Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Articulation of English
Uploaded by
Azat Arna0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views13 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views13 pagesArticulation of English
Uploaded by
Azat ArnaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Понятие об артикуляционной базе английского языка
The concept of English articulation
Ағылшын тілінің артикуляциялық базасы туралы
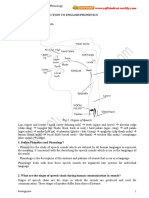
•The main principles of vowel and
consonant formation.
•The articulatory and auditory
difference between vowel and
consonant phonemes.
•There are two major classes of sounds
traditionally distinguished by
phoneticians in any language.
•They are termed consonants and
vowels.
•The distinction between them is based
mainly on auditory effect.
•Consonants are known to have voice
and noise combined, while vowels are
sounds consisting of voice only.
•From the articulatory point of view the
difference is due to the work of speech
organs.
• Vowels are formed by means of periodic vibrations of the
vocal cords-голосовые связки in the larynx-гортань. The
resulting sound waves are transmitted to resonance chamber -
the supralaryngeal cavities (the pharynx-глотка and the
mouth cavity), where vowels receive their characteristic
tamber.
• The quality of vowels depends on the shape and size of the
resonance chamber which is made to vary, depending on the
different positions of the tongue in the mouth cavity, on any
slight alternations in the position of the back walls of the
pharynx, in the position of the soft palate and of the lips,
which form the outlet of the resonance chamber.
•In vowel articulation no obstruction is
made and the muscular tension is spread
all over the speech organs. The force of
exhalation is rather weak for it is
expended when the air stream passes
through the larynx and causes the vocal
cords to vibrate.
• In case of consonants various obstructions are made in
one of the supralaryngeal cavities. So consonants are
characterized by so-called close articulation, that is
by a complete, partial or intermittent blockage of
the airpassage by an organ or organs. The closure is
made in such a way that the airstream is blocked or
hindered or otherwise gives rise to audible friction
which acoustically results in noise. In consonant
articulation the muscular tension is concentrated at the
point of obstruction and a stronger air stream is
required.
• According to the degree of noise consonants are
divided into noise and sonorant.
• Sonorants are sounds intermediate between
consonants and vowels.
• Because they have features common to both,
that is why some sonorants are called
semivowels.
• In the production of sonorants the obstruction
is complete or incomplete but not narrow enough
to produce noise. In other words, the air passage
between the two organs of speech is much wider
than in the production of noise consonants.
• In sonorants articulation muscular tension is
concentrated in the place of obstruction, but the
exhaling force is rather weak.
• Summing up the articulatory difference
between vowels, noise consonants and
sonorants, one can single out three criteria:
the presence or absence of obstruction to the
airstream;
the concentrated or diffused character of
muscular tension;
the force of exhalation.
General principles of the
classification of English vowel
and consonant phonemes.
English vowels are classified according to the following principles:
1. Position of the lips.
2. Position of the tongue.
3. Length.
4. Degree of tenseness.
5. The character of the end.
6. Stability of articulation.
English consonants are classified according to the following principles:
1. Work of the vocal cords and the force of
exhalation.
2. Active organ of speech and the place of
obstruction
3. Manner of the noise production and the type of
obstruction.
4. Position of the soft palate.
You might also like
- The Pronunciation of English: A Reference and Practice BookFrom EverandThe Pronunciation of English: A Reference and Practice BookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Mystery of the Seven Vowels: In Theory and PracticeFrom EverandThe Mystery of the Seven Vowels: In Theory and PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- VowelsDocument43 pagesVowelskeihoina keihoinaNo ratings yet
- PheoneticsDocument27 pagesPheoneticsShivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Week - 2 - Consonants - and - Vowels - PPT Filename - UTF-8''Week 2 - Consonants and VowelsDocument30 pagesWeek - 2 - Consonants - and - Vowels - PPT Filename - UTF-8''Week 2 - Consonants and VowelsDũng Trần ViệtNo ratings yet
- Speech OrganDocument35 pagesSpeech OrganAnonymous AisyzyNo ratings yet
- Sofl Library Answers To PhoneticsDocument32 pagesSofl Library Answers To PhoneticsOanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To English Phonetics A. Theory # Organs of Speech: InwardsDocument32 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To English Phonetics A. Theory # Organs of Speech: InwardsYermek RamazanovNo ratings yet
- Sofl Library Answers To PhoneticsDocument32 pagesSofl Library Answers To PhoneticsYermek RamazanovNo ratings yet
- Fonetyka 15.01Document4 pagesFonetyka 15.01Karolina KNo ratings yet
- How Speech Organs Work in Producing The Speech Sounds?Document33 pagesHow Speech Organs Work in Producing The Speech Sounds?shangar omerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Articulatory PhoneticsDocument29 pagesLecture 3 Articulatory Phoneticsdavegreenwood100% (1)
- Phonetics Textbook Unit 1-6 PDFDocument50 pagesPhonetics Textbook Unit 1-6 PDFVirág KovácsNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - копияDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 2 - копияLucifer LightburnNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology: Ling. 501 April 15, 2009Document81 pagesPhonetics and Phonology: Ling. 501 April 15, 2009Rosalie BaybayonNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Vowels and ConsonantsDocument8 pagesDifferences Between Vowels and Consonantsschiatti3071No ratings yet
- Articulatory Phonetics 1Document5 pagesArticulatory Phonetics 1KhlifibrahimNo ratings yet
- Theme 8: The Phonological System of The English Language (Ii) - The Consonants. Phonetic Symbols. Comparison With The Phonological System of SpanishDocument11 pagesTheme 8: The Phonological System of The English Language (Ii) - The Consonants. Phonetic Symbols. Comparison With The Phonological System of SpanishminimunhozNo ratings yet
- Articulation and AcousticDocument13 pagesArticulation and AcousticNhã Trâm TrầnNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-02-16 at 10.45.23 AMDocument130 pagesScreenshot 2023-02-16 at 10.45.23 AMduaaghanim45No ratings yet
- Elng 101 Module 2Document24 pagesElng 101 Module 2Mutya Kismet LogroñoNo ratings yet
- Phonetics BGGDocument89 pagesPhonetics BGGSan SanNo ratings yet
- What Is Definition of PhonologyDocument12 pagesWhat Is Definition of PhonologyIsriani IshakNo ratings yet
- Phonetics IDocument40 pagesPhonetics Iサイ-ドさんNo ratings yet
- ConsonantsDocument43 pagesConsonantsdarya adiNo ratings yet
- Lectures On English Phonetics and PhonologyDocument92 pagesLectures On English Phonetics and PhonologyCẩm LinhNo ratings yet
- The Subject-Matter of Phonetics, Its Practical AimsDocument48 pagesThe Subject-Matter of Phonetics, Its Practical AimsЕвгения ХвостенкоNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Presentation PDF StudentsDocument9 pagesPhonetics Presentation PDF StudentsNasratullah AmanzaiNo ratings yet
- The Speaking ProcessDocument29 pagesThe Speaking ProcessJoshua AbadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 The Consonant System of EnglishDocument8 pagesLecture 5 The Consonant System of Englishzarifaashurova052No ratings yet
- Tools in Effective Oral CommunicationDocument35 pagesTools in Effective Oral CommunicationlinenpiteousNo ratings yet
- Phonetic ADocument28 pagesPhonetic ANina BandalacNo ratings yet
- ConsonantsDocument65 pagesConsonantskeihoina keihoinaNo ratings yet
- English: PhoneticsDocument19 pagesEnglish: PhoneticsdhruvNo ratings yet
- Resumen Primer Parcial FonéticaDocument28 pagesResumen Primer Parcial FonéticaGuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Linguistics 2Document45 pagesLinguistics 2Bani AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics PPT Week 1Document26 pagesPhonetics PPT Week 1Ahmed Ali JanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 EnglishDocument17 pagesLesson 1 EnglishIsabel Luque RamirezNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology - PPTX - Google Slides PDFDocument13 pagesPhonetics and Phonology - PPTX - Google Slides PDFSalwa abNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument23 pagesPhonetics and Phonologykhalifi pramudianaNo ratings yet
- Speech Assessment and Nasopharyngoscopy HO 11 07 11Document164 pagesSpeech Assessment and Nasopharyngoscopy HO 11 07 11catatutuNo ratings yet
- Phonetics in Complete Denture Prosthesis2Document15 pagesPhonetics in Complete Denture Prosthesis2Nikita AggarwalNo ratings yet
- SOL-week 2Document40 pagesSOL-week 2kn9zrmpn82No ratings yet
- Resumen FinalDocument9 pagesResumen FinalmacarenaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Phonetics and PhonologyDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Phonetics and PhonologyCarlos Antonio Mancebo HerediaNo ratings yet
- THE INTRODUCTION OF Phonetic and PhonologyDocument46 pagesTHE INTRODUCTION OF Phonetic and PhonologyMinh ChauNo ratings yet
- Phonetics & Phonology LecturesDocument10 pagesPhonetics & Phonology LecturesJo O ConnorNo ratings yet
- Linguistics 3Document4 pagesLinguistics 3Rijal QalbiNo ratings yet
- The Articulatory SystemDocument5 pagesThe Articulatory SystemSukma Dwiaugita RahardjoNo ratings yet
- Phonology and PhoneticsDocument23 pagesPhonology and PhoneticsFranz Gerard AlojipanNo ratings yet
- English Phonetics and PhonologyDocument4 pagesEnglish Phonetics and PhonologyCandela Navarro RomeroNo ratings yet
- Speech Consideration IN COMPLETE Dentures: by Ekramul Haque Under The Guidance of DR Shaista AfrozDocument55 pagesSpeech Consideration IN COMPLETE Dentures: by Ekramul Haque Under The Guidance of DR Shaista AfrozPremshith CpNo ratings yet
- Types of PhoneticDocument5 pagesTypes of PhoneticDwiqha Qatrunnada100% (2)
- An Introduction To Phonology by Francis: Katamba Chapters 1 & 2Document46 pagesAn Introduction To Phonology by Francis: Katamba Chapters 1 & 2zaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Intro Phonetics & Phonology I CAECE 2020Document18 pages1 - Intro Phonetics & Phonology I CAECE 2020archer70No ratings yet
- Unit One 2015 Part 1Document17 pagesUnit One 2015 Part 1Luan DreizNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonoDocument24 pagesPhonetics and PhonoMOHAMMAD AGUS SALIM EL BAHRINo ratings yet
- Speech Organs and ArticulationsDocument19 pagesSpeech Organs and ArticulationsNur Wahidah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Classification of Sound UnitsDocument14 pagesLecture 2 - Classification of Sound UnitsDaniel CNo ratings yet
- I Year B. Tech. Lab NotesDocument39 pagesI Year B. Tech. Lab Notesbalajichakilam2012No ratings yet
- Theoretical Grammar 12Document11 pagesTheoretical Grammar 12Azat ArnaNo ratings yet
- Traveling 1Document4 pagesTraveling 1Azat ArnaNo ratings yet
- Презентация1Document6 pagesПрезентация1Azat ArnaNo ratings yet
- Ашык сабакDocument13 pagesАшык сабакAzat ArnaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument197 pagesUntitledAzat ArnaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management PlanDocument3 pagesClassroom Management PlankatieNo ratings yet
- My Learning Essentials: Nstruction WordsDocument3 pagesMy Learning Essentials: Nstruction WordsMakan ApaNo ratings yet
- Basic Greetings and Alphabet Knowledge in SpanishDocument3 pagesBasic Greetings and Alphabet Knowledge in Spanishmaya_shardaNo ratings yet
- Philips - Shortlist - 2025 BatchDocument136 pagesPhilips - Shortlist - 2025 BatchAdi HafeezNo ratings yet
- Experiment-10 (Adder & Subtractor)Document7 pagesExperiment-10 (Adder & Subtractor)M BalajiNo ratings yet
- IBM® DB2 Universal Database™ Replication Guide and ReferenceDocument789 pagesIBM® DB2 Universal Database™ Replication Guide and ReferenceKuzumichNo ratings yet
- Ceh v12 Lesson 3 - Netbios, SNMP & Ldap NetworDocument89 pagesCeh v12 Lesson 3 - Netbios, SNMP & Ldap NetworUddesh WaghNo ratings yet
- Framework OrangeHRMDocument4 pagesFramework OrangeHRMAkash lokhandeNo ratings yet
- Pre CompDocument7 pagesPre Complucky43g2No ratings yet
- Amstext 54.eDocument647 pagesAmstext 54.ePaul PerezNo ratings yet
- Tamil Christian Songs With ChordsDocument178 pagesTamil Christian Songs With ChordsPAUL PRAVEEN A 15PHD005367% (3)
- L. Strauss - On The Intention of RousseauDocument52 pagesL. Strauss - On The Intention of RousseauKristiaan Knoester0% (1)
- 10 Curses That Block The BlessingDocument21 pages10 Curses That Block The BlessingFERNS88% (8)
- Oop 12Document30 pagesOop 12mohammad bilalNo ratings yet
- Moses MendelssohnDocument2 pagesMoses Mendelssohncoolio_94No ratings yet
- Learn Tamil Through TeluguDocument6 pagesLearn Tamil Through TeluguSáshí Kïràñ44% (9)
- Unlock Unit 1Document10 pagesUnlock Unit 1mariodavid33% (3)
- Digital Design Flow Eda ToolDocument94 pagesDigital Design Flow Eda ToolKrish GokulNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Subject Verb AgreementDocument41 pagesWeek 5 Subject Verb AgreementreeseNo ratings yet
- Hiragana Course PDFDocument30 pagesHiragana Course PDFJericho EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Face Technology PDFDocument495 pagesFace Technology PDFRadhaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Application Framework (OAF) Training ManualDocument239 pagesOracle Application Framework (OAF) Training ManualIsa Sarreira Mendes100% (1)
- MKTG 2126 - Assignment 1Document2 pagesMKTG 2126 - Assignment 1omar mcintoshNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document2 pagesHW 2kalaputraNo ratings yet
- Brochure-Curso Español para ExtranjerosDocument4 pagesBrochure-Curso Español para ExtranjerosKanoLeoNo ratings yet
- HW #3 - 2D Motion and Projectiles Mastering Physics AnswersDocument41 pagesHW #3 - 2D Motion and Projectiles Mastering Physics AnswersQusizle72% (18)
- Tle 8 IllustrationDocument12 pagesTle 8 IllustrationAmy Andrea MenorNo ratings yet
- Junit Mock Test IVDocument5 pagesJunit Mock Test IVSubendu RakshitNo ratings yet
- Usage Connective Words Addition of Ideas Condition or ConcessionDocument4 pagesUsage Connective Words Addition of Ideas Condition or ConcessionMidoriya IzukuNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect Vs Past SimpleDocument4 pagesPast Perfect Vs Past SimpleVirginia Ruiz JimenezNo ratings yet