Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 1
Lecture 1
Uploaded by
biot tukseOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 1
Lecture 1
Uploaded by
biot tukseCopyright:
Available Formats
Technological University (Kyaukse)
Industrial Biotechnology
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Strain Development
Mutation
Lecture 1
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Main purposes
From wild type to mutant
High product yield
Low cost
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Mutation
Spontaneous and Induce Mutation
Point Mutation (Silence, Missense, Nonsense)
Frameshift Mutation
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Errors of enzyme function
DNA polymerase enzymes
Recombination enzymes
DNA repair enzymes
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Spontaneous and Induce Mutation
Spontaneous
A result of natural changes in DNA structure
All types of point mutation can occur spontaneously
Induce
Result from changes caused by environmental chemicals or radiation
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Genome mutation
changes in the number of chromosomes
Chromosome mutation
change the order of the genes within the chromosome. (deficiency, deletion,
inversion, duplication, translocation)
Gene or point mutation
changes in the base sequence in a gene
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Mutagen
Any environmental agent that
significantly increases the rate of
mutation above the spontaneous rate Types of mutations
1. substitutions
2. deletions
3. insertion
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
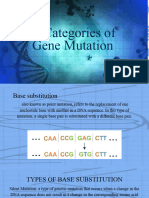
Substitution
Substitution mutations are a type of mutation in which a single nucleotide is
substituted with a different nucleotide.
Substitution mutation is sometimes referred to as point mutation.
However, point mutation is defined particularly as a type of mutation involving a
change of only one nucleotide.
A base pair in the wild type allele may be replaced by by another base in the
mutant allele.
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
There are two situations!
Transition
Occur when a purine is substituted with another purine or a pyrimidine is
substituted with another pyrimidine ( A to G or G to A, T to C or C to T)
Transversion
When a purine is substituted for a pyrimidine or a pyrimidine replaces a purine (T
to C or A to G)
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Substitution mutations may also be typified into:
silent mutations
missense mutations
nonsense mutations
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Silent mutation
If a base substitution occurs in the third position of the codon there is a good
chance that a synonymous codon will be generated.
Thus, amino acid sequence encoded by the gene is not changed and the mutation
is said to be silent
Figure – Source from Internet
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Missense mutation
When base substitution results in the generation of a codon that specifies a
different amino acid and hence leads to a different polypeptide sequence
Figure – Source from Internet
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Nonsense mutation
When a base substitution results in a stop codon ultimately trucating translation and
the most likely leading to a nonfunctional protein
Figure – Source from Internet
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Deletion
One or more base pairs are lost from DNA
One or two bases are deleted the translational frame is altered resulting in grabled
message and non functional product
Deletion of three or more bases leave the reading frame intact
A deletion of one or more codons results in a protein missing one or more amino
acids. This may be deleterious or not
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Insertion
The insertion of additional base pairs may lead to frameshifts depending on
whether or not multiples of three base pairs are inserted.
Combination of insertion and deletions leading to a variety of outcomes are also
possible.
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Point Mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed,
inserted or deleted from a sequence of DNA or RNA.
Point mutation occurs when a base pair of a gene is changed.
Point mutation may also pertain to substitution mutation when one nucleotide is
substituted with a different nucleotide.
Point mutations are the most common types of mutation and there are two types;
1.transition
2.transversion
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Point mutation occurring in noncoding sequences often does not result in an
altered amino acid sequence during translation.
However, if a mutation in the promoter sequence of a gene occurs, the effect may
be apparent since the expression of the gene may cause changes in the amino acid
sequence, as well as the structure and function of the protein product.
Sometimes, point mutation also covers mutations caused by single nucleotide
insertions or deletions (which are types of frameshift mutation).
Point mutations that occur in DNA sequences encoding proteins are either silent,
missense or nonsense
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Figure – Source from Internet
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Frameshift Mutation
A mutation caused by the addition or deletion of a base pair or base pairs in the DNA
of a gene resulting in the translation of the genetic code in an unnatural reading
frame from the position of the mutation to the end of the gene.
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
Figure – Source from Internet
Department of Biotechnology, TU (KSE) BioT – 42024 Industrial Biotechnology
You might also like
- Mouse Molecular Genetics Student Activity 2Document7 pagesMouse Molecular Genetics Student Activity 2Jonathan ZhouNo ratings yet
- Dna MutationsDocument27 pagesDna MutationslowellaNo ratings yet
- A Short Notes On Point Mutation and Its Types and FunctionDocument1 pageA Short Notes On Point Mutation and Its Types and FunctionGalina NenkovaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 437 DNA Repair and Mutagenesis: Textbook Chapter 1-3 September 10, 2009Document25 pagesBIOL 437 DNA Repair and Mutagenesis: Textbook Chapter 1-3 September 10, 2009Chris TuttleNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Mutation Types, Mechanisms and Mutant Detection Methods: A ReviewDocument11 pagesBacterial Mutation Types, Mechanisms and Mutant Detection Methods: A ReviewBobby SeroNo ratings yet
- Mutation and Types of MutationDocument5 pagesMutation and Types of MutationShahriar ShamimNo ratings yet
- Microbial GeneticsDocument42 pagesMicrobial GeneticsShimelis Teshome AyalnehNo ratings yet
- Abdallah Al Obaidi Student Genetic Mutations POGILDocument4 pagesAbdallah Al Obaidi Student Genetic Mutations POGILBen Koffi100% (1)
- Chapter 7: Genetics Lesson 4: MutationsDocument8 pagesChapter 7: Genetics Lesson 4: Mutationssudhu sudsNo ratings yet
- Changes in Molecular Genetics - Effects of Point Mutations - Adit BhadriDocument3 pagesChanges in Molecular Genetics - Effects of Point Mutations - Adit BhadriPoppy SmokeNo ratings yet
- Changes in Molecular Genetics - Effects of Point Mutations - Adit BhadriDocument3 pagesChanges in Molecular Genetics - Effects of Point Mutations - Adit BhadriPoppy SmokeNo ratings yet
- L 16 & L 17 Genetic VariationDocument11 pagesL 16 & L 17 Genetic VariationAhmed AlbagerNo ratings yet
- (H2) CI2.4 - Gene MutationDocument17 pages(H2) CI2.4 - Gene MutationTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Mutations 120415183711 Phpapp02 PDFDocument48 pagesMutations 120415183711 Phpapp02 PDFDonald SmithNo ratings yet
- MG - L4 - Mutation & Dna Repair - Part 1Document25 pagesMG - L4 - Mutation & Dna Repair - Part 1Vy KhánhNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code & Transcriptional ControlDocument13 pagesGenetic Code & Transcriptional Controlapi-19824406No ratings yet
- Means To Optimize Protein Expression in Transgenic Plants: SciencedirectDocument7 pagesMeans To Optimize Protein Expression in Transgenic Plants: Sciencedirectluluatul maghfirohNo ratings yet
- Mutagenesis: Site-Specific: September 2005Document13 pagesMutagenesis: Site-Specific: September 2005Sarnam SinghNo ratings yet
- Evolution and DNA RepairDocument88 pagesEvolution and DNA RepairEdward GanggangNo ratings yet
- Microbial GeneticsDocument47 pagesMicrobial Geneticsjimoji7012No ratings yet
- 2022 Article 1882Document16 pages2022 Article 1882BRUNA COELHO DE ANDRADENo ratings yet
- Genetically Encoded Biosensors Based On Innovative ScaffoldsDocument8 pagesGenetically Encoded Biosensors Based On Innovative Scaffoldspolle.arnaudNo ratings yet
- 4582 Presentation Myocilin PDFDocument33 pages4582 Presentation Myocilin PDFkNo ratings yet
- CMB Lect 8 2011 Colour 2 Slides Per PageDocument14 pagesCMB Lect 8 2011 Colour 2 Slides Per Pageyr0668No ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics Pt. 2Document3 pagesMolecular Genetics Pt. 2rana elshaNo ratings yet
- Sw3 Types of Point MutationsDocument2 pagesSw3 Types of Point MutationsBeaver Sean Felix CaraanNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Genetics: (Chapter 7)Document12 pagesBacterial Genetics: (Chapter 7)aditi_joshee419No ratings yet
- Muta GenesisDocument8 pagesMuta GenesisOphy FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- MutationDocument35 pagesMutationemail4ishanNo ratings yet
- Protein Engineering Reference ArticleDocument27 pagesProtein Engineering Reference ArticleSiddhant BanwatNo ratings yet
- X Rays, Gamma Rays, Cosmic Rays: Types of MutagensDocument9 pagesX Rays, Gamma Rays, Cosmic Rays: Types of MutagensNi Wayan SuliartiniNo ratings yet
- Mutation 1Document13 pagesMutation 1Louise Mae LolorNo ratings yet
- Xóa 2Document15 pagesXóa 2Rin TohsakaNo ratings yet
- How Cellular Information Is AlteredDocument15 pagesHow Cellular Information Is Alteredjohn rhen uyNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Post-Translational Modifications On Protein-Protein and protein-DNA Interactions in Genetically Engineered Systems Studied With Atomic Force Microscopy.Document7 pagesThe Impact of Post-Translational Modifications On Protein-Protein and protein-DNA Interactions in Genetically Engineered Systems Studied With Atomic Force Microscopy.Subarna Hoque RiaNo ratings yet
- University of Alkafeel Faculty of Medical & Health Techniques Dept. of Medical Laboratory TechniquesDocument3 pagesUniversity of Alkafeel Faculty of Medical & Health Techniques Dept. of Medical Laboratory Techniquesحسن الأسديNo ratings yet
- Chen 2020Document8 pagesChen 2020JaancaarloDiiazNo ratings yet
- 2022 Article 112Document26 pages2022 Article 112ruqaia.alshamiNo ratings yet
- MICRO Bacterial GeneticsDocument9 pagesMICRO Bacterial GeneticsJani KhanNo ratings yet
- Agrobacterium and Plant Genes Involved in T-Dna Transfer and IntegrationDocument36 pagesAgrobacterium and Plant Genes Involved in T-Dna Transfer and IntegrationkuangNo ratings yet
- Mutation HandoutsDocument3 pagesMutation HandoutsReymark NovecioNo ratings yet
- 2 Categories of Gene MutationDocument8 pages2 Categories of Gene MutationMohammad MataoNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 5Document29 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 5Amara ValleNo ratings yet
- Genetic Mutation: AsmarinahDocument38 pagesGenetic Mutation: AsmarinahNoor AiniNo ratings yet
- Presentasi MutasiDocument33 pagesPresentasi MutasimilatiNo ratings yet
- IB Biolohy HL Mutations & Gene EditingDocument18 pagesIB Biolohy HL Mutations & Gene Editingwaleed.khashoggiNo ratings yet
- CHP 9 MutationnDocument53 pagesCHP 9 MutationnSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- Chan Et Al 2015 (Biocontainment 01)Document7 pagesChan Et Al 2015 (Biocontainment 01)Felix Moronta BarriosNo ratings yet
- 1501755083geneticengineeringetextpathshaala (Corrected PDFDocument33 pages1501755083geneticengineeringetextpathshaala (Corrected PDFNilpa PatelNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Jbiotec 2005 06 005 PDFDocument189 pages10 1016@j Jbiotec 2005 06 005 PDFNurismy RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- 18 6 Ebook Biosimilars RaderDocument11 pages18 6 Ebook Biosimilars RaderBalaNo ratings yet
- Glossary: Point MutationDocument3 pagesGlossary: Point Mutationzahidtech801No ratings yet
- DNA Delivery Systems 2 ModDocument23 pagesDNA Delivery Systems 2 ModAurelia WetondieNo ratings yet
- Methods For Site-Directed MutagenesisDocument3 pagesMethods For Site-Directed MutagenesisSailaja26No ratings yet
- Gene Expression 2011Document50 pagesGene Expression 2011ALFYANNo ratings yet
- 7 InheritanceDocument22 pages7 InheritanceWalar Arkar WinNo ratings yet
- 16 Genetic Mutations-S PDFDocument7 pages16 Genetic Mutations-S PDFHelp Me Study TutoringNo ratings yet
- Outline: Detection of Nucleic Acids and Proteins Gene Function in EukaryotesDocument43 pagesOutline: Detection of Nucleic Acids and Proteins Gene Function in EukaryotesKrista ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Missense Mutation. Unlike Neutral Mutations, A Missense Mutation Results When An Altered TripletDocument10 pagesMissense Mutation. Unlike Neutral Mutations, A Missense Mutation Results When An Altered TripletraniNo ratings yet
- Production of Recombinant Pharmaceutical ProteinsDocument25 pagesProduction of Recombinant Pharmaceutical ProteinsJuliana DiazNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Analysis and DesignFrom EverandProteins: Analysis and DesignRuth Hogue AngelettiNo ratings yet
- Annual Plant Reviews, Plant MitochondriaFrom EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, Plant MitochondriaDavid C. LoganNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Sec 3 NotesDocument24 pagesCH 13 Sec 3 NotesJanet BarcimoNo ratings yet
- 2001annex - Pages 8-160Document156 pages2001annex - Pages 8-160Laurentiu RadoiNo ratings yet
- Mutations NotesDocument4 pagesMutations NotesYukiichris Lam0% (1)
- Case StudyDocument5 pagesCase StudyArooj HectorNo ratings yet
- Mutation NoteDocument16 pagesMutation NoteAidah AmirNo ratings yet
- NESTAandPlSci Final RS BookletDocument89 pagesNESTAandPlSci Final RS BookletsaipathNo ratings yet
- Gene MutationDocument3 pagesGene MutationNoa SiewNo ratings yet
- Patho 2.1 - Genetic and Pediatric DiseasesDocument76 pagesPatho 2.1 - Genetic and Pediatric DiseasesAshley Contorno100% (1)
- MutationDocument9 pagesMutationsyukriNo ratings yet
- Mutation NomenclaturDocument43 pagesMutation NomenclaturHakimRifqiNo ratings yet
- Video Recap of Mutations v2 by Amoeba Sisters PDFDocument2 pagesVideo Recap of Mutations v2 by Amoeba Sisters PDFsyifaNo ratings yet
- KBG y ANKRD11 y ResonanciaDocument8 pagesKBG y ANKRD11 y ResonanciaAlberto Fernández JaénNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Nucleic Acids Converted PagesDocument8 pagesGroup 2 - Nucleic Acids Converted PagesSophia BiacoNo ratings yet
- DNA Mutations Worksheet 12.3Document2 pagesDNA Mutations Worksheet 12.3HS TUCKER0% (1)
- Original DNA Sequence: TAC ACC TTG GCG ACG ACT: (Circle Any Changes)Document3 pagesOriginal DNA Sequence: TAC ACC TTG GCG ACG ACT: (Circle Any Changes)Joelle AssafNo ratings yet
- VCE BIOLOGY UnitDocument24 pagesVCE BIOLOGY Unitjess_heathNo ratings yet
- Gene Mutation: Presentated By: - Abida Khan - Shumaila Gull - Mehwish RahmanDocument15 pagesGene Mutation: Presentated By: - Abida Khan - Shumaila Gull - Mehwish RahmanMehwish RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mutationmap PahDocument1 pageMutationmap PahAlvi-pba Santiago0% (1)
- Genetic Code Introduction PDFDocument10 pagesGenetic Code Introduction PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Scie10 Q3 Mod5 Mutation v3Document45 pagesScie10 Q3 Mod5 Mutation v3Jeffrey FarillasNo ratings yet
- Mutations: What Is A Mutation?Document4 pagesMutations: What Is A Mutation?Miriam Du BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Types of Mutations:: DELETION (A Base Is Lost) INSERTION (An Extra Base Is Inserted)Document3 pagesTypes of Mutations:: DELETION (A Base Is Lost) INSERTION (An Extra Base Is Inserted)Ri TruongNo ratings yet
- Uoh Mutations Lesson01 Presentation v2 TedlDocument23 pagesUoh Mutations Lesson01 Presentation v2 TedlSamuel Morales NavarroNo ratings yet
- 2016 HGVS Recommendations For The Description of SequenceVariants (2016 Update)Document6 pages2016 HGVS Recommendations For The Description of SequenceVariants (2016 Update)Alfonso PeñarroyaNo ratings yet
- MutationsDocument29 pagesMutationsiariajay100% (1)
- Mutations WorksheetDocument2 pagesMutations WorksheetSarah LowtherNo ratings yet
- Mutations and ExamplesDocument28 pagesMutations and ExamplesSylvestar DarvinNo ratings yet
- DNA MutationsDocument44 pagesDNA MutationsYashika A.No ratings yet