100% found this document useful (2 votes)
381 views18 pagesOverview of Electric Vehicles and Their Impact
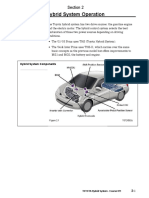
This seminar presented by Kanakam Manikanta Kumar discusses electrical vehicles. It provides a brief history of electric vehicles beginning in the 1830s. The key components of electric vehicles are described as the motor, controller, charger, DC converter, contactors, and batteries. The advantages of electric vehicles include reducing dependence on oil/gasoline, being pollution and noise free, and having lower maintenance/operation costs. However, disadvantages include currently high prices, long recharge times, and limited range.
Uploaded by
Manju RoyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
381 views18 pagesOverview of Electric Vehicles and Their Impact
This seminar presented by Kanakam Manikanta Kumar discusses electrical vehicles. It provides a brief history of electric vehicles beginning in the 1830s. The key components of electric vehicles are described as the motor, controller, charger, DC converter, contactors, and batteries. The advantages of electric vehicles include reducing dependence on oil/gasoline, being pollution and noise free, and having lower maintenance/operation costs. However, disadvantages include currently high prices, long recharge times, and limited range.
Uploaded by
Manju RoyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd