Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1711910
Uploaded by
hamza A.lafta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesThe document summarizes key information about alkanes. Alkanes are hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2. Their physical properties like melting point, boiling point, and density increase with the number of carbon atoms. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that are quite unreactive. They are insoluble in water but soluble in non-aqueous solvents. The document also provides information about processes for alkane production, including process streams and energy balances.
Original Description:
Original Title
1711910.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key information about alkanes. Alkanes are hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2. Their physical properties like melting point, boiling point, and density increase with the number of carbon atoms. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that are quite unreactive. They are insoluble in water but soluble in non-aqueous solvents. The document also provides information about processes for alkane production, including process streams and energy balances.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pages1711910
Uploaded by
hamza A.laftaThe document summarizes key information about alkanes. Alkanes are hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2. Their physical properties like melting point, boiling point, and density increase with the number of carbon atoms. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that are quite unreactive. They are insoluble in water but soluble in non-aqueous solvents. The document also provides information about processes for alkane production, including process streams and energy balances.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
ALKANES
INTRODUCING ALKANES
Petroleum and natural gas contain lots of hydrocarbons, most of
2
which are alkanes.
ALKANES are hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2.
Space-filling models of methane, ethane, propane and butane.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKANES
Physical properties of some straight-chain alkanes.
Melting point, boiling point and density
5
(a) LPG (consisting of lower alkanes)
burns with a non-sooty blue flame. (b) A candle (consisting of higher
alkanes) burns with a sooty
yellow/orange flame.
Viscosity
The viscosity of liquid alkanes increases with a greater
number of carbon atoms.
6
Solubility
Alkanes are insoluble in water. On the other hand, alkanes
are soluble in many non-aqueous solvents (e.g.
methylbenzene).
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKANES
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. They are quite unreactive.
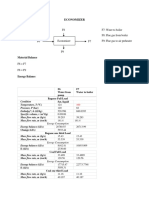
production first step
second step
first process
CO2 H2S
Stream CO (mol/s) (mol/s) H2 (mol/s) N2 (mol/s) (mol/s) Ash (mol/s)
Inlet 0.033031 0.023316 0.023316 0.0145725 0.0291 5.7354e-4
Outlet 3.92347155 0 0.98540121 0.0165155 0 0
second process
Stream CO C2H4 CO2 H2 N2 H2S Ash
(kg/s) kg/s (kg/s) (kg/s) (kg/s) (kg/s) (kg/s)
Inlet 109.8425 0 0 1.970802 0.462924 0 0
76
Outlet 21.96851 87.87406 0 0.394160 0.462924 0 0
52 08 4
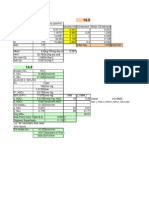
first process
Stream Flow rate (kg/s) Enthalpy (kJ/kg) Energy output
(kW)
CH4 0.925868 -802.2 -25.95
CO 109.842576 -283.6 -262.87
CO2 1.025824 -393.5 -403.76
H2 1.970802 -241.8 -476.14
N2 0.40866 -17.22 -7.03
H2S 0.98814 -20.0 -19.76
Ash 0.034524 -94.55 -3.27
Jacket - - 10,965.63
Total -
second process
- 9,792.8
Component Energy Required (kW)
Boiler 3059.1
Condenser 2361.3
Thanks
You might also like
- 8th Edition Cengel-Thermodynamics-An-Engineering-Approach PDFDocument177 pages8th Edition Cengel-Thermodynamics-An-Engineering-Approach PDFyash0% (2)
- Project DesignDocument31 pagesProject DesignGunjan SolankiNo ratings yet
- Economize R 3 TrialDocument19 pagesEconomize R 3 TrialNitish AmnerkarNo ratings yet
- Property Tables and Charts (Si Units) With Conversion FactorsDocument24 pagesProperty Tables and Charts (Si Units) With Conversion Factorsnur hananiNo ratings yet
- Çengel - Thermodynamics (An Engineering Approach) 8th Ed (TABELAS) PDFDocument91 pagesÇengel - Thermodynamics (An Engineering Approach) 8th Ed (TABELAS) PDFJorge Vieira100% (2)
- Combustion CalcsDocument8 pagesCombustion Calcs31331311313No ratings yet
- Combustion CalcsDocument8 pagesCombustion CalcsZhaqir HusseinNo ratings yet
- CHE 322 - Gaseous Fuel Problems PDFDocument26 pagesCHE 322 - Gaseous Fuel Problems PDFDanice LunaNo ratings yet
- 05 CombustionDocument15 pages05 CombustionMKPashaPasha100% (1)
- CHE 322 - Gaseous Fuel ProblemsDocument26 pagesCHE 322 - Gaseous Fuel ProblemsDanice LunaNo ratings yet
- Gas Liquid Separator DesignDocument3 pagesGas Liquid Separator DesignSoheil MoradiNo ratings yet
- Equipment Analysis in Design of Sulphuric Acid Plant: Yogeesh Sharma B. Tech (Mechanical & Automation Engg.)Document18 pagesEquipment Analysis in Design of Sulphuric Acid Plant: Yogeesh Sharma B. Tech (Mechanical & Automation Engg.)yogeeshs123No ratings yet
- BoilerDocument29 pagesBoilerhonchoabhiNo ratings yet
- Boiler Efficiency Calculations - FinalDocument50 pagesBoiler Efficiency Calculations - FinalDilip MishraNo ratings yet
- Plant Design For The Production of Sodium CarbonateDocument29 pagesPlant Design For The Production of Sodium CarbonateMuhammad Adeel KhalidNo ratings yet
- 6 Ammonia PlantDocument29 pages6 Ammonia PlantMunawar Lal Joshi100% (1)
- Production of Lime: Chemical Engineering DepartmentDocument17 pagesProduction of Lime: Chemical Engineering DepartmentDon Aries EidosNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Input Correction FactorDocument11 pagesHeat Exchanger Input Correction FactorTrần Tuấn VũNo ratings yet
- Mass ConverterDocument18 pagesMass ConverterDinesh CR7No ratings yet
- Comparative Performance Analysis of Various Pre-Combustion CO Capture TechniquesDocument26 pagesComparative Performance Analysis of Various Pre-Combustion CO Capture TechniquesUsama ShakilNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan BB Cangkang Kelapa Sawit YeayDocument24 pagesPerhitungan BB Cangkang Kelapa Sawit YeayBillyRadianNo ratings yet
- Specific Gas Ratio - SwapnilDocument33 pagesSpecific Gas Ratio - SwapnilYhane100% (1)
- Heat Balance-1Document85 pagesHeat Balance-1Ravi sharmaNo ratings yet
- Sulfuric Acid Manufacture: Analysis, Control and OptimizationFrom EverandSulfuric Acid Manufacture: Analysis, Control and OptimizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Cutting-Edge Technology for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and StorageFrom EverandCutting-Edge Technology for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and StorageKarine Ballerat-BusserollesNo ratings yet
- Merged Heat BalanceDocument56 pagesMerged Heat Balancehmaza shakeel100% (2)
- Garbage IncineratorDocument59 pagesGarbage IncineratorgsdaundhNo ratings yet
- 4470 Lecture 3 2013Document24 pages4470 Lecture 3 2013ZakyKikyNo ratings yet
- GasificationDocument24 pagesGasificationJamilu SalihuNo ratings yet
- Base Parameters & Results:: ENGY4000 - Week 2 TutorialDocument4 pagesBase Parameters & Results:: ENGY4000 - Week 2 TutorialKatty TsaiNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Fuels and CombustionDocument45 pages1.0 Fuels and CombustionGH Eco RJNo ratings yet
- Deepika (Ammonia)Document2 pagesDeepika (Ammonia)suhailkpuaeNo ratings yet
- Boiler 1Document11 pagesBoiler 1Krishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Bailey Alkanes PowerpointDocument31 pagesBailey Alkanes PowerpointBritney PattersonNo ratings yet
- Lampiran A Sudah FinalDocument20 pagesLampiran A Sudah FinalBayu Handika PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- 15-12-2009 Blr#1effDocument5 pages15-12-2009 Blr#1effpulakjaiswal85No ratings yet
- Bailey Alkanes PowerpointDocument31 pagesBailey Alkanes PowerpointBritney PattersonNo ratings yet
- Ef2002074 Si 001Document13 pagesEf2002074 Si 001Bidesh M KirtaniaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Biomass GasificationDocument6 pagesAn Overview of Biomass GasificationFrank MedrosNo ratings yet
- Properties and Testing of CoalDocument13 pagesProperties and Testing of CoalMohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Unlicensed-The Carbon Dioxide Pollution When Burning Solid - MIRICADocument7 pagesUnlicensed-The Carbon Dioxide Pollution When Burning Solid - MIRICADinca DumitruNo ratings yet
- Sim WorkBookDocument20 pagesSim WorkBookMuhammad Umer RanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter No.3 Material Balance: 3.1 Fluidized Bed ReactorDocument14 pagesChapter No.3 Material Balance: 3.1 Fluidized Bed Reactorsagar dasguptaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Problem: Laurito, E. R. (N.D.) - Stoichiometry of Fuel Combustion andDocument20 pagesComprehensive Problem: Laurito, E. R. (N.D.) - Stoichiometry of Fuel Combustion andVilma GaelaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 14 Answer Key 2012Document11 pagesCh. 14 Answer Key 2012tmtennisNo ratings yet
- Sec AdoDocument3 pagesSec AdoMarcos BrionesNo ratings yet
- Thermophysical PropertiesDocument7 pagesThermophysical PropertiesWei JianNo ratings yet
- Goga Sent FileDocument19 pagesGoga Sent FileShah Ali NaqviNo ratings yet
- Properties of WaterDocument3 pagesProperties of WatertaylorknoNo ratings yet
- Tugas Perancangan Pabrik Kimia 2 Nama Nikai Hermawan Amrullah NPM 08.2017.1.90212Document21 pagesTugas Perancangan Pabrik Kimia 2 Nama Nikai Hermawan Amrullah NPM 08.2017.1.90212Nikai Hermawan AmrullahNo ratings yet
- Pde ReportDocument10 pagesPde ReportChellam Siva Chellam SivaNo ratings yet
- Mass Balance2Document20 pagesMass Balance2barbadosiyNo ratings yet
- Neraca Massa AmmoniakDocument10 pagesNeraca Massa AmmoniakMuhammad FadilNo ratings yet
- Rich Gas and Lean GasDocument7 pagesRich Gas and Lean GasManish GautamNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document9 pagesLab Report 3mali.abbas555110No ratings yet
- Methanol SynthesisDocument2 pagesMethanol Synthesischinnadche95158No ratings yet
- Komponen BM (Kg/kmol) INPUT (KG/HR)Document11 pagesKomponen BM (Kg/kmol) INPUT (KG/HR)AchmadJa'farShodiqShahabNo ratings yet
- Systems in Photocatalytic DegradationDocument12 pagesSystems in Photocatalytic Degradationhamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Project 1 7/31/2022Document3 pagesProject 1 7/31/2022hamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Active Catalyst Development For Deep Hydro-Desulfurization of Gas Oil in Dual Bed ReactorDocument1 pageActive Catalyst Development For Deep Hydro-Desulfurization of Gas Oil in Dual Bed Reactorhamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Certificate: Rajaa Hanoun KazemDocument1 pageCertificate: Rajaa Hanoun Kazemhamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Project 1 7/31/2022Document3 pagesProject 1 7/31/2022hamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Wastewater TreatmentDocument7 pagesIndustrial Wastewater Treatmenthamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument77 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documenthamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Viewer - Free Online File ViewerDocument1 pageAutodesk Viewer - Free Online File Viewerhamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Santos 2015Document9 pagesSantos 2015hamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Oil Water Separator SizingDocument6 pagesOil Water Separator Sizinghamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id2984527Document7 pagesSSRN Id2984527GEORGE ANTHONY TUÑONNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word Document (2) 3Document160 pagesNew Microsoft Word Document (2) 3hamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word Document (2) 3Document160 pagesNew Microsoft Word Document (2) 3hamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 16 Designof Experimentsv 2Document30 pagesLesson 16 Designof Experimentsv 2hamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- The Basic of RSMDocument26 pagesThe Basic of RSMhamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Submitted by Sravya Dandamudi-B130832Ch Sree Sanjana-B130185Ch Sruthy S Kumar-B130390ChDocument11 pagesSubmitted by Sravya Dandamudi-B130832Ch Sree Sanjana-B130185Ch Sruthy S Kumar-B130390Chhamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Design and Sample Size Determination: Karl W Broman Department of Biostatistics Johns Hopkins UniversityDocument37 pagesExperimental Design and Sample Size Determination: Karl W Broman Department of Biostatistics Johns Hopkins UniversityLeah AbenerNo ratings yet
- When Knowledge Becomes PowerDocument12 pagesWhen Knowledge Becomes Powerhamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Psuedo Steady State Diffusion Through A Stagnant FilmDocument10 pagesPsuedo Steady State Diffusion Through A Stagnant Filmhamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Sulfur Removal From Natural GasDocument12 pagesSulfur Removal From Natural Gashamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Edp 660 Notes Chapter 11Document14 pagesEdp 660 Notes Chapter 11ElynElynNo ratings yet
- Nox Reduction For Combustion TreatmentDocument12 pagesNox Reduction For Combustion Treatmenthamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Systems in Photocatalytic DegradationDocument12 pagesSystems in Photocatalytic Degradationhamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Discussion 2Document7 pagesChapter 11 - Discussion 2hamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Alkylate Production From Isoparaffin and Olefins: Asmaa Sattar Lateef Mariam Ryadh A.Al-JabbarDocument12 pagesAlkylate Production From Isoparaffin and Olefins: Asmaa Sattar Lateef Mariam Ryadh A.Al-Jabbarhamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Production of MibkDocument11 pagesProduction of Mibkhamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics1: How We Use EnergyDocument21 pagesThermodynamics1: How We Use Energyhamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- L 17 - Thermodynamics (2) : Today's TopicsDocument25 pagesL 17 - Thermodynamics (2) : Today's Topicshamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document11 pagesPresentation 2hamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow and Bernoulli's Principle - Airplanes and Curveballs - Properties of "Real Fluids"Document23 pagesFluid Flow and Bernoulli's Principle - Airplanes and Curveballs - Properties of "Real Fluids"sdfasdgNo ratings yet