Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Uploaded by
ASFAR ALI0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views26 pagesThis lecture introduces an operating systems course, covering topics like computer system organization, the purpose of operating systems, and an outline of topics to be discussed over the course. The lecture agenda includes introductions to hardware, operating systems, applications, and users. It also provides an overview of computer system components and the course outline which covers operating system concepts, processes, memory management, file systems, and more.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis lecture introduces an operating systems course, covering topics like computer system organization, the purpose of operating systems, and an outline of topics to be discussed over the course. The lecture agenda includes introductions to hardware, operating systems, applications, and users. It also provides an overview of computer system components and the course outline which covers operating system concepts, processes, memory management, file systems, and more.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views26 pagesUntitled
Uploaded by
ASFAR ALIThis lecture introduces an operating systems course, covering topics like computer system organization, the purpose of operating systems, and an outline of topics to be discussed over the course. The lecture agenda includes introductions to hardware, operating systems, applications, and users. It also provides an overview of computer system components and the course outline which covers operating system concepts, processes, memory management, file systems, and more.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
Lecture 1
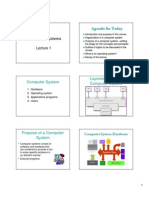
Agenda for Today
Introduction and purpose of the course
Organization of a computer system
Purpose of a computer system—setting
the stage for OS concepts and principles
Outline of topics to be discussed in the
course
What is an operating system?
Recap of the lecture
1. Hardware
2. Operating system
3. Applications programs
4. Users
Computer systems consist of
software and hardware that are
combined to provide a tool to
solve specific problems in an
efficient manner
Execute programs
Computer System Hardware
Integer Control Keyboard Mouse
Unit Unit
CD
Floating Point
Unit
Cache
Processor
System Bus
HD
Mem
Bus
RAM/ROM Printer Monitor
Course Outline
Operating system concepts
Operating system structures
Introduction to UNIX/Linux user interface
Processes and threads—scheduling,
concurrency, synchronization, etc.
Deadlocks
Memory management
Virtual memory
File system
Secondary storage management
April 10, 2023
Single-user systems
Batch systems
Multiprogrammed systems
Time-sharing systems
Real-time systems
Interrupts, traps, and software interrupts (UNIX
signals)
Hardware protection
April 10, 2023
Operating system services
System calls
Semantics of system call execution
Operating system structures (monolithic,
microkernel-based, layered, virtual machines,
DOS-Windows, UNIX)
System design and implementation
April 10, 2023
Directory structure
Browsing directory structure
Useful commands
April 10, 2023
Process concept (process, states, attributes,
etc.)
Process scheduling (scheduler)
Context switching (dispatcher)
Operations on processes (creation,
termination, signaling, suspend, foreground,
background, etc.)
Process management in UNIX (fork, wait, exec,
exit, etc.)
April 10, 2023
Sample code for UNIX/Linux process
management
Cooperating processes
Interprocess communication (IPC)
IPC in UNIX/Linux (pipe, FIFO, socket,
message queue, etc.)
April 10, 2023
Communication between UNIX/Linux
processes (pipe, mkfifo, read, write, close, etc.)
Sample code
UNIX/Linux processes (process images,
control structures, etc. explained with sample
code)
Managing UNIX/Linux processes (ps, top, fg,
bg, <Ctrl-Z>, <Ctrl-C>, etc.)
April 10, 2023
Thread concept (thread, states,
attributes, etc.)
User- and kernel-level threads
POSIX threads (the pthread
library)
Sample code
April 10, 2023
Basic concepts
Scheduling criteria
Scheduling triggers
Scheduling algorithms
UNIX System V scheduling algorithm
Optimal scheduling
Algorithm evaluation
April 10, 2023
Basic concept
The Critical Section Problem
Solutions for the Critical Section Problem
Software-based solutions—the Bakery
Algorithm
Hardware-based solutions
Semaphores
Binary and counting semaphores
April 10, 2023
Classic problems of synchronization
Deadlocks and starvation
Critical regions
Monitors
Synchronization tools used in Solaris, Linux,
and Windows
Deadlocks and starvation
Pthread library functions
April 10, 2023
Basic concept
Deadlock characterization
Deadlock handling (prevention, avoidance,
detection and recovery)
Banker’s algorithm
April 10, 2023
Basic concepts
Various techniques for memory management
Logical to physical address translation
Swapping
Contiguous memory allocation: MFT, MVT
External fragmentation
Paging
Hardware support for paging
Internal fragmentation
April 10, 2023
Performance of paging
Protection and sharing
Page table issues: Multi-level paging, Hashed
page tables, Inverted page tables
Segmentation
Protection and sharing
Segmentation with paging
Intel P4 example
April 10, 2023
Basic concept
Demand paging\
Page fault
Performance of demand paging
Page replacement
Allocation of frames
Thrashing
Operating-system examples
Other considerations (I/O locking, page size, …)
April 10, 2023
Basic concepts (file attributes, operations, types,
structure, etc.)
Access methods (sequential, random, etc.)
Directory structure
UNIX/Linux directory structure (links in UNIX)
File system mounting, sharing, and protection
UNIX/Linux examples for sharing and protection,
and relevant commands (chmod, ln, ln –s, etc.)
April 10, 2023
Basic concepts (overview of disk structure, file
structure, boot control block, super block, inode,
per process file descriptor table, system-wide
open-file table, etc.)
Directory implementation
Free space management methods
Space Allocation Methods
Time and space performance of allocation
methods
Brief introduction to Network File System (NFS)
April 10, 2023
Disk structure and scheduling
Disk management (formatting,
boot block, bad blocks, etc.)
Course Recap
April 10, 2023
What is an Operating System?
A program that acts as an intermediary
between a user of a computer and the
computer hardware—provides the user a
simpler (virtual) machine to work with
A program that allocates and deallocates
computer system resources in an efficient,
fair, and secure manner—a resource
manager
April 10, 2023
Execute user programs and make solving user
problems easier.
Make the computer system convenient to use.
Use the computer hardware in an efficient
manner.
April 10, 2023
You might also like
- Operating Systems - CS604 Power Point Slides LectureDocument27 pagesOperating Systems - CS604 Power Point Slides LectureLohith Gk100% (3)
- Modern Operating SystemDocument401 pagesModern Operating SystemMuhammad ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Lecture Notes-1Document15 pagesOperating Systems Lecture Notes-1Arun Sasidharan100% (1)
- USB Mass Storage: Designing and Programming Devices and Embedded HostsFrom EverandUSB Mass Storage: Designing and Programming Devices and Embedded HostsNo ratings yet
- Windows Kernel Internals II: University of Tokyo - July 2004Document16 pagesWindows Kernel Internals II: University of Tokyo - July 2004Randall Jordan MoreiraNo ratings yet
- 6500 Series QTOF Support Parts ListDocument66 pages6500 Series QTOF Support Parts ListПетр КрасновNo ratings yet
- Multicore Software Development Techniques: Applications, Tips, and TricksFrom EverandMulticore Software Development Techniques: Applications, Tips, and TricksRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Operating SystemsDocument27 pagesOperating SystemsPunjab Commission ShopNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument26 pagesOperating SystemLa Ode SafarNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems - Lecture 01 PDFDocument29 pagesOperating Systems - Lecture 01 PDFAbolghasem Sadeghi-NiarakiNo ratings yet
- Ue18Cs240: Introduction To Operating Systems: Course ObjectivesDocument2 pagesUe18Cs240: Introduction To Operating Systems: Course ObjectivesPruthvi PutuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 OSDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 OSHassan ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Rns Institute of Technology: RN Shetty TrustDocument56 pagesRns Institute of Technology: RN Shetty Trustanu radhaNo ratings yet
- OS Micro 2022 Final Exam WorksheetDocument78 pagesOS Micro 2022 Final Exam Worksheetjan luNo ratings yet
- 1 - Operating SystemsDocument76 pages1 - Operating SystemsElian NjoriNo ratings yet
- OS and Linux - PG-DMC Aug 2016: CPU SchedulingDocument3 pagesOS and Linux - PG-DMC Aug 2016: CPU SchedulingAziz ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemsDocument24 pagesOperating SystemskaylarobertsNo ratings yet
- A Short Introduction To Operating SystemsDocument105 pagesA Short Introduction To Operating SystemsscribdNo ratings yet
- OS - All-5-UnitDocument185 pagesOS - All-5-UnithariNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems: Lecture NotesDocument222 pagesOperating Systems: Lecture NotesMinuJose JojyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document6 pagesUnit 2Tushar ShindeNo ratings yet
- TMC 103 Operating SystemsDocument2 pagesTMC 103 Operating SystemsMs. Ranu TyagiNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Computer Systems in HRM Course OutlineDocument2 pagesFoundations of Computer Systems in HRM Course Outlineksylviakinyanjui2No ratings yet
- OS SyllabusDocument6 pagesOS SyllabusKhushHali ModiNo ratings yet
- The Kernel: Basic Organization: HapterDocument38 pagesThe Kernel: Basic Organization: HapterFacer DancerNo ratings yet
- M 317: Operating Systems: Class OutlineDocument19 pagesM 317: Operating Systems: Class OutlineMomen abd ElrazekNo ratings yet
- M 317: Operating Systems: Class OutlineDocument19 pagesM 317: Operating Systems: Class OutlineMomen abd ElrazekNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document20 pagesLecture 2faheem tariqNo ratings yet
- Com3109 1Document13 pagesCom3109 1alcinialbob1234No ratings yet
- An Operating SystemDocument2 pagesAn Operating Systemamanterefe99No ratings yet
- RTOS Based Embedded System DesignDocument16 pagesRTOS Based Embedded System DesignSagar DhapkeNo ratings yet
- Lovely Profession UniversityDocument14 pagesLovely Profession UniversityYogesh GandhiNo ratings yet
- Intro To Operating SystemDocument10 pagesIntro To Operating SystemAvik BachharNo ratings yet
- OS Unit1Document60 pagesOS Unit1Vijay JangidNo ratings yet
- Adina Institute of Science & Technology Department of Computer Science & Engineering Lecture PlanDocument3 pagesAdina Institute of Science & Technology Department of Computer Science & Engineering Lecture Plansaurabhkher19No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Operating-System StructuresDocument31 pagesChapter 3: Operating-System StructuresDiamond MindglanceNo ratings yet
- A Simple, Unix-Like Teaching Operating System: Russ Cox Frans Kaashoek Robert Morris Xv6-Book@pdos - Csail.mit - EduDocument102 pagesA Simple, Unix-Like Teaching Operating System: Russ Cox Frans Kaashoek Robert Morris Xv6-Book@pdos - Csail.mit - Edustudent36521No ratings yet
- 0 Course OutlinesDocument3 pages0 Course Outlineskonainali046No ratings yet
- Os PPT Galvin Chapter1Document29 pagesOs PPT Galvin Chapter1Vishal ThakurNo ratings yet
- Course Outline-1Document3 pagesCourse Outline-1Bright Alike ChiwevuNo ratings yet
- Components of Operating System2Document8 pagesComponents of Operating System2gsssbheemsanaNo ratings yet
- A Short Introduction To Operating Systems PDFDocument115 pagesA Short Introduction To Operating Systems PDFtotherethym100% (1)
- Operating Systems OverviewDocument20 pagesOperating Systems Overviewmohsinabbas1984No ratings yet
- Unit OS1: Overview of Operating SystemsDocument15 pagesUnit OS1: Overview of Operating SystemsEzekiel Ogakhan NyamuNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument24 pagesIntroMrutyunjay SethyNo ratings yet
- An Operating System, What For?: Operating System Tasks Survey of Operating System PrinciplesDocument18 pagesAn Operating System, What For?: Operating System Tasks Survey of Operating System Principlesnayak1234No ratings yet
- Unit 1 of Operating System: StructureDocument25 pagesUnit 1 of Operating System: Structuresadia3No ratings yet
- OSStructsDocument25 pagesOSStructssaifulNo ratings yet
- Cs8493 - Operating SystemsDocument9 pagesCs8493 - Operating SystemsPawan NaniNo ratings yet
- OS Definations and TypesDocument19 pagesOS Definations and TypesLinda BrownNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems: Computer System Layered View of A Computer SystemDocument5 pagesOperating Systems: Computer System Layered View of A Computer Systemtayaba171No ratings yet
- OS Notes 1Document20 pagesOS Notes 1whiteitan2No ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument2 pagesOperating SystemBhavesh SoniNo ratings yet
- Intro To Computer OrganizationDocument59 pagesIntro To Computer OrganizationDmytroNo ratings yet
- History of Unix, Uses and Unix Features History of UnixDocument47 pagesHistory of Unix, Uses and Unix Features History of UnixNarmatha ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- File System Case StudyDocument23 pagesFile System Case StudyV snehaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Components, Functionalities & Types of OSDocument15 pages2 - Components, Functionalities & Types of OSManan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Course Outcomes CSC 4103Document3 pagesCourse Outcomes CSC 4103dishatiwariNo ratings yet
- Mod 1Document123 pagesMod 1hey hiNo ratings yet
- Asfar Ali CVDocument2 pagesAsfar Ali CVASFAR ALINo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument24 pagesUntitledASFAR ALINo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledASFAR ALINo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument22 pagesUntitledASFAR ALINo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument25 pagesUntitledASFAR ALINo ratings yet
- Lesson 12: PC Operating Systems in ReviewDocument18 pagesLesson 12: PC Operating Systems in ReviewASFAR ALINo ratings yet
- Lesson 11: Operating System BasicsDocument27 pagesLesson 11: Operating System BasicsASFAR ALINo ratings yet
- ES FileDocument41 pagesES FileAman GargNo ratings yet
- PDC 1 - PD ComputingDocument12 pagesPDC 1 - PD ComputingmishaNo ratings yet
- Project PDFDocument57 pagesProject PDFSuraj YadavNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Upgrade PC FinanceDocument9 pagesSpesifikasi Upgrade PC FinanceIrfan NurdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Materi PaparanDocument11 pagesMateri Paparanasubarkah22No ratings yet
- Chennamadhavuni's ResumeDocument2 pagesChennamadhavuni's ResumeChennamadhavuni SahithiNo ratings yet
- An5042 How To Calibrate The Hse Clock For RF Applications On stm32 Wireless Mcus StmicroelectronicsDocument67 pagesAn5042 How To Calibrate The Hse Clock For RF Applications On stm32 Wireless Mcus StmicroelectronicsBinh DaoNo ratings yet
- Đề Cương TACNDocument6 pagesĐề Cương TACNĐặng M.TùngNo ratings yet
- SYNC IEC60870-5 101 Master Interface Usermanual Rev1.0.6Document24 pagesSYNC IEC60870-5 101 Master Interface Usermanual Rev1.0.6Thành CôngNo ratings yet
- SF DumpDocument15 pagesSF DumpRuth GonzálezNo ratings yet
- PC Rakitan, Printer Tinta 2022Document1 pagePC Rakitan, Printer Tinta 2022glomed tekNo ratings yet
- Machines Simulator Quick GuideDocument18 pagesMachines Simulator Quick GuideObdulio PinheiroNo ratings yet
- Enx Aa?) : Ajaj D G Josj CrioDocument87 pagesEnx Aa?) : Ajaj D G Josj CrioBasavapatna N PhanirajaNo ratings yet
- September 10, 2021 - Proposal - Server - REF#21-0910 - 2Document1 pageSeptember 10, 2021 - Proposal - Server - REF#21-0910 - 2AnonpcNo ratings yet
- Ict Final QuestionsDocument8 pagesIct Final QuestionsEchuserang FrogletNo ratings yet
- ASR1013 Datasheet: Quick SpecsDocument4 pagesASR1013 Datasheet: Quick SpecsRobison Meirelles juniorNo ratings yet
- CSS 12 - 1st - 3rd Quarter Summative TestDocument3 pagesCSS 12 - 1st - 3rd Quarter Summative TestGeejan Galaroza PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Dir-885l Reva Firmware Patch Notes 1.21b03 BetaDocument2 pagesDir-885l Reva Firmware Patch Notes 1.21b03 BetaSeventoolNo ratings yet
- Assembly Language Programming:: 8085 Program To Add Two 8 Bit NumbersDocument9 pagesAssembly Language Programming:: 8085 Program To Add Two 8 Bit NumbersAnkit ratan pradhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture-16 CH-04 4Document21 pagesLecture-16 CH-04 4Osama RousanNo ratings yet
- DNT20 - Rockwell Visualization Full OverviewDocument80 pagesDNT20 - Rockwell Visualization Full OverviewMauricio OliveiraNo ratings yet
- dp533 SeriesDocument114 pagesdp533 SeriesДмитрий ЧеNo ratings yet
- Quanta Zu2 R1a SchematicsDocument36 pagesQuanta Zu2 R1a SchematicsBalaji Pharmacy - GMNo ratings yet
- Preparing Hand Tools and Equipment For Computer Hardware ServicingDocument31 pagesPreparing Hand Tools and Equipment For Computer Hardware ServicingJeric Enteria CantillanaNo ratings yet
- 6 Stack and SubroutinesDocument33 pages6 Stack and SubroutinesRajat BoraNo ratings yet
- A161 - Bizhub C224 - C284 - C364Document116 pagesA161 - Bizhub C224 - C284 - C364vecuNo ratings yet
- V11 1 EngDocument9 pagesV11 1 Engyusif samNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Manual 8s661fxm-775 20 eDocument88 pagesMotherboard Manual 8s661fxm-775 20 eRigger StayboeNo ratings yet
- IoT (15CS81) Module 5 Arduino UnoDocument30 pagesIoT (15CS81) Module 5 Arduino UnoRijo Jackson TomNo ratings yet