Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Facotors Affecting Drug Absorption
Uploaded by
Bareera Nudrat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views5 pagesThe key factors that affect the rate of diffusion across a membrane include the steepness of the concentration gradient, temperature, mass and size of diffusing particles, permeability and thickness of the membrane, solubility of substances, surface area available for diffusion, and diffusion distance. Specifically, a steeper gradient, higher temperature, smaller/lighter particles, higher permeability, thinner membrane, higher solubility, larger surface area, and shorter distance result in a faster rate of diffusion.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe key factors that affect the rate of diffusion across a membrane include the steepness of the concentration gradient, temperature, mass and size of diffusing particles, permeability and thickness of the membrane, solubility of substances, surface area available for diffusion, and diffusion distance. Specifically, a steeper gradient, higher temperature, smaller/lighter particles, higher permeability, thinner membrane, higher solubility, larger surface area, and shorter distance result in a faster rate of diffusion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views5 pagesFacotors Affecting Drug Absorption
Uploaded by
Bareera NudratThe key factors that affect the rate of diffusion across a membrane include the steepness of the concentration gradient, temperature, mass and size of diffusing particles, permeability and thickness of the membrane, solubility of substances, surface area available for diffusion, and diffusion distance. Specifically, a steeper gradient, higher temperature, smaller/lighter particles, higher permeability, thinner membrane, higher solubility, larger surface area, and shorter distance result in a faster rate of diffusion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
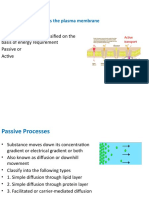
Factors affecting diffusion
• Steepness of the concentration gradient
• Greater the difference in concentration
• Higher the rate of diffusion
• Steepness of the electrochemical gradient
• Determines the diffuse ion rate across the
membrane
• Temperature
• Higher the temperature, the faster the rate of
diffusion
• Mass of the diffusing substance
• Larger the mass of the diffusing particle
• Slower its diffusion rate
• Smaller molecules diffuse more rapidly
• Permeability of the Cell Membrane
• Rate of diffusion is directly proportional to
membrane permeability
• Cell membrane is selectively permeable
• Solubility of the Substance
• Diffusion rate is directly proportional to the
solubility of substances
• Lipid-soluble substances easily
• Thickness of the Cell Membrane
• Rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to the
thickness of the cell membrane
• Increase thickness decrease slow down the
diffusion
• Size of the Molecules
• Rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to the
size of the molecules
• Smaller molecules diffuse rapidly than the
substances with larger molecules
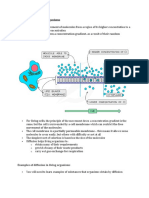
• Surface area
• The larger the surface area available for diffusion
• Faster the diffusion rate
• Air sacs of the lungs have a large surface area
available
• Emphysema
• Diffusion distance
• Greater the distance over which diffusion occur
• The longer it takes
• Diffusion across a plasma membrane takes only a
fraction of a second
• In pneumonia fluid collects in the lungs
You might also like
- Drug Absorption Across Plasma MemDocument8 pagesDrug Absorption Across Plasma MemBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- Facrot Affecting Drug AbsorptionDocument24 pagesFacrot Affecting Drug AbsorptionBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument1 pageDiffusionapi-296833859No ratings yet
- B2.2 Movement in and Out of The CellDocument14 pagesB2.2 Movement in and Out of The Cellmenaga ilangkovanNo ratings yet
- Celldivisiontextdraft 2Document76 pagesCelldivisiontextdraft 2api-278654596No ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level Biology (5090) : Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument55 pagesCambridge O Level Biology (5090) : Movement Into and Out of CellsMoinuddin SummitNo ratings yet
- NgasalDocument2 pagesNgasalNaomi JuntakNo ratings yet
- Who Discovered The Nucleus: 1. Robert Hooke 2. Robert Brown 3. Leuwenhoek 4. Henn DutrochetDocument19 pagesWho Discovered The Nucleus: 1. Robert Hooke 2. Robert Brown 3. Leuwenhoek 4. Henn DutrochetDarius MovsessianNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report FinalDocument11 pagesSeminar Report FinalGurunath MetriNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Rate of DiffusionDocument1 pageFactors Affecting The Rate of DiffusionEthan-Dale BrownNo ratings yet
- Movement of SubstancesDocument25 pagesMovement of Substancesapi-305909325No ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells - Lesson 2Document12 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells - Lesson 2Jayasree BuddhavarapuNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 Diffusion Experiment Result: The Diffusion of Methylene Blue Crystals in Cold Water Is SlowerDocument2 pages1.1.1 Diffusion Experiment Result: The Diffusion of Methylene Blue Crystals in Cold Water Is SlowerDea Angela BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Lab 3Document23 pagesCell Membrane Lab 3Hama JamalNo ratings yet
- Cell Membranes and Transport 2Document49 pagesCell Membranes and Transport 2Rohan PaneruNo ratings yet
- Diffusion WpsDocument1 pageDiffusion WpsDavia ShawNo ratings yet
- 4 Scientific PrinciplesDocument100 pages4 Scientific PrinciplesAhmed Zidan100% (1)
- Mechanism of Stomatal Regulation PPT MMDocument20 pagesMechanism of Stomatal Regulation PPT MMTouseef IjazNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Summary 20Document65 pagesGCSE Biology Summary 20rghph6wwqtNo ratings yet
- The Nature of MatterDocument29 pagesThe Nature of MatterPaul AckermannNo ratings yet
- Transport in Cells: GCSE BiologyDocument41 pagesTransport in Cells: GCSE BiologyMaryam NaeemNo ratings yet
- ICGSE Chemistry Chapter 1 - The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument29 pagesICGSE Chemistry Chapter 1 - The Particulate Nature of MatterVentus TanNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument105 pagesTransport MechanismMAY FULGENCIONo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument105 pagesTransport MechanismMarimay Lumaban100% (1)
- Lesson Note 3 - Investigating Diffusion-Unit 6.3Document6 pagesLesson Note 3 - Investigating Diffusion-Unit 6.3navidu dasisNo ratings yet
- Kaumaram Sushila International Residential School Grade:-9 IGCSE Sub: - Biology CHAPTER: - UNIT 3 NotesDocument10 pagesKaumaram Sushila International Residential School Grade:-9 IGCSE Sub: - Biology CHAPTER: - UNIT 3 NotesAkil BabujiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Transport of SubstancesDocument25 pages1.1 Transport of SubstancesRayonesh RayanaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Final NotesDocument16 pagesDiffusion Final NotesBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2. Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument48 pagesUNIT 2. Transport Across The Cell Membranemunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Diffusion PresentationDocument20 pagesDiffusion PresentationMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Bio NoteDocument6 pagesQ2 Bio NoteJessica HuangNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument17 pagesCell Membranealandanwar266No ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument12 pagesMovement in and Out of CellssaraNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Rate of Diffusion.Document2 pagesFactors Affecting The Rate of Diffusion.Abdul Samad50% (2)
- Transport Across Membranes 2018Document43 pagesTransport Across Membranes 2018SUNDARI SIVASANKARNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of The CellDocument17 pagesMovement Into and Out of The CellsamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Cell Lecture 5-1Document45 pagesCell Lecture 5-1gracechirangoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Movement Into and Out of The CellDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - Movement Into and Out of The CellshammmssNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument23 pagesChemistry ProjectMohil KakdiyaNo ratings yet
- Cell n2Document73 pagesCell n2ketyleenbNo ratings yet
- Membrane TransportDocument24 pagesMembrane Transportolawandeilo123No ratings yet
- CELL TRANSPORTPOWEPOINT (Recovered)Document140 pagesCELL TRANSPORTPOWEPOINT (Recovered)ntakirutimana valensNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument14 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membraneapi-292439032No ratings yet
- Ch-3 Movement Into & Out of CellDocument27 pagesCh-3 Movement Into & Out of CellHaziq KhanNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Cell Pgy-Transport - 035038Document23 pages1.3 Cell Pgy-Transport - 035038FAITH KANGWANo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3diffusion in Living OrganismsDocument10 pagesChapter - 3diffusion in Living OrganismsBoney StephenNo ratings yet
- Sbi4u1-Cell Bio-Cell Transport 4Document15 pagesSbi4u1-Cell Bio-Cell Transport 4alathena alathenaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document13 pagesLecture 3Abdul AhadNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument12 pagesMovement Into and Out of Cellsf8sdh6xvzyNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: Physics Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument20 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy: Physics Notes GCE Study Buddyanwar9602020No ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument17 pagesStates of MatterhelperforeuNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Membrane TransportDocument175 pages1.4 Membrane TransportSenam DzakpasuNo ratings yet
- Demo LessonDocument17 pagesDemo LessonDeborah LaurenNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: Concepts of The Cell TheoryDocument18 pagesCells and Tissues: Concepts of The Cell TheoryAccey RamirezNo ratings yet
- Week # 9 MR Chapter 7: - Tutorial #9Document30 pagesWeek # 9 MR Chapter 7: - Tutorial #9Gábor MátyásiNo ratings yet
- PhyScie A HandOutDocument12 pagesPhyScie A HandOutJin FirLibNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances PDFDocument28 pagesMovement of Substances PDFDELVIN CARRIENo ratings yet
- Section 4Document14 pagesSection 4Jana Moataz Mohamed G02No ratings yet
- B1.6 DiffusionDocument3 pagesB1.6 DiffusionYevonNo ratings yet
- Liquid Glass Transition: A Unified Theory From the Two Band ModelFrom EverandLiquid Glass Transition: A Unified Theory From the Two Band ModelNo ratings yet
- Volume of DistributionDocument9 pagesVolume of DistributionBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- TerminologyDocument14 pagesTerminologyBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- The Adrenergic DrugsDocument13 pagesThe Adrenergic DrugsBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- The Adrenergic DrugsDocument25 pagesThe Adrenergic DrugsBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- ReceptorsDocument31 pagesReceptorsBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- Drug TargetsDocument6 pagesDrug TargetsBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- Plasma Half LifeDocument7 pagesPlasma Half LifeBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- Drug EliminationDocument14 pagesDrug EliminationBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- Drug Distribution & MetabolismDocument23 pagesDrug Distribution & MetabolismBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- ConstipationDocument30 pagesConstipationBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument13 pagesIntroductionBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- Bio A ViabilityDocument8 pagesBio A ViabilityBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- Drug ActionDocument20 pagesDrug ActionBareera NudratNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument46 pagesPoliomyelitisBareera Nudrat100% (1)