Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Labno6: Charging and Discharging of Capacitors
Uploaded by
Mugheera Malik0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views13 pagesThis lab document outlines an experiment on charging and discharging capacitors. Students will understand how capacitors work in series circuits and plot voltage over time graphs for charging and discharging. The equipment needed includes a DC power supply, resistor, capacitor, breadboard, wires, multimeter and stopwatch. The document explains capacitors store charge, their operation involves plates separated by a dielectric, and the time constant formula to calculate how long it takes a capacitor to charge. The procedure instructs students to construct a circuit and record voltage measurements over time to calculate the time constant and observe charging behavior.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis lab document outlines an experiment on charging and discharging capacitors. Students will understand how capacitors work in series circuits and plot voltage over time graphs for charging and discharging. The equipment needed includes a DC power supply, resistor, capacitor, breadboard, wires, multimeter and stopwatch. The document explains capacitors store charge, their operation involves plates separated by a dielectric, and the time constant formula to calculate how long it takes a capacitor to charge. The procedure instructs students to construct a circuit and record voltage measurements over time to calculate the time constant and observe charging behavior.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views13 pagesLabno6: Charging and Discharging of Capacitors
Uploaded by
Mugheera MalikThis lab document outlines an experiment on charging and discharging capacitors. Students will understand how capacitors work in series circuits and plot voltage over time graphs for charging and discharging. The equipment needed includes a DC power supply, resistor, capacitor, breadboard, wires, multimeter and stopwatch. The document explains capacitors store charge, their operation involves plates separated by a dielectric, and the time constant formula to calculate how long it takes a capacitor to charge. The procedure instructs students to construct a circuit and record voltage measurements over time to calculate the time constant and observe charging behavior.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
LAB NO 6
Charging and Discharging of Capacitors.
Lab outcomes
After completing this lab students will be able to:
• Understand the working of capacitors in series circuit.
• Plot the voltage time graph of charging and discharging of capacitors.
Equipments:
• DC Power supply.
• Resistor.
• Capacitor.
• Breadboard.
• Jumper wires.
• Digital multi meter.
• Stop Watch.
• Graph paper.
Theory
• Passive device with two terminals,
capable of storing electrical energy
in an electric field, much like a small
rechargeable battery.
• But unlike Batteries, Capacitor
charges and discharges very quickly.
• Capacitors are used in almost every
electronic device like PC, cellphones
and even in electrical appliances like
fan.
• Capacitors works as a voltage
regulator in small electronic circuit
as it opposes any change in voltage.
Working of Capacitor:
• Capacitors are basically, two parallel plates
separated by any dielectric medium (i.e. Mica,
Glass, air etc…)
• Dielectric is an insulating material or a poor
conductor of electric current. No current flows
through a dielectric when it is placed in an
electric field.
• When we connect a battery across a capacitor, an
electric field develops across the dielectric,
causing a net positive charge to collect on one
conductor and an equal net negative charge to
collect on the other conductor. As a result, no
current flows through the dielectric, and the total
charge of the capacitor is zero.
• The electric field generated in the region.
• Capacitance is the capacity of capacitor to store
charge.
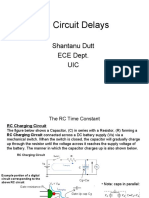
Time constant : the time required by capacitor to reach 63% of voltage
applied is called time constant or tor (T).
Where , T=Resistance x Capacitance.
T=R x C.
The value of T depends upon the value of capacitance. As capacitors
with higher capacitance will charge and discharge slowly as compare to
capacitors with low capacitance.
• Fully Charged?
After 5 Time constants capacitor will be
fully charge as voltage across capacitor
becomes same as voltage across battery.
Note: initially when voltage is applied the
capacitor will charge quickly till it reaches
62.3 % of voltage applied. After this point
charging will be much slower.
• Discharging
When the capacitor is discharging the
same CR formula applies, as the capacitor
also discharges in an exponential fashion,
quickly at first and then more slowly.
During discharge the voltage will FALL by
63.2% to 36.8% of its maximum value in
one time constant period T.
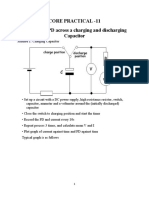
Circuit Diagram
Procedure
• CAPACITOR CHARGING:
Write down the procedure of constructing the circuit along with the use
of DMM and stop watch.
• Calculating Time Constant:
We know that, Time constant (T)= Resistance x Capacitance.
T= RC
Put the values in above equation to find Time constant.
•Time constant (T) = ?
Results •Capacitor is fully charged at = 5 T
Sr. Voltage Time
No
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Procedure
• Capacitor Charging:
Write down the procedure of constructing the circuit along with the
use of DMM and stop watch.
• Calculating Time Constant:
We know that, Time constant (T)= Resistance x Capacitance.
T= RC
Put the values in above equation to find Time constant.
•Time constant (T) = ?
Results •Capacitor is fully charged at = 5 T
Sr. Voltage Time
No
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Conclusion
You might also like
- Lab 7 RC Time ConstantDocument8 pagesLab 7 RC Time ConstantMalith Madushan100% (1)
- 24 CapacitorsDocument5 pages24 CapacitorsJoey the LifterNo ratings yet
- Ee102 Lab 5Document12 pagesEe102 Lab 5Khuresh ShahNo ratings yet
- The Study of DC Transients in RC CircuitDocument2 pagesThe Study of DC Transients in RC CircuitNur Muhammad Alif RamliNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Cbse Investigatory Project On RC CircuitDocument4 pagesClass 12 Cbse Investigatory Project On RC CircuitRishav Sureka0% (1)
- AbstractDocument5 pagesAbstractsnehasishNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment No.09: To Trace The Response of Capacitor During Charging and Discharging CapacitorDocument4 pagesLab Experiment No.09: To Trace The Response of Capacitor During Charging and Discharging Capacitorsara hafeezNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument21 pagesCapacitorsNathan BerhanuNo ratings yet
- AP LAB Report 6 by Group 1 ChE-15ADocument6 pagesAP LAB Report 6 by Group 1 ChE-15AHamzah KamranNo ratings yet
- DE UNIT 3 Timing Circuit and OscillatorsDocument29 pagesDE UNIT 3 Timing Circuit and Oscillatorsjosephryanbeloria45No ratings yet
- Physics PraticalDocument4 pagesPhysics PraticalRohit MishraNo ratings yet
- Objective: RequirementsDocument5 pagesObjective: RequirementssnehasishNo ratings yet
- Capacitance Meter: Theory & DesignDocument3 pagesCapacitance Meter: Theory & DesigndNo ratings yet
- 6a - Capa RemixDocument48 pages6a - Capa Remixsarcasticb15No ratings yet
- Alternating Current CircuitsDocument8 pagesAlternating Current CircuitsShafiq HafizullahNo ratings yet
- Lab #6 Capacitance & RC Circuits: Portions of This Activity Adapted From VernierDocument5 pagesLab #6 Capacitance & RC Circuits: Portions of This Activity Adapted From Vernieralpha omegaNo ratings yet
- CORE PRACTICAL - 11 Investigating Charging and Discharging CapacitorsDocument4 pagesCORE PRACTICAL - 11 Investigating Charging and Discharging CapacitorsDanialNo ratings yet
- Kirchoffs Law & RC CircuitsDocument7 pagesKirchoffs Law & RC Circuitsrajput1287No ratings yet
- Quiz 1 IsDocument19 pagesQuiz 1 IsNathan KingNo ratings yet
- RC Circuits: PHYS 2211L Lab 5Document10 pagesRC Circuits: PHYS 2211L Lab 5Angelica CanoNo ratings yet
- 9 Capacitor Charging and DischargingDocument2 pages9 Capacitor Charging and DischargingMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 2: ObjectiveDocument12 pagesExperiment # 2: ObjectiveAizaz Khan ZäziíììNo ratings yet
- PHYS 2426 Lab 7 - The RC Circuit - ManualDocument6 pagesPHYS 2426 Lab 7 - The RC Circuit - Manualwhatis you nameNo ratings yet
- Kendriya VidyalayaDocument21 pagesKendriya Vidyalayahamdanharish7No ratings yet
- RC Charging CircuitDocument43 pagesRC Charging Circuitleonard1971No ratings yet
- Lab 01-Transient Response of A Series RC CircuitDocument4 pagesLab 01-Transient Response of A Series RC CircuitAly HuzmurNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 - ReportDocument7 pagesLab 9 - Reportasyya_410100% (1)
- Artigo Lab 1 - Prática João Paulo e Cassiano - Capacitores em Regime DCDocument6 pagesArtigo Lab 1 - Prática João Paulo e Cassiano - Capacitores em Regime DCJoão Paulo Araujo SantosNo ratings yet
- LabReport 3 FinaleDocument16 pagesLabReport 3 FinaleChiara CalvoNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics notes-CAPACITORSDocument17 pagesBasic Electronics notes-CAPACITORSEphraem RobinNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument4 pagesCapacitorsShern Ren TeeNo ratings yet
- Time Constant (RC Constant)Document17 pagesTime Constant (RC Constant)dawoodNo ratings yet
- School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering Nust Applied Physics Lab Report # 5 Ac DC ElectronicsDocument6 pagesSchool of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering Nust Applied Physics Lab Report # 5 Ac DC ElectronicsSalmanNo ratings yet
- Charging Phase and Discharging Phase - Electric CircuitsDocument11 pagesCharging Phase and Discharging Phase - Electric CircuitsRayhan KabirNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument5 pagesCapacitorsluis casasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15Document42 pagesLecture 15amitNo ratings yet
- 5 Time ConstantDocument17 pages5 Time ConstantRayyanNo ratings yet
- RC CircuitDocument5 pagesRC CircuitSatish BunnyyNo ratings yet
- The RC Circuit: Pre-Lab QuestionsDocument8 pagesThe RC Circuit: Pre-Lab QuestionsMd. Sazidul Haque SazzadNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document21 pagesLab 5Sindbad HooNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument7 pagesCapacitorsමේනුක සූවින්දNo ratings yet
- Operation of Single Stage Impulse Voltage GeneratorDocument6 pagesOperation of Single Stage Impulse Voltage Generatoralfredlim2250% (2)
- RC CircuitsDocument3 pagesRC CircuitsGerald Tristan ReedNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 Exponential FuntionDocument9 pagesLab 01 Exponential FuntionfarhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Electric CircuitDocument23 pagesLab Manual Electric CircuitEngr. AbdullahNo ratings yet
- PE - Mini Project ReportDocument6 pagesPE - Mini Project Reportchemistryraja123No ratings yet
- Lab5 2Document21 pagesLab5 2Sindbad HooNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Time Constant of RC CircuitsDocument4 pagesLab 5 - Time Constant of RC CircuitshamzaNo ratings yet
- PAG 09.2 - Investigating Capacitors in Series and ParallelDocument3 pagesPAG 09.2 - Investigating Capacitors in Series and ParalleljmsonlNo ratings yet
- RC Charging CircuitDocument6 pagesRC Charging CircuitNguyen Tran Quoc TuanNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit Delays: Shantanu Dutt ECE Dept. UICDocument6 pagesRC Circuit Delays: Shantanu Dutt ECE Dept. UICPARTH RAMANUJNo ratings yet
- Experiment 21 RC Time Constants: Advanced ReadingDocument2 pagesExperiment 21 RC Time Constants: Advanced ReadingAlicia AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit and Its ApplicationTerm PaperDocument13 pagesRC Circuit and Its ApplicationTerm PapersummitzNo ratings yet
- RC Delay of Integrated CircuitDocument6 pagesRC Delay of Integrated CircuitSazzad HossainNo ratings yet
- Circuitos RCDocument5 pagesCircuitos RCRonald GuichayNo ratings yet
- RC Circuits 0Document8 pagesRC Circuits 0Reddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- LAB NO 02 (Ohm Law)Document11 pagesLAB NO 02 (Ohm Law)Mugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 8Document13 pagesLab 8Mugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document10 pagesLab 7Mugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 9Document4 pagesLab 9Mugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab#9Document9 pagesLab#9Mugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Resistance Measurement by Color Code and Its Comparison With The Ohm-Meter ReadingDocument9 pagesResistance Measurement by Color Code and Its Comparison With The Ohm-Meter ReadingMugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab No. 02: Study of Ohm'S LawDocument13 pagesLab No. 02: Study of Ohm'S LawMugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document10 pagesLab 6Mugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Resistor Color Codes, Ohm Law: Principle of Electrical EngineeringDocument36 pagesResistor Color Codes, Ohm Law: Principle of Electrical EngineeringMugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab No. 03: Kirchhoff's Voltage LawDocument12 pagesLab No. 03: Kirchhoff's Voltage LawMugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab No. 05: Current Divider RuleDocument12 pagesLab No. 05: Current Divider RuleMugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Lab No. 04: Kirchhoff's Current LawDocument12 pagesLab No. 04: Kirchhoff's Current LawMugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- Konark ReportDocument4 pagesKonark ReportPriyank PatelNo ratings yet
- HART Modem IC HT2012-PL DatasheetDocument13 pagesHART Modem IC HT2012-PL DatasheetTodorosss JjNo ratings yet
- Weekly Programmable Electronic Timer DHC15Document2 pagesWeekly Programmable Electronic Timer DHC15Marc CMNo ratings yet
- Flatpack2 48/2000: Rectifier ModuleDocument2 pagesFlatpack2 48/2000: Rectifier ModulecristiNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of FPGA-Based Systems - ADocument23 pagesDesign and Implementation of FPGA-Based Systems - Asavithri123anuragNo ratings yet
- Ccna 3Document64 pagesCcna 3lynjazmin abalusNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Study Presentation8Document13 pagesEnhanced Study Presentation8Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Transistor D1406-SavantICDocument4 pagesTransistor D1406-SavantICEdgar MartinezNo ratings yet
- NPCL Electronics & Instrumentation PapersDocument9 pagesNPCL Electronics & Instrumentation PapersJoyita BiswasNo ratings yet
- DSD Syll - Merged DSD GtuDocument8 pagesDSD Syll - Merged DSD GtuSandeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: ACPL-C78A, ACPL-C780, ACPL-C784Document17 pagesData Sheet: ACPL-C78A, ACPL-C780, ACPL-C784Ivana PrezimeNo ratings yet
- Ibanez PT909 SchematicDocument1 pageIbanez PT909 Schematicfrederikd_01No ratings yet
- Audio Tda8567q Spec enDocument20 pagesAudio Tda8567q Spec envetchboyNo ratings yet
- Installation & Commissioning: Layan MadukaDocument23 pagesInstallation & Commissioning: Layan MadukanahussainNo ratings yet
- Ec8452 Ec-Ii Unit-1Document122 pagesEc8452 Ec-Ii Unit-1Ananda Sailesh KNo ratings yet
- Mt190aw01 V5Document24 pagesMt190aw01 V5Orangelin SantaellaNo ratings yet
- Density Based Traffic Light Controller Using Wireless Sensor Network and Arm ProcessorDocument4 pagesDensity Based Traffic Light Controller Using Wireless Sensor Network and Arm ProcessorqaaaziNo ratings yet
- SMD Transistor Mark V75 083-30173-Ne3503m04Document7 pagesSMD Transistor Mark V75 083-30173-Ne3503m04Isaias RodriguesNo ratings yet
- MSP 430 F 2132Document81 pagesMSP 430 F 2132rickseltNo ratings yet
- Loren Mae Aguantar Laboratory 4 LED CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesLoren Mae Aguantar Laboratory 4 LED Characteristicsjason mr.perfect11No ratings yet
- BEEE CP Doc (2022-23)Document21 pagesBEEE CP Doc (2022-23)Akshat goyalNo ratings yet
- Nexo PS15 LautsprecherDocument2 pagesNexo PS15 Lautsprecher1234No ratings yet
- Triumph Board Led LCD Service ManualDocument18 pagesTriumph Board Led LCD Service ManualJani LeoNo ratings yet
- CEA201-Trương Vĩnh Thịnh-SE17D09Document6 pagesCEA201-Trương Vĩnh Thịnh-SE17D09Ookami GinjiNo ratings yet
- P4SMA6.8A (CA) - P4SMA440A (CA) : Surface Mount Transient Volage Suppessor DiodeDocument5 pagesP4SMA6.8A (CA) - P4SMA440A (CA) : Surface Mount Transient Volage Suppessor DiodeCristobalzqNo ratings yet
- Parts of ComputerDocument12 pagesParts of ComputerSaroj KumarNo ratings yet
- Q7-TI8168 Datasheet PDFDocument3 pagesQ7-TI8168 Datasheet PDFmertikNo ratings yet
- Digitrip 520&520M Trip Units For Series NRX Circuit BreakersDocument40 pagesDigitrip 520&520M Trip Units For Series NRX Circuit BreakersEdwinNo ratings yet
- Synopsis of GSM Based Home Security SystemDocument4 pagesSynopsis of GSM Based Home Security SystemGany HarwalNo ratings yet
- MBRF20200CT Switchmodet Schottky Power RectifierDocument4 pagesMBRF20200CT Switchmodet Schottky Power RectifierMohamed MohamedNo ratings yet