Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maintenance Definition
Uploaded by
Mekonnen Ayal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views23 pagesMaintenance involves technical and administrative actions to keep equipment functioning properly. It includes preventive maintenance to protect equipment and prevent failures, corrective maintenance performed after failures to restore equipment, and improvement maintenance to reduce future maintenance needs. The goals of maintenance are to maximize uptime and productivity at minimum cost.
Original Description:
automotive maintenance ppt
Original Title
1. Maintenance Definition
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMaintenance involves technical and administrative actions to keep equipment functioning properly. It includes preventive maintenance to protect equipment and prevent failures, corrective maintenance performed after failures to restore equipment, and improvement maintenance to reduce future maintenance needs. The goals of maintenance are to maximize uptime and productivity at minimum cost.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views23 pagesMaintenance Definition
Uploaded by
Mekonnen AyalMaintenance involves technical and administrative actions to keep equipment functioning properly. It includes preventive maintenance to protect equipment and prevent failures, corrective maintenance performed after failures to restore equipment, and improvement maintenance to reduce future maintenance needs. The goals of maintenance are to maximize uptime and productivity at minimum cost.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 23
Maintenance Definition
The combination of all technical and
administrative actions, including supervision
actions, intended to retain an item in, or restore
it to, a state in which it can perform a required
function
Maintenance Definition
Maintenance is a set of organised activities
that are carried out in order to keep an item in
its best operational condition with minimum
cost acquired.
Maintenance Activities
Activities of maintenance function could be either
repair or replacement activities, which are necessary
for an item to reach its acceptable productivity
condition and these activities, should be carried out
with a minimum possible cost.
Maintenance Objectives
Maintenance objectives should be consistent with and
subordinate to production goals.
The relation between maintenance objectives and
production goals is reflected in the action of keeping
production machines and facilities in the best possible
condition.
Types of Maintenance
• Run to Failure Maintenance (RTF)
• Preventive Maintenance (PM)
• Corrective Maintenance (CM)
• Improvement Maintenance (IM)
• Predictive Maintenance (PDM)
Run to Failure Maintenance (RTF)
• The required repair, replacement, or restore action
performed on a machine or a facility after the
occurrence of a failure in order to bring this
machine or facility to at least its minimum
acceptable condition.
• It is the oldest type of maintenance.
Run to Failure Maintenance (RTF)
• It is subdivided into two types:
– Emergency maintenance: it is carried out as fast
as possible in order to bring a failed machine or
facility to a safe and operationally efficient
condition.
– Breakdown maintenance: it is performed after
the occurrence of an advanced considered failure
for which advanced provision has been made in
the form of repair method, spares, materials,
labour and equipment.
Preventive Maintenance (PM)
It is a set of activities that are performed on plant
equipment, machinery, and systems before the
occurrence of a failure in order to protect them and
to prevent or eliminate any degradation in their
operating conditions.
Preventive Maintenance (PM)
The maintenance carried out at
predetermined intervals or according to
prescribed criteria and intended to reduce the
probability of failure or the degradation of
the functioning and the effects limited.
Preventive Maintenance (PM)
• The factors that affect the efficiency of this type of
maintenance:
1. The need for an adequate number of staff in the maintenance
department in order to perform this type of maintenance.
2. The right choice of production equipment and machinery
that is suitable for the working environment and that can
tolerate the workload of this environment.
3. The required staff qualifications and skills, which can be
gained through training.
4. The support and commitment from executive management
to the PM programme.
5. The proper planning and scheduling of PM programme.
6. The ability to properly apply the PM programme .
Preventive Maintenance (PM)
• It is good for those machines and facilities which
their failure would cause serious production losses.
• Its aim is to maintain machines and facilities in
such a condition that breakdowns and emergency
repairs are minimised.
• Its activities include replacements, adjustments,
major overhauls, inspections and lubrications.
Preventive Maintenance (PM)
• Researchers subdivided preventive maintenance into
different kinds according to the nature of its activities:
• Routine maintenance which includes those maintenance
activities that are repetitive and periodic in nature such as
lubrication, cleaning, and small adjustment.
• Running maintenance which includes those maintenance
activities that are carried out while the machine or
equipment is running and they represent those activities that
are performed before the actual preventive maintenance
activities take place.
Preventive Maintenance (PM)
• Opportunity maintenance which is a set of maintenance
activities that are performed on a machine or a facility when
an unplanned opportunity exists during the period of
performing planned maintenance activities to other
machines or facilities.
• Window maintenance which is a set of activities that are
carried out when a machine or equipment is not required for
a definite period of time.
• Shutdown preventive maintenance, which is a set of
preventive maintenance activities that are carried out when
the production line is in total stoppage situation.
Corrective Maintenance (CM)
• In this type, actions such as repair, replacement, or
restore will be carried out after the occurrence of a
failure in order to eliminate the source of this failure or
reduce the frequency of its occurrence.
In the British Standard 3811:1993 Glossary of terms,
corrective maintenance is defined as:
The maintenance carried out after recognition and
intended to put an item into a state in which it can
perform a required function.
Corrective Maintenance (CM)
• This type of maintenance is subdivided into three types:
• Remedial maintenance, which is a set of activities that
are performed to eliminate the source of failure without
interrupting the continuity of the production process.
The way to carry out this type of corrective maintenance is
by taking the item to be corrected out of the production line
and replacing it with reconditioned item or transferring its
workload to its redundancy.
Corrective Maintenance (CM)
• Deferred maintenance, which is a set of corrective
maintenance activities that are not immediately
initiated after the occurrence of a failure but are
delayed in such a way that will not affect the
production process.
• Shutdown corrective maintenance, which is a set of
corrective maintenance activities that are performed
when the production line is in total stoppage
situation.
Corrective Maintenance (CM)
• The main objectives of corrective maintenance are the
maximisation of the effectiveness of all critical plant systems,
the elimination of breakdowns, the elimination of unnecessary
repair, and the reduction of the deviations from optimum
operating conditions.
• The difference between corrective maintenance and
preventive maintenance is that for the corrective maintenance,
the failure should occur before any corrective action is taken.
• Corrective maintenance is different from run to failure
maintenance in that its activities are planned and regularly
taken out to keep plant’s, machines and equipment in
optimum operating condition.
Corrective Maintenance (CM)
• The way to perform corrective maintenance activities is by
conducting four important steps:
1. Fault detection.
2. Fault isolation.
3. Fault elimination.
4. Verification of fault elimination.
In the fault elimination step several actions could be taken
such as adjusting, aligning, calibrating, reworking,
removing, replacing or overhaul.
Improvement Maintenance (IM)
• It aims at reducing or eliminating entirely the need for
maintenance.
• This type of maintenance is subdivided into three types as
follows:
1. Design-out maintenance which is a set of activities that are
used to eliminate the cause of maintenance, simplify
maintenance tasks, or raise machine performance from the
maintenance point of view by redesigning those machines and
facilities which are vulnerable to frequent occurrence of
failure and their long term repair or replacement cost is very
expensive.
Improvement Maintenance (IM)
2. Engineering services which includes construction and
construction modification, removal and installation, and
rearrangement of facilities.
3. Shutdown improvement maintenance, which is a set of
improvement maintenance activities that are performed
while the production line is in a complete stoppage situation.
Predictive Maintenance (PDM)
• Predictive maintenance is a set of activities that detect
changes in the physical condition of equipment (signs of
failure) in order to carry out the appropriate maintenance
work for maximising the service life of equipment without
increasing the risk of failure.
• It is classified into two kinds according to the methods of
detecting the signs of failure:
– Condition-based predictive maintenance
– Statistical-based predictive maintenance
Predictive Maintenance (PDM)
• Condition-based predictive maintenance depends on
continuous or periodic condition monitoring equipment to
detect the signs of failure.
• Statistical-based predictive maintenance depends on
statistical data from the careful recording of the stoppages of
the in-plant items and components in order to develop
models for predicting failures.
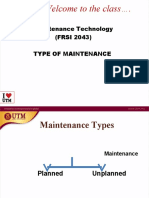
Types of Maintenance
MAINTENANCE
PLANNED UNPLANNED
MAINTENANCE MAINTENANCE
(PROACTIVE) (REACTIVE)
EMERGENCY BREAKDOWN
PREDECTIVE PREVENTIVE IMPROVEMENT CORRECTIVE
MAINTENANCE MAINTENANCE MAINTENANCE MAINTENANCE
STATISTICAL CONDITION - DEFERRED REMEDIAL
ENGINEERING DESIGN - OUT
- BASED BASED
SERVICES
WINDOW RUNNING ROUTINE OPPORTU- SHUTDOWN SHUTDOWN SHUTDOWN
NITY PREVENTIVE IMPROVEMENT CORRECTIVE
Maintenance Types
You might also like
- #5 Maintenance CostDocument49 pages#5 Maintenance CostKhoirul Be100% (1)
- Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedDocument25 pagesMaintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedMinhaj UllahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1pptDocument46 pagesChapter 1pptEjizen LowNo ratings yet
- LEC1 Maintenance DefinitionDocument31 pagesLEC1 Maintenance DefinitionSaba ShaikhNo ratings yet
- CHP 5 FRSI 2043 Type of MaintenanceDocument41 pagesCHP 5 FRSI 2043 Type of MaintenanceFusi MokoenaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesMaintenance DefinitionVaraGoudNo ratings yet
- LEC1-Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesLEC1-Maintenance DefinitionMilin SutharNo ratings yet
- Types of MaintenanceDocument10 pagesTypes of MaintenanceAbishek JainNo ratings yet
- Medical Equipment Maintenance: Dr. Mahmoud Al-RumaimaDocument28 pagesMedical Equipment Maintenance: Dr. Mahmoud Al-Rumaimaمحمد الاشولNo ratings yet
- Maintenance ManagementDocument40 pagesMaintenance ManagementAmila ThibbotuwawaNo ratings yet
- Southern Range Nyanza LTDDocument17 pagesSouthern Range Nyanza LTDspindles2No ratings yet
- Maintenance and Installation of Machinery: (Meng 5231)Document21 pagesMaintenance and Installation of Machinery: (Meng 5231)Milion dugumaNo ratings yet
- Study On Maintenance Process and Maintenance ToolsDocument17 pagesStudy On Maintenance Process and Maintenance ToolsKawsar AlamNo ratings yet
- Aintenance: Ain Concepts and DefinitionsDocument21 pagesAintenance: Ain Concepts and DefinitionsMostafa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Maintenence BasicsDocument51 pagesMaintenence BasicsKarim Magdy100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Maintenance PoliciesDocument50 pagesChapter 3 Maintenance Policiesrobel metikuNo ratings yet
- Unit No, 4Document17 pagesUnit No, 4Rohini mohiteNo ratings yet
- Met82 Maintenanceandsafetyengineering (3 0 0 3) Unit-IDocument51 pagesMet82 Maintenanceandsafetyengineering (3 0 0 3) Unit-IM.ThirunavukkarasuNo ratings yet
- Maintenance ManagementDocument14 pagesMaintenance ManagementAasishPatilNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Medical EquipmentDocument33 pagesMaintenance of Medical EquipmentAbe CyberCrewPlusDotmy100% (1)
- Aircraft Maintenance and TypesDocument12 pagesAircraft Maintenance and TypesRaamaChandiranNo ratings yet
- New Topic 1 Introduction To Maintenance ManagementDocument41 pagesNew Topic 1 Introduction To Maintenance ManagementNurul Nabila Sahri100% (1)
- Chapter Five - TEED 2106 - Maintenance Engineering NotesDocument23 pagesChapter Five - TEED 2106 - Maintenance Engineering Notesodeke aronNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document51 pagesChapter 1arayaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Management: Stalin A Lecturer in Management DistDocument10 pagesMaintenance Management: Stalin A Lecturer in Management DistNithin BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Plant MaintenanceDocument2 pagesAssignment 3 - Plant MaintenanceAkash NavaleNo ratings yet
- MGT MNT PLN PRST2NDDraftDocument139 pagesMGT MNT PLN PRST2NDDraftchibssa alemayehuNo ratings yet
- Training On Maintenance SystemDocument32 pagesTraining On Maintenance SystemmubashirNo ratings yet
- MEE Unit 2Document23 pagesMEE Unit 2dipak1980No ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 5Document19 pagesPertemuan Ke 5BerlianNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Maintenance System LatestDocument77 pagesTopic 1 - Maintenance System LatestAfhnan TemiziNo ratings yet
- What Is Maintenance?: The Objective of Plant MaintenanceDocument4 pagesWhat Is Maintenance?: The Objective of Plant MaintenanceabdullahNo ratings yet
- Plant MaintenanceDocument10 pagesPlant MaintenanceGatut SulianaNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document63 pagesCH 4girma workuNo ratings yet
- General Maintenance - Presentation TranscriptDocument6 pagesGeneral Maintenance - Presentation TranscriptPadmasiri BandaraNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Maintenance: Maintenance For Rotating EquipmentDocument37 pagesMechanical Maintenance: Maintenance For Rotating EquipmentsaniNo ratings yet
- E.maintenance Chapter III Primciple and Horizons of Maintenance ManagmentDocument76 pagesE.maintenance Chapter III Primciple and Horizons of Maintenance ManagmentSamuel GideyNo ratings yet
- MEE 506 Lecture 1Document14 pagesMEE 506 Lecture 1Akunwa GideonNo ratings yet
- MaintenanceDocument18 pagesMaintenancemohammad baniissaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Works For Slabs, Beams and ColumnsDocument23 pagesMaintenance Works For Slabs, Beams and ColumnsHaritz ShukoNo ratings yet
- Maintenance 02 b7Document28 pagesMaintenance 02 b7M Soban Furqan0% (1)
- Unit 8 - Maintenance MGTDocument41 pagesUnit 8 - Maintenance MGTHarsh ChachanNo ratings yet
- Lect-4-Maintenance TypesDocument20 pagesLect-4-Maintenance TypesRNo ratings yet
- MEP 283 Lecture NotesDocument57 pagesMEP 283 Lecture NotesPkay TandohNo ratings yet
- EMS311 Chap1Document26 pagesEMS311 Chap1saidyharuna000No ratings yet
- Maintenance ManagementDocument4 pagesMaintenance ManagementAnand MauryaNo ratings yet
- 4.7 (Maintenance Management) MaintenanceDocument4 pages4.7 (Maintenance Management) MaintenanceAnand MauryaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of MaintenanceDocument35 pagesIntroduction of Maintenanceekhwan82100% (1)
- Lect-5-Maintenance TypesDocument19 pagesLect-5-Maintenance TypesRNo ratings yet
- Maintenance ManagementDocument29 pagesMaintenance ManagementRk SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Maintenance and Replacement Models: Chapter - 1Document38 pagesIntroduction To Maintenance and Replacement Models: Chapter - 1engineer engrNo ratings yet
- MM 25th AugustDocument12 pagesMM 25th AugustAbhishek ChaubeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Run-to-Failure Management, PM EtcDocument16 pagesLecture 8 Run-to-Failure Management, PM EtcMinhaj UllahNo ratings yet
- Define Maintenance MergedDocument73 pagesDefine Maintenance MergedBipul Verma100% (1)
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument50 pagesMaintenance DefinitionVinitSinhaNo ratings yet
- Machine Reliability and Condition Monitoring: A Comprehensive Guide to Predictive Maintenance PlanningFrom EverandMachine Reliability and Condition Monitoring: A Comprehensive Guide to Predictive Maintenance PlanningRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- CH 7 Engine ComponentDocument24 pagesCH 7 Engine ComponentMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- MIXTURE Priparation CIDocument18 pagesMIXTURE Priparation CIMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document104 pagesChapter 1Mekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- DesalebtegDocument16 pagesDesalebtegMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Proposal On Soap Research ProjectDocument26 pagesProposal On Soap Research ProjectMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- New 5 LectureDocument28 pagesNew 5 LectureMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Mixture Preparation SIDocument42 pagesMixture Preparation SIMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- The Current Medical Device Used To Detection of Kidney FailuDocument1 pageThe Current Medical Device Used To Detection of Kidney FailuMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- AaaaaaaaaaDocument33 pagesAaaaaaaaaaMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- The Current Medical Device Used To Detection of Kidney FailureDocument2 pagesThe Current Medical Device Used To Detection of Kidney FailureMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- DJDocument1 pageDJMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Mekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Engine Presentation 3Document134 pagesEngine Presentation 3Mekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- CorruptionDocument2 pagesCorruptionMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- MechanicalDocument94 pagesMechanicalMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- AbcdefgDocument5 pagesAbcdefgMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- CHPPT 3Document28 pagesCHPPT 3Mekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document39 pagesChapter 2Mekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Internship Report: University of Gondar Inistitute of TechnologyDocument41 pagesInternship Report: University of Gondar Inistitute of TechnologyMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document32 pagesChapter 1Mekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Ada 99Document7 pagesAda 99Mekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document36 pagesChapter 1Mekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Chhapter 3Document85 pagesChhapter 3Mekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document44 pagesChapter 2Mekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialDocument63 pagesStrength of MaterialMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 InstrumentationDocument55 pagesChapter 1 InstrumentationMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Impact WDocument16 pagesImpact WMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Applied1 Bagashaw Maltot-1-1Document329 pagesApplied1 Bagashaw Maltot-1-1Mekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials I (Chapter 1)Document37 pagesEngineering Materials I (Chapter 1)Mekonnen Ayal100% (1)
- Moral C-H 1Document30 pagesMoral C-H 1Mekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Iatf-Qm-08 - Operation 8.5.1.1Document22 pagesIatf-Qm-08 - Operation 8.5.1.1SATISH HALGEKARNo ratings yet
- MHD56159 Z Rail Overhead Rail System Alum & SteelDocument56 pagesMHD56159 Z Rail Overhead Rail System Alum & SteelGeneroso GarzaNo ratings yet
- Kami 2Document37 pagesKami 2Muhammad Afzal HashmiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Corrective MaintenanceDocument15 pagesLecture 9 Corrective MaintenanceMinhaj UllahNo ratings yet
- SDU 2200 ManualDocument13 pagesSDU 2200 ManualГабит ЖунисовNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20-14-00, 201 Chapter 20-15-00, 201: Table 201. Tools/Equipment and Recommended MaterialsDocument18 pagesChapter 20-14-00, 201 Chapter 20-15-00, 201: Table 201. Tools/Equipment and Recommended MaterialsDAVID QUINONo ratings yet
- OSD 18-0196-067 - Instruction Manual and Parts List - Ed. 806Document218 pagesOSD 18-0196-067 - Instruction Manual and Parts List - Ed. 806Centrifugal Separator67% (3)
- Regloplas 90S RT33 ManualDocument29 pagesRegloplas 90S RT33 ManualJoão Cavaco100% (1)
- s50mc Vol IIDocument778 pagess50mc Vol IIcengiz kutukcu100% (2)
- Digital Procurement: From Myth, To Unleashing The Full PotentialDocument38 pagesDigital Procurement: From Myth, To Unleashing The Full PotentialAthah100% (1)
- CP-40L - V - + Reference Manual Ver3 - ENG (001-030)Document30 pagesCP-40L - V - + Reference Manual Ver3 - ENG (001-030)Davis GarciaNo ratings yet
- CD 60 - 2020 Specification DocumentDocument14 pagesCD 60 - 2020 Specification Documentsharif sayyid al mahdalyNo ratings yet
- R9800 - ExcavatorDocument22 pagesR9800 - Excavatorhendryn100% (1)
- Oil Test Solutions: Simple To Use & Economical. Fuel and Lube Oil Testing Made EasyDocument6 pagesOil Test Solutions: Simple To Use & Economical. Fuel and Lube Oil Testing Made EasyKyaw Win TunNo ratings yet
- Condor Scissors Lift v1833xl v2033xl 92388 Parts BookDocument20 pagesCondor Scissors Lift v1833xl v2033xl 92388 Parts Bookrenato100% (55)
- What Are Data Center Tiers - FS CommunityDocument5 pagesWhat Are Data Center Tiers - FS CommunityTritech internationalNo ratings yet
- Manual de Operación Mantenimiento y Partes Compresora Doosan 9235 HADocument121 pagesManual de Operación Mantenimiento y Partes Compresora Doosan 9235 HAPercy CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Material Management, PROCUREMENT, STORAGE AND DISTRIBUTIONDocument24 pagesMaterial Management, PROCUREMENT, STORAGE AND DISTRIBUTIONMonisha LingamNo ratings yet
- Operating and Installation Instructions: Straight Through Control Valves - STEVI 440 / 441, 445 / 446Document20 pagesOperating and Installation Instructions: Straight Through Control Valves - STEVI 440 / 441, 445 / 446widuri nirmalaNo ratings yet
- Sad AliDocument5 pagesSad AliMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Phil Roberts HVAC Technician Resume ExampleDocument2 pagesPhil Roberts HVAC Technician Resume ExampleengineezNo ratings yet
- Skyjack Scissor LiftDocument152 pagesSkyjack Scissor LiftJesson Jade Pahit100% (1)
- Building Maintenance Final NotesDocument12 pagesBuilding Maintenance Final NotesMicomyiza Edouard100% (1)
- Electrical ContractorDocument23 pagesElectrical ContractorHenry BarasaNo ratings yet
- Compresor Up6-50pe-125Document208 pagesCompresor Up6-50pe-125AngelNo ratings yet
- Cranes & ComponentsDocument13 pagesCranes & ComponentsdenyNo ratings yet
- 1 - PAVEAIR Workshop 9-13-12 PDFDocument77 pages1 - PAVEAIR Workshop 9-13-12 PDFAnonymous MklNL77No ratings yet
- Civil Engineer - TemplateDocument12 pagesCivil Engineer - TemplateSreedhar BhuduruNo ratings yet
- Akhtar Sir's AssignmentDocument3 pagesAkhtar Sir's Assignmentvicky upretiNo ratings yet
- UM00206G04 - Ventocheck1Document130 pagesUM00206G04 - Ventocheck1Darshana ChathurangaNo ratings yet