Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I Am Sharing 'Science730' With You
Uploaded by
Killes Smile0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views17 pagesEVOLUTION
Original Title
I am sharing 'science730' with you
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEVOLUTION
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views17 pagesI Am Sharing 'Science730' With You
Uploaded by
Killes SmileEVOLUTION
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
SOURCES OF EVIDENCE FOR REVOLUTION
Organisms inhabiting the earth have changed
overtime, their structures, traits, and abilities
allowed them to adapt and survive in their
environment. Data from fossil records,
anatomy and morphology, embryonic
development and biochemistry could be
analyzed to demonstrate if evolution of life on
earth has taken place.
EVIDENCE FROM
FOSSIL RECORDS
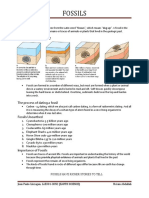
WHAT ARE FOSSILS?
Fossils are preserved remains or traces of
animals, plants, and other organisms from the
past. Fossils are examples of evidences that
paleontologists use in studying evolution.
They are remains such as bones, shells,
teeth, and also feces embedded in rocks,
peat, resin and ice.
TYPES OF FOSSILS
MOLD FOSSILS
Is a fossilized imprint made in the substrate. The
substrate is the rock or sediment on which a fossil
makes its mark. Unlike cast fossils, mold fossil are
hollow. Due to the way this type of fossil is formed,
the resulting image is a negative image of the part
of the organism’s body that made the impression.
Common mold fossils include skin, leaves, teeth,
claws and embryos.
MOLD FOSSILS
CAST FOSSILS
Are like mold fossils in that they formed, at
least in part, with an imprint made in a rock or
sediment. However, cast fossils go one step
further. Once the hollow mold is present, they
are subsequently filled in with minerals that
later harden for form solid rock. In other
words, mold fossils take up negative space
and cast fossils take up positive space.
CAST FOSSILS
TRACE FOSSILS
Also called ichnofossils, do not
contain information about the
organism itself. Rather, they contain
information on traces left by the
organism. Common examples of trace
fossils include burrows, nests,
footprints, dung and tooth marks.
TRACE FOSSILS
TRUE FORM FOSSILS
Are large body parts of an
organism that has been replaced
by minerals. True form fossils are
formed by a process called
petrification.
TRUE FORM FOSSILS
GEOLOGIC TIME SCALE
The geologic time scale is the calendar for
events in Earth history. It subdivides all time
into name units of abstract time called Eons,
Eras, Periods, Epochs, and ages. Era is the
largest division of Geologic Time Scale,
namely Late Proterozoic, Paleozoic,
Mesozoic, and Cenozoic. Each Era is also
divided into Period.
DETERMINING THE AGE OF FOSSILS
Many fossils have no living representatives today.
By comparing the fossils in the different rock
layers, scientists were able to infer the changes
that occurred in the characteristics of various
organisms and to reconstruct the order of changes
that these generations of organisms have
undergone.
The period at which the various fossilized
organisms existed on Earth can be estimated.
DETERMINING THE AGE OF FOSSILS
ABSOLUTE DATING- method used in analyzing
the age of rocks where fossils are found using
radioactive elements or radioisotopes to determine
the rate of decay of certain radioactive isotopes.
RELATIVE DATING – method used to determine
the age of the rocks by comparing them with the
rocks in the other layers. The younger rock is
found on the top layer and the older rock is found
in the bottom layer.
EVIDENCE FROM
FOSSIL RECORDS
You might also like
- 1.1. Fossils: Picture 3.1 Cast and Mold FossilDocument6 pages1.1. Fossils: Picture 3.1 Cast and Mold Fossilsushan19No ratings yet
- SPC英文版教材Document83 pagesSPC英文版教材bing cai100% (2)
- EvolutionDocument88 pagesEvolutionKatelyn ValeraNo ratings yet
- Fossils & EvolutionDocument11 pagesFossils & EvolutionDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Fossil Detectives Field GuideDocument38 pagesFossil Detectives Field Guideaoife12394% (17)
- A History of The Jewish People in The Time of Jesus Christ (1891) Index Schürer, Emil, 1844-1910Document132 pagesA History of The Jewish People in The Time of Jesus Christ (1891) Index Schürer, Emil, 1844-1910David Bailey100% (2)
- L6 Imaging and Design For ONLine EvironmentDocument52 pagesL6 Imaging and Design For ONLine EvironmentKilles SmileNo ratings yet
- Adding True Bypass To A Vintage Big MuffDocument8 pagesAdding True Bypass To A Vintage Big MuffOliver SuttonNo ratings yet
- Trace FossilDocument19 pagesTrace FossilPierre Yusalman LesmanaNo ratings yet
- Amco Veba Marine - Brochure - LRDocument24 pagesAmco Veba Marine - Brochure - LRHươngTpuNo ratings yet
- Simulation of bitumen upgrading processes modelling and optimisationDocument6 pagesSimulation of bitumen upgrading processes modelling and optimisationDonato MontroneNo ratings yet
- Fossil: Navigation Search Fossil (Disambiguation)Document15 pagesFossil: Navigation Search Fossil (Disambiguation)Zed Navarro100% (1)
- 3.trace FossilDocument104 pages3.trace FossilAldo IDNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 6 LAS Q4Document127 pagesMathematics 6 LAS Q4Jake Padua100% (1)
- Earth Science For STEM: Quarter 2 - Module 12Document23 pagesEarth Science For STEM: Quarter 2 - Module 12Cheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- Evidence of Evolution - Module 6Document35 pagesEvidence of Evolution - Module 6Reign PabloNo ratings yet
- Trace Fossil1Document104 pagesTrace Fossil1rajaderyNo ratings yet
- Fosil Dan BatuanDocument12 pagesFosil Dan BatuanReza Pina LestariNo ratings yet
- Evolution Ppt 2024Document47 pagesEvolution Ppt 2024zyrl1235No ratings yet
- Earth's History Through FossilsDocument19 pagesEarth's History Through FossilsAya Shine MagistradoNo ratings yet
- FossilsDocument21 pagesFossilsclaudia gomesNo ratings yet
- Fossils provide clues to life's evolutionDocument2 pagesFossils provide clues to life's evolutionC ButtNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity & Evolution Science 10- Quarter 3Document29 pagesBiodiversity & Evolution Science 10- Quarter 3Debbie Ann LaguindabNo ratings yet
- M5 EvolutionDocument3 pagesM5 EvolutionLiyahlynn MangaoangNo ratings yet
- Research FossilsDocument2 pagesResearch FossilsmanthadumpNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Fascinating World of FossilsDocument3 pagesWelcome To The Fascinating World of FossilsAmr MostafaNo ratings yet
- Lessons in Earth and Life ScienceDocument19 pagesLessons in Earth and Life ScienceMeil EdwardNo ratings yet
- Fossil Notes UPDATEDa-1Document18 pagesFossil Notes UPDATEDa-1Kaylee Geraldine BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- FossilsDocument7 pagesFossilsBrian Christian EganaNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument94 pagesEvolutionFrance Jhemilee MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Evidences of Evolution - FossilDocument17 pagesEvidences of Evolution - Fossilzp1x1eproNo ratings yet
- Index FossilsDocument27 pagesIndex FossilsBernadeth GetuyaNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Do Now 3-4Document2 pagesKami Export - Do Now 3-4Isaac AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Earth History 8Document95 pagesEarth History 8Hoonie LeeNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument41 pagesBiodiversityRia PerezNo ratings yet
- Handout No. 6 in Earth Science: Co Qah + Melc LWDocument5 pagesHandout No. 6 in Earth Science: Co Qah + Melc LWRey DemitNo ratings yet
- Paleontology: Palaeobotany Palynology PalaeozoologyDocument42 pagesPaleontology: Palaeobotany Palynology PalaeozoologyShanza KhanumNo ratings yet
- Fossils: A Guide to Preserved RemainsDocument1 pageFossils: A Guide to Preserved RemainsLittlemommy2009No ratings yet
- Fossils and Geological TimeDocument14 pagesFossils and Geological TimeSto RaNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Trace FossilsDocument4 pagesKinds of Trace FossilsHafa FannanNo ratings yet
- 2Document3 pages2Kyrish DaceraNo ratings yet
- Lab2 - Classification PaleoDocument7 pagesLab2 - Classification PaleoAsselya NygmanovaNo ratings yet
- EVOLUTIONDocument35 pagesEVOLUTIONMariel CondesaNo ratings yet
- How Index Fossils Define and Identify Subdivisions of the Geologic Time ScaleDocument28 pagesHow Index Fossils Define and Identify Subdivisions of the Geologic Time ScaleChin Chin GuerreroNo ratings yet
- EVIDENCES OF EVOLUTION Activity To Be PrintedDocument3 pagesEVIDENCES OF EVOLUTION Activity To Be PrintedMikasa AckermanNo ratings yet
- Earth Geologic HistoryDocument53 pagesEarth Geologic HistoryMarilyn RebatoNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 HandoutDocument5 pagesLab 1 HandoutESTUARYNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1palaeontology Handout..Document8 pagesUNIT 1palaeontology Handout..getnet gizachewNo ratings yet
- Trimmed 23 Es q2 Week 4.2Document10 pagesTrimmed 23 Es q2 Week 4.2Nikha Mae BautistaNo ratings yet
- Fossils and Fossilization: No Photographs. Drawing Is AnDocument9 pagesFossils and Fossilization: No Photographs. Drawing Is AnBarez Ahmad HsenNo ratings yet
- Study of FossilsDocument32 pagesStudy of Fossilstawab haiderNo ratings yet
- p69 77Document9 pagesp69 77justandrianNo ratings yet
- GME I Chap 4 - by DR Solomomn - 3paleontology and StratigraphyDocument40 pagesGME I Chap 4 - by DR Solomomn - 3paleontology and StratigraphyBereket BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Fossil - WikipediaDocument13 pagesFossil - Wikipediaskline3No ratings yet
- Fauzia Surya Kencana - Simulasi Pembentukan Fosilisasi Konvensional PDFDocument10 pagesFauzia Surya Kencana - Simulasi Pembentukan Fosilisasi Konvensional PDFFauzia Surya KencanaNo ratings yet
- FOSSIL TITLEDocument4 pagesFOSSIL TITLERamesh AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Teacher'sDocument4 pagesGroup 4 Teacher'sAdrian GabrielNo ratings yet
- Lab6 Fossilization PDFDocument9 pagesLab6 Fossilization PDFjimmypsNo ratings yet
- FossilsDocument1 pageFossilsJuan Paulo LinzaganNo ratings yet
- Daily Assignment (3/11 Wednesday) : Essential QuestionDocument2 pagesDaily Assignment (3/11 Wednesday) : Essential QuestionGnaWYrreJNo ratings yet
- Bioweb Cs Earlham Edu FossilsDocument2 pagesBioweb Cs Earlham Edu Fossilsapi-248112516No ratings yet
- FossilsDocument33 pagesFossilsXavi MixNo ratings yet
- The First Life Forms on Earth: The Golden Serie of History: From the First Life Forms to the Latest Humanoid Robot, #1From EverandThe First Life Forms on Earth: The Golden Serie of History: From the First Life Forms to the Latest Humanoid Robot, #1No ratings yet
- Biology Fossil Research PaperDocument3 pagesBiology Fossil Research PaperBrian MachariaNo ratings yet
- Evidence of EvolutionDocument34 pagesEvidence of EvolutionCarlos Jordan Datu.No ratings yet
- VS (1)Document1 pageVS (1)Killes SmileNo ratings yet
- L3 The MS WORDDocument34 pagesL3 The MS WORDKilles SmileNo ratings yet
- L5 Advanced Spreadsheet SkillsDocument26 pagesL5 Advanced Spreadsheet SkillsKilles SmileNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY-of-OUTPUT-2023-2024Document1 pageSUMMARY-of-OUTPUT-2023-2024Killes SmileNo ratings yet
- l4 Advanced Presentation SkillsDocument33 pagesl4 Advanced Presentation SkillsKilles SmileNo ratings yet
- MS WORD Handout - 1Document5 pagesMS WORD Handout - 1Killes SmileNo ratings yet
- Alamat NG StandsDocument2 pagesAlamat NG StandsKilles SmileNo ratings yet
- Percentage CompositionDocument1 pagePercentage CompositionKilles SmileNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Online Class To The Mental HealthDocument3 pagesThe Effect of Online Class To The Mental HealthKilles SmileNo ratings yet
- Why Abortion Should Be Legalized - 10 ReasonsDocument1 pageWhy Abortion Should Be Legalized - 10 ReasonsKilles SmileNo ratings yet
- MS Excel Handout 3Document3 pagesMS Excel Handout 3Killes SmileNo ratings yet
- The Lottery ReactionDocument1 pageThe Lottery ReactionKilles SmileNo ratings yet
- LanguageDocument8 pagesLanguageKilles SmileNo ratings yet
- Module1 Ict Grade 10Document16 pagesModule1 Ict Grade 10Killes SmileNo ratings yet
- Robotics M3Document2 pagesRobotics M3Killes SmileNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument69 pagesThe Nervous SystemKilles SmileNo ratings yet
- 30-300 MHZ Transmission Line Trainer Tla05Document1 page30-300 MHZ Transmission Line Trainer Tla05Kishor HandoreNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology 4325 2H Mark SchemeDocument14 pagesIGCSE Biology 4325 2H Mark SchememuhajireenNo ratings yet
- Popular CultureDocument25 pagesPopular CultureVibhuti KachhapNo ratings yet
- Differences in Left Ventricular and Left Atrial FuDocument10 pagesDifferences in Left Ventricular and Left Atrial FueugeniaNo ratings yet
- Manual Hoist ProductsDocument40 pagesManual Hoist Productskavin bhagavathyNo ratings yet
- z1875 Caton (BMJ) Electric Currents of The BrainDocument23 pagesz1875 Caton (BMJ) Electric Currents of The BrainUnholy VladNo ratings yet
- Wda 201Document72 pagesWda 201MoussaNo ratings yet
- FT Aeroterme GEADocument15 pagesFT Aeroterme GEACrisTimNo ratings yet
- RCS England Trainees Guide To A Quality Improvement Project 2021Document17 pagesRCS England Trainees Guide To A Quality Improvement Project 2021Wee K WeiNo ratings yet
- Chap 5. Beam Analysis and Design PDFDocument61 pagesChap 5. Beam Analysis and Design PDFRafael Joshua LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Acute Severe Asthma Hospital ManagementDocument1 pageAcute Severe Asthma Hospital ManagementItharshan IndreswaranNo ratings yet
- AABB Accredited DNA Testing FacilitiesDocument2 pagesAABB Accredited DNA Testing Facilitiesjosueduran75No ratings yet
- PT2E-1723 Gas Detector Operating ManualDocument54 pagesPT2E-1723 Gas Detector Operating ManualAsad Raza QureshiNo ratings yet
- Jigoku Shoujo Eikyuu No SonzaiDocument166 pagesJigoku Shoujo Eikyuu No Sonzaiapi-224188021No ratings yet
- Am 363 PDFDocument4 pagesAm 363 PDFsunsirNo ratings yet
- HEAT EFFECTS (Cha 4) : Outline of Chapter OneDocument65 pagesHEAT EFFECTS (Cha 4) : Outline of Chapter OneAdam MekonnenNo ratings yet
- SR. NO. Capacity/Descirption of Machine Client: A.C. Generator StatorsDocument5 pagesSR. NO. Capacity/Descirption of Machine Client: A.C. Generator Statorsmtj4uNo ratings yet
- Deskripsi (Caffein)Document4 pagesDeskripsi (Caffein)jibefahlaNo ratings yet
- Mass DisasterDocument70 pagesMass DisasterJoseph RadovanNo ratings yet
- Genética, Modificaciones y MutacionesDocument12 pagesGenética, Modificaciones y MutacionespokemaniacoplancheNo ratings yet
- Kyocera Servise ManualDocument613 pagesKyocera Servise ManualleukadiosNo ratings yet
- Preferred Drug ListDocument2 pagesPreferred Drug ListRamNo ratings yet
- Preformed Expansion Joint Filler For Concrete (Bituminous Type)Document2 pagesPreformed Expansion Joint Filler For Concrete (Bituminous Type)Katerin HernandezNo ratings yet
- Image Forgery DetectionDocument17 pagesImage Forgery DetectionanlemacoNo ratings yet