Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group Pres-Circulation and Nervous
Group Pres-Circulation and Nervous
Uploaded by
Diana ScoartaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group Pres-Circulation and Nervous
Group Pres-Circulation and Nervous
Uploaded by
Diana ScoartaCopyright:
Available Formats
CIRCULATION
MAIN FEATURES GENERAL FUNCTIONS
The functional parts of the circulation are as follows:
• The arteries which transport blood under high pressure to the tissues
act as control conduits through which blood is released into the capillaries.
• The arterioles
which exchange fluids, nutrients,
waste products of metabolism, and other substances between the blood
• The capillaries and the interstitial fluid.
which collect blood from the capillaries into progressively larger
veins.
• The venules
conduits to transport blood from the tissues back to the heart; veins also
• The veins serve as reservoirs for blood.
• Contraction of the left side of the heart propels blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta, which
empties into smaller arteries, arterioles, and eventually capillaries.
• Blood leaving the tissues enters the venules and then flows into increasingly larger veins, which carry the
blood to the right heart.
• The right side of the heart then pumps the blood through the pulmonary artery, small arteries, arterioles, and
capillaries, where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the blood and the tissues. From the
pulmonary capillaries, blood flows into venules and large veins and empties into the left atrium and left
ventricle before it is again pumped into the systemic
circulation.
Guyton and Hall (2021)
NERVOUS SISTEM
MAIN FEATURES GENERAL FUNCTIONS
Neurons are the The four main functions of the nervous system are:
basic functional unit of the nervous system.
1)Control of body's internal environment to maintain
• nervous system is 'homeostasis’
composed of 80 to 100 billion neurons. An example of this is the regulation of body temperature . 2)Programming
of spinal cord reflexes.
Much of the activity in the nervous system arises from An example of this is the stretch reflex.
stimulation of sensory receptors located at distal 3)Memory and learning.
terminations of sensory neurons.
4)Voluntary control of movement.
Signals travel over peripheral nerves to reach the
spinal cord and are then transmitted throughout the
brain.
Guyton and Hall (2021) Nervous System:Anatomy and Function- PT Direct
You might also like
- Motion To TravelDocument6 pagesMotion To TravelEdward V. ByrneNo ratings yet
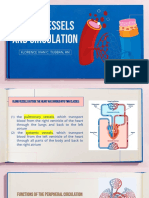
- Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation: Student Learning OutcomesDocument10 pagesCardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation: Student Learning Outcomeslily1liang-1No ratings yet
- Genetic Screening, Prenatal DiagnosisDocument56 pagesGenetic Screening, Prenatal DiagnosisLunaLure100% (1)
- Calgary Cambridge ModelDocument25 pagesCalgary Cambridge ModelHumera Sarwar100% (1)
- Student Name: - Date: - Evaluator Name: - Skill Performance Checklist: HEENT ExaminationDocument2 pagesStudent Name: - Date: - Evaluator Name: - Skill Performance Checklist: HEENT ExaminationAji PicanteNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Digestion: FunctionsDocument2 pagesMechanical Digestion: FunctionsAna MárquezNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument25 pagesANATOMYLeslie Lara DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Genzoo Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesGenzoo Circulatory SystemAbram TicmanNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary SystemDocument47 pagesCardiopulmonary SystemMaxxdlc 16No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument24 pagesCardiovascular Systemjimjose antonyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesCardiovascular SystemMayim LouiseNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Cardiovascular SystemDocument36 pagesTopic 9 Cardiovascular SystemAlejandra CastilloNo ratings yet
- Arterial, Arteriolar, Capillary, Venous & Lymphatic Circulations Feyitimi AaDocument67 pagesArterial, Arteriolar, Capillary, Venous & Lymphatic Circulations Feyitimi Aaintarebatinya32No ratings yet
- 46.1 The Circulatory SystemDocument15 pages46.1 The Circulatory Systemapi-520057338No ratings yet
- CH 11 Vessels PDFDocument10 pagesCH 11 Vessels PDFIbra TutorNo ratings yet
- 6.2 The Blood System IB PDFDocument69 pages6.2 The Blood System IB PDFEva OrtizNo ratings yet
- Transe 3Document8 pagesTranse 3lija.medija.swuNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Intro To Circulation 2014 2Document51 pagesTissues and Intro To Circulation 2014 2Chantae JulienNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Blood Vessels Lab - HandoutDocument7 pagesAnaphy Blood Vessels Lab - HandoutAEGEL DARO TORRALBANo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemBobong blyatNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System 1Document4 pagesCirculatory System 1Jhes D.No ratings yet
- XI-1 Adinda Caesaria Bunga Astiti Hanin Rialsa Meitha Anindya Raisa CeciliaDocument20 pagesXI-1 Adinda Caesaria Bunga Astiti Hanin Rialsa Meitha Anindya Raisa CeciliaadiriadheeNo ratings yet
- Copy For Students Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument45 pagesCopy For Students Respiratory and Circulatory SystemKarla AlegreNo ratings yet
- This Powerpoint Is Hosted On Please Visit For 100's More Free PowerpointsDocument21 pagesThis Powerpoint Is Hosted On Please Visit For 100's More Free PowerpointsMisbakhul MunirNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System PDFDocument5 pagesCirculatory System PDFNibshian Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- 2024-Nursing-Arterial and Venous SystemDocument38 pages2024-Nursing-Arterial and Venous SystemSyed Husnain Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Blood Vessels and CirculationDocument6 pagesChapter 13: Blood Vessels and CirculationPrecious Faith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYDocument12 pagesANAPHYchrstiannNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 LEC Module 3Document8 pagesPMLS 2 LEC Module 3Peach DaquiriNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory Systemparitosh7_886026No ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument48 pagesBlood VesselsGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- 6.2 The Blood SystemDocument43 pages6.2 The Blood SystemPhilip ForintonNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems - Circulatory System-3Document11 pagesHuman Body Systems - Circulatory System-3benjaminblakkNo ratings yet
- Human Body System InfographicDocument12 pagesHuman Body System InfographicDiana VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory / Transport System: For 1O Grade Igcse Semesta Bilingual Boarding SchoolDocument52 pagesCirculatory / Transport System: For 1O Grade Igcse Semesta Bilingual Boarding SchoolThe Deep Sea IdNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System 1Document14 pagesCardiovascular System 1Lucero Itala Samame Laura100% (1)
- Animal Organ SystemDocument139 pagesAnimal Organ SystemMilyn Mae PalganNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument43 pagesBlood VesselsJessica AcostaNo ratings yet
- 10) Circulatory SysDocument60 pages10) Circulatory SysyohdeforemostNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience ReviewerWayne AngeloNo ratings yet
- Endocardial Tubes EpimyocardiumDocument3 pagesEndocardial Tubes EpimyocardiumAngel IsalesNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Entire Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesOverview of The Entire Cardiovascular SystemSpuipt PanagtasanNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System ReviewerDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory System ReviewerKaten KyoukotsuNo ratings yet
- Circulation Practice Exam QuestionDocument9 pagesCirculation Practice Exam QuestionUyenNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument23 pagesCirculatory SystemErika MatiasNo ratings yet
- Topic 10. Cardiovascular SystemDocument17 pagesTopic 10. Cardiovascular SystemJanine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument5 pagesBlood VesselsAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Blood VesslesDocument19 pagesBlood VesslesnidhiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System HandoutsDocument4 pagesCirculatory System HandoutsCzarae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 024-Premedical Circulatory SystemDocument31 pages024-Premedical Circulatory Systemchealzea asuncsionNo ratings yet
- Intro On Circulatory System-UoC - 191123Document29 pagesIntro On Circulatory System-UoC - 191123Hidayah Mohamad raniNo ratings yet
- The Mass Transport in AnimalsDocument45 pagesThe Mass Transport in AnimalsCereal KillerNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: (Parts and Functions) Prepared By: Wilfred D. ManingasDocument30 pagesThe Circulatory System: (Parts and Functions) Prepared By: Wilfred D. ManingasAngelica OlivarNo ratings yet
- Human Cardiovascular System: Introduction ToDocument76 pagesHuman Cardiovascular System: Introduction ToJunje SemeonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Circulatory SystemDocument56 pagesAnatomy of Circulatory SystemLina Wijaya100% (2)
- Circulatory SystemDocument34 pagesCirculatory SystemBruce Been Jr.No ratings yet
- Exchange and Transport Heart and CirculationDocument37 pagesExchange and Transport Heart and Circulationhannahangella5949No ratings yet
- Circulatory System REVIEWERDocument6 pagesCirculatory System REVIEWERClyde BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Circulatory SystemDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Circulatory SystemPrisha ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Cardio SystemDocument3 pagesCardio SystemAlowee AbelloNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument3 pagesBlood VesselsRabia KhalilNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Cell ComponentsDocument2 pagesCell ComponentsDiana ScoartaNo ratings yet
- Vdoc - Pub Spanish Visual Phrase BookDocument194 pagesVdoc - Pub Spanish Visual Phrase BookDiana Scoarta100% (2)
- Joints ClassificationDocument26 pagesJoints ClassificationDiana ScoartaNo ratings yet
- Root Cause AnalysisDocument1 pageRoot Cause AnalysisDiana ScoartaNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmia NeonatorumDocument3 pagesOphthalmia NeonatorumDyraWirasasmitaMirsanNo ratings yet
- Ten Teacher Single Best .AnswerDocument4 pagesTen Teacher Single Best .Answera7332773No ratings yet
- Stroke Dan Sepsis: Pembimbing: Dr. Bambang Supriadi, SP.SDocument24 pagesStroke Dan Sepsis: Pembimbing: Dr. Bambang Supriadi, SP.SIcha NathaliaNo ratings yet
- Causes of Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument8 pagesCauses of Acute GlomerulonephritisShielah YacubNo ratings yet
- TriFold - Preventing ACL Injuries and Enhancing PerformanceDocument2 pagesTriFold - Preventing ACL Injuries and Enhancing PerformanceDarin PaduaNo ratings yet
- MCN 2-Pedia-Clinical Scenario 6-RLE-PlanDocument3 pagesMCN 2-Pedia-Clinical Scenario 6-RLE-PlanMark oliver GonzalesNo ratings yet
- DSM-5 Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument12 pagesDSM-5 Autism Spectrum DisorderJennifer Guard100% (1)
- Post Test - Abnormal PsychDocument6 pagesPost Test - Abnormal Psychpapa.pradoNo ratings yet
- Basic Lower Limb Assessment Flow SheetDocument2 pagesBasic Lower Limb Assessment Flow Sheetمحمد نعمة جياد100% (1)
- MENTOR 13 Lionel Rammamurthy Oet For NursingDocument4 pagesMENTOR 13 Lionel Rammamurthy Oet For NursingAnjana Varghese0% (1)
- Hand Washing Basics To Help Your Family Stay SafeDocument4 pagesHand Washing Basics To Help Your Family Stay Safechandy Rendaje100% (1)
- Risk Factos and Causes of Emotional and BehavioralDocument22 pagesRisk Factos and Causes of Emotional and BehavioralTrisha Mae LlagasNo ratings yet
- Let Them Eat DirtDocument2 pagesLet Them Eat DirtSouthern California Public Radio0% (1)
- Path122 Diabetes MellitusDocument12 pagesPath122 Diabetes MellitusGwendolaine PicaNo ratings yet
- NCP CKDDocument6 pagesNCP CKDBenjie Dimayacyac100% (2)
- Nursing Board ExamDocument13 pagesNursing Board ExamKira100% (49)
- Full Ebook of Cloherty and Stark S Manual of Neonatal Care 9Th Edition Anne R Hansen Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of Cloherty and Stark S Manual of Neonatal Care 9Th Edition Anne R Hansen Online PDF All Chapterbelviapeaah100% (3)
- Referensi SMT 4Document4 pagesReferensi SMT 4Afi YemaraNo ratings yet
- IM Skills ChecklistDocument2 pagesIM Skills ChecklistBerlon LacsonNo ratings yet
- Co Occurring Mental Illness and Substance Use Disorders A Guide To Diagnosis and Treatment 1st Edition Jonathan D Avery John W BarnhillDocument70 pagesCo Occurring Mental Illness and Substance Use Disorders A Guide To Diagnosis and Treatment 1st Edition Jonathan D Avery John W Barnhillmark.proctor794100% (10)
- Cabg Package StudyDocument22 pagesCabg Package Studypavan jainNo ratings yet
- Avoid Spot Treat HeatDocument1 pageAvoid Spot Treat HeatMichael CooperNo ratings yet
- Abdullah AlNuaim-2Document36 pagesAbdullah AlNuaim-2Mohan DesaiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Scenarios Slide Set Powerpoint 2183787181Document58 pagesClinical Case Scenarios Slide Set Powerpoint 2183787181saheefaNo ratings yet
- Associates of Applied Science Degree RequirementsDocument1 pageAssociates of Applied Science Degree Requirementsapi-608273689No ratings yet
- ETHICS 2 FinalsDocument83 pagesETHICS 2 FinalsDenisse RoblesNo ratings yet