Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Objectives
Uploaded by
Nupelda Tomurcuk0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views7 pages1) The Calvin cycle is the second set of reactions in photosynthesis that produces organic compounds using energy from ATP and NADPH generated in the light reactions.
2) During the Calvin cycle, CO2 is fixed into organic compounds through carbon fixation reactions. RuBP reacts with CO2 to form a six-carbon molecule that is split into two PGA molecules.
3) PGA is converted into PGAL, regenerating RuBP and producing ATP and NADPH. Most PGAL is converted back to RuBP to continue the cycle, fixing more carbon and producing organic compounds and oxygen. Environmental factors can influence the rate of photosynthesis.
Original Description:
Original Title
G 11 , CH 2 , SEC 2 (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The Calvin cycle is the second set of reactions in photosynthesis that produces organic compounds using energy from ATP and NADPH generated in the light reactions.
2) During the Calvin cycle, CO2 is fixed into organic compounds through carbon fixation reactions. RuBP reacts with CO2 to form a six-carbon molecule that is split into two PGA molecules.
3) PGA is converted into PGAL, regenerating RuBP and producing ATP and NADPH. Most PGAL is converted back to RuBP to continue the cycle, fixing more carbon and producing organic compounds and oxygen. Environmental factors can influence the rate of photosynthesis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views7 pagesObjectives
Uploaded by
Nupelda Tomurcuk1) The Calvin cycle is the second set of reactions in photosynthesis that produces organic compounds using energy from ATP and NADPH generated in the light reactions.
2) During the Calvin cycle, CO2 is fixed into organic compounds through carbon fixation reactions. RuBP reacts with CO2 to form a six-carbon molecule that is split into two PGA molecules.
3) PGA is converted into PGAL, regenerating RuBP and producing ATP and NADPH. Most PGAL is converted back to RuBP to continue the cycle, fixing more carbon and producing organic compounds and oxygen. Environmental factors can influence the rate of photosynthesis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
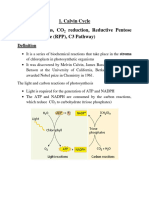
THE CALVIN CYCLE
OBJECTIVES :
1. Summarise the main events of Calvin cycle.
2. Explain what happen to those compounds made in Calvin cycle.
3. Explain how environmental factors influences photosynthesis.
Second set of reactions in photosynthesis involves biochemical reaction
known as the Calvin cycle .
So what is Calvin cycle ?
Is the pathway which produce organic compounds , by using
the energy stored in ATP and NADPH during light dependant
reactions .
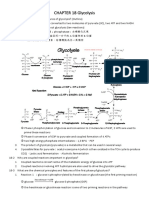
CARBON FIXATION BY CALVIN CYCLE
CO₂ are bounded or fixed into organic compound by process
called carbon fixation .
Carbon fixation: incorporation of CO₂ into organic compound
that occurred in stroma.
Ribulose 1,5-
CO₂ diffuse into stroma from
bisphosphate cytosol , an enzyme combine
(RuBP) CO₂ with five carbon sugar
called RuBP to produce a six
carbon molecule then
immediately split into two
three carbon molecule known
as PGA
phosphoglyceric acid (PGA).
PGA is converted into two
another three carbon
molecule PGAL :
1. Each PGA receive a
Phosphoglyceraldehyde phosphate group from
ATP
2. Then receive a proton
Most PGAL is converted back into RuBP . And this from NADPH and
reaction require phosphate group from another release phosphate to
produce PGAL .
molecule of ATP which is changed into ADP .by
This reaction produce ADP,
regenerating the RuBP that was consumed in step 1 . NADP⁺, phosphate
LIGHT DEPENDANT AND LIFGHT INDEPENDENT REACTION :
The balance sheet for photosynthesis :
• Each turn of Calvin cycle fix one molecule of CO₂.
• PGAL is a three carbon molecule so it needs three
turn of cycle to produce one PGAL.
• For each turn of cycle two ATP with another extra
ATP and two NADPH are needed.
• So at the end 9 ATP are converted to 9 ADP with
6 NADPH are converted to 6 NADP.
Carbohydrate
CO₂ + H₂O + light energy (CH₂O) + O₂
Glucose
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
RATE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
You might also like
- Notes Calvin CycleDocument2 pagesNotes Calvin Cycleneelp331No ratings yet
- Light Dependent Reaction QuestionsDocument14 pagesLight Dependent Reaction QuestionsSevilay CaferogluNo ratings yet
- The Calvin Cycle Dark Reaction G1Document15 pagesThe Calvin Cycle Dark Reaction G1GeminiNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle Reaction of Photosynthesis Reflection PaperDocument1 pageCalvin Cycle Reaction of Photosynthesis Reflection PaperMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- The Krebs CycleDocument4 pagesThe Krebs CycleAliaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Document5 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Maria Bettina DizonNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument4 pagesThe Calvin CycleVerena Raga100% (1)
- The Calvin CycleDocument1 pageThe Calvin CyclepeachyskizNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Document3 pagesPhotosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Althea EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Calvi CycleDocument16 pagesCalvi CycleLenor TunacNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle UpdatedDocument31 pagesCalvin Cycle UpdatedClipNo ratings yet
- Match Structure and FunctionDocument27 pagesMatch Structure and FunctionDiyon JohnNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument4 pagesGeneral BiologyCIANO, Dellaney Joy A.No ratings yet
- A227 RuBP CarboxylaseDocument4 pagesA227 RuBP Carboxylaseramloghun veer100% (1)
- Calvin CycleDocument7 pagesCalvin Cyclehasan jamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Photosynthesis Carbon MetabolismDocument46 pagesChapter 6 - Photosynthesis Carbon Metabolismsayidah nafisahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Bioenergetics (Part 2)Document19 pagesChapter 4 - Bioenergetics (Part 2)Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- 8.3.1 Carbon FixationDocument12 pages8.3.1 Carbon Fixationnersyanhariri71No ratings yet
- BIO121 Chapter 7 Releasing Chemical EnergyDocument45 pagesBIO121 Chapter 7 Releasing Chemical EnergyggttettanNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument15 pagesCalvin CycleBukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- 5.12C The Calvin CycleDocument2 pages5.12C The Calvin Cyclemadeline macalaladNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 c4 and CAMDocument15 pagesBio 11 c4 and CAMBik WodeNo ratings yet
- Significant Events of The Calvin CycleDocument15 pagesSignificant Events of The Calvin CycleClaire MNo ratings yet
- 206 L6 Photosynthesis C3Document48 pages206 L6 Photosynthesis C3craigNo ratings yet
- Edexcel B A Level Biology 2015 Topics 5-10 Revision Notes PDFDocument120 pagesEdexcel B A Level Biology 2015 Topics 5-10 Revision Notes PDFMaha NaserNo ratings yet
- Bio Worksheet (Calvin Cycle)Document2 pagesBio Worksheet (Calvin Cycle)jerell100% (1)
- Bio Worksheet (Calvin Cycle)Document2 pagesBio Worksheet (Calvin Cycle)jerell100% (1)
- The Basics of Photosynthesis in Plants Educational Presentation in Green and Yellow Illustrative StyleDocument53 pagesThe Basics of Photosynthesis in Plants Educational Presentation in Green and Yellow Illustrative Styleefesonbantillo18No ratings yet
- Cellular MetabolismDocument5 pagesCellular MetabolismAshNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Catabolism: Glycolysis Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument1 pageCarbohydrate Catabolism: Glycolysis Pentose Phosphate PathwayKurt BiduaNo ratings yet
- The Light Reaction Events and Calvin Cycle of PhotosynthesisDocument17 pagesThe Light Reaction Events and Calvin Cycle of PhotosynthesisAngel Mae Masa FloresNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument21 pagesCalvin CycleBelac ZepolNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesCalvin Cycleela ravenaNo ratings yet
- Q2Week-2 PhotosynthesisDocument36 pagesQ2Week-2 Photosynthesisjustin charles jerimy raymundoNo ratings yet
- Light Independent Reactions Calvin Cycle Lecture GuideDocument3 pagesLight Independent Reactions Calvin Cycle Lecture GuideRogianna IsidroNo ratings yet
- Light IndependentDocument31 pagesLight IndependentMadame UrsulaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5. (Photosynthesis 3)Document3 pagesLesson 5. (Photosynthesis 3)Cristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1 2Document8 pagesPhotosynthesis 1 2Jhon Excell SanoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Ms. Zaidatul Shakila Mohamad AshariDocument11 pagesPhotosynthesis: Ms. Zaidatul Shakila Mohamad Asharililpidas54No ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument2 pagesCalvin CycleJoyce Anne Mae AdorioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Part 7Document11 pagesChapter 3 - Part 7Adibah Qistina QistinaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle General Biology Short SummaryDocument1 pageCarbon Cycle General Biology Short SummaryANO BYNOUUSNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument14 pagesGen BioGerome LoreteNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 Biosynthetic PhaseDocument14 pagesPresentation1 Biosynthetic PhaseKalyani SreejithNo ratings yet
- Light IndepDocument19 pagesLight IndepiasdfasfsfasfsNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesThe Calvin CycleNeha SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument7 pagesCalvin CyclertfNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration: General BiologyDocument12 pagesAerobic Respiration: General BiologyV KimNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument5 pagesCalvin Cyclemingibabie2025No ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument5 pagesCalvin CycleSaman ArshadNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism 1Document22 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism 1Affie SaikolNo ratings yet
- Photosynthetic Carbohydrate synthesis (Calvin Cycle) : Lectured by Dr. Qin Yongmei (秦咏梅) :Nov. 28, 2007Document55 pagesPhotosynthetic Carbohydrate synthesis (Calvin Cycle) : Lectured by Dr. Qin Yongmei (秦咏梅) :Nov. 28, 2007bbaaddaarrNo ratings yet
- Reactions of The Calvin CycleDocument1 pageReactions of The Calvin CycleFred CanamaNo ratings yet
- Calvin-Cycle ReviewerDocument2 pagesCalvin-Cycle Reviewer2JoshDaveTernedaNo ratings yet
- Lect # 3 GluconeogenesisDocument40 pagesLect # 3 GluconeogenesisUbaid ur Rahman100% (1)
- Calvin CycleDocument3 pagesCalvin Cyclekumarscribd5482No ratings yet
- The Calvin Cycle Uses ATP and NADPH To Convert CO To Sugar:: 3-Phosphate (G3P)Document2 pagesThe Calvin Cycle Uses ATP and NADPH To Convert CO To Sugar:: 3-Phosphate (G3P)Almighty HunyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 18 GlycolysisDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 18 Glycolysis楊畯凱No ratings yet
- Glycolysis 14 40Document4 pagesGlycolysis 14 40ehnzdhmNo ratings yet
- Nanoporous Catalysts for Biomass ConversionFrom EverandNanoporous Catalysts for Biomass ConversionFeng-Shou XiaoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Chapter 2-CellsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Biology Chapter 2-CellsJiya ChhugeraNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYLOVEDocument43 pagesBIOLOGYLOVEOrkid Fazz93% (14)
- Module b4 The Processes of Life Scheme of Work and Lesson PlanDocument30 pagesModule b4 The Processes of Life Scheme of Work and Lesson PlanSaba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Anafi Kayser and Raizen Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2018Document8 pagesAnafi Kayser and Raizen Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2018Francisco MtzNo ratings yet
- 3 Photosynthesis MS PDFDocument18 pages3 Photosynthesis MS PDFeric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- Final Semester Test Ii ACADEMIC YEAR 2007 / 2008: Sma Negeri 1 CilacapDocument8 pagesFinal Semester Test Ii ACADEMIC YEAR 2007 / 2008: Sma Negeri 1 CilacapAstiNitsaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Monera - Group 1 - BSPH1ADocument20 pagesKingdom Monera - Group 1 - BSPH1ACamila Barzaga100% (1)
- Chlorophylls and Other PigmentsDocument6 pagesChlorophylls and Other PigmentsHope Ladyline EspanolaNo ratings yet
- Content Standard Performance Standard Learning Competency I. Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesContent Standard Performance Standard Learning Competency I. Learning ObjectivesNur ShaNo ratings yet
- What Is Natueco Farm ScienceDocument11 pagesWhat Is Natueco Farm ScienceAniruddha Malpani100% (3)
- Land Plants Vs Aquatic PlantsDocument19 pagesLand Plants Vs Aquatic PlantsRaja Rao KamarsuNo ratings yet
- Pdfbio El11 PDFDocument18 pagesPdfbio El11 PDFSwagatika KhatuaNo ratings yet
- Agar Propogation Lit ReviewDocument28 pagesAgar Propogation Lit ReviewRameshiari CheNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis New BioHackDocument9 pagesPhotosynthesis New BioHackMohammed HamedNo ratings yet
- C Plants and Photosynthesis Unit Guide 3unit CPDF C Plants and PhotosynthesisDocument101 pagesC Plants and Photosynthesis Unit Guide 3unit CPDF C Plants and PhotosynthesisKamin Kain SiriwatwetchakulNo ratings yet
- 0610 - w23 - QP - 12 Bio 2023 Multiple ChoiceDocument16 pages0610 - w23 - QP - 12 Bio 2023 Multiple ChoicezoyaNo ratings yet
- 2010 Year ScheduleDocument4 pages2010 Year SchedulededeyopiNo ratings yet
- May 2021 Mark Scheme 1BDocument25 pagesMay 2021 Mark Scheme 1BMeenakshie Chaudrie100% (3)
- Elodea Lab Experiment Report EditedDocument5 pagesElodea Lab Experiment Report Editedapi-253293388No ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan KSSM Science DLP Form 1 2021Document45 pagesYearly Lesson Plan KSSM Science DLP Form 1 2021Nurasyikin SaidinNo ratings yet
- Class X CH-6 WS Answer KeyDocument6 pagesClass X CH-6 WS Answer KeyYASHVI MODINo ratings yet
- Alexa Kirsten Marundan - Photosynthesis Exploration Lab - Understanding The Movement of CarbonDocument3 pagesAlexa Kirsten Marundan - Photosynthesis Exploration Lab - Understanding The Movement of CarbonAlexa Kirsten MarundanNo ratings yet
- Bom 807 4759 Finalstudymaterial2ndterm8science1Document52 pagesBom 807 4759 Finalstudymaterial2ndterm8science1Mohamed AliNo ratings yet
- The Text Is For Questions 1 and 2.: 1. SoalDocument13 pagesThe Text Is For Questions 1 and 2.: 1. SoalTom N JerryNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Soalan Chapter 2, Biology Form 4.Document6 pagesKoleksi Soalan Chapter 2, Biology Form 4.SyahirahMohdAriffNo ratings yet
- MicrometabolismDocument41 pagesMicrometabolismMohammed Mansour AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Ex. 2 PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesEx. 2 PhotosynthesisMEKAH ELINo ratings yet
- Set 1 Cell Biology Grades 1 3Document22 pagesSet 1 Cell Biology Grades 1 3ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- 8 Lesson Plan Oxygen-IntegrationDocument6 pages8 Lesson Plan Oxygen-IntegrationDhen NacaNo ratings yet
- Chlorella Distintos Fotoperiodos e IrradianciaDocument9 pagesChlorella Distintos Fotoperiodos e IrradianciaDelfina AlmeydaNo ratings yet