano GelmoNo ratings yet
- Neet Pyq Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument4 pagesNeet Pyq Cell - The Unit of LifeAyush DuttaNo ratings yet
- Gnbio1 Module 2Document35 pagesGnbio1 Module 2Ggggnek OhculNo ratings yet
- Cell Division, 5.2Document6 pagesCell Division, 5.2PK100% (1)
- WORKSHEET 5.7 Comparing Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 5.7 Comparing Mitosis and Meiosiswienna1987No ratings yet
- Cell Class 9 Question PDFDocument8 pagesCell Class 9 Question PDFJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Atlas Patrones ANADocument56 pagesAtlas Patrones ANAkemitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document4 pagesLesson 6Thea MillanesNo ratings yet
- FerraterThe Plant and Animal Cell Final DemoDocument7 pagesFerraterThe Plant and Animal Cell Final DemoBriget Diana MulawanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Genetic ControlDocument57 pagesCell Structure and Genetic ControlMOHANNAD ALNEMAHNo ratings yet
- Cell Fractionation & Marker EnzymesDocument20 pagesCell Fractionation & Marker EnzymesVivek PNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle and Parts Review Table - Chapter 6 Organelle/Cell Function Structure Plant/Animal/Proka Ryote?Document3 pagesCell Organelle and Parts Review Table - Chapter 6 Organelle/Cell Function Structure Plant/Animal/Proka Ryote?Lehman042No ratings yet
- Ch. 12-The Endomembrane System and Protein SortingDocument35 pagesCh. 12-The Endomembrane System and Protein Sortingnkorkmaz1357No ratings yet
- Cell QuizDocument9 pagesCell QuizAhdzorizm PlcnNo ratings yet
- ShohayokDocument36 pagesShohayokSafiqa TasfiaNo ratings yet
- 5e5f1afd-ba20-4315-aa34-cba1006821f5Document17 pages5e5f1afd-ba20-4315-aa34-cba1006821f5layanhaliloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and OrganellesDocument42 pagesChapter 2 Structure of Cells and OrganellesAnonymous wj0YtncYYINo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: General Facts of CellsDocument16 pagesCell Biology: General Facts of CellsbibhabNo ratings yet