Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Models of Communication
Models of Communication
Uploaded by
Prin Ce0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views19 pagesCommunication involves sending and receiving verbal and non-verbal messages between individuals to build understanding. Several models of communication are described, including the linear model involving a one-way message from sender to receiver, the transactional model which views communication as generating social realities within contexts, and the interactive model where participants alternate as sender and receiver to generate meaning.
Original Description:
Original Title
Models of Communication (1).pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCommunication involves sending and receiving verbal and non-verbal messages between individuals to build understanding. Several models of communication are described, including the linear model involving a one-way message from sender to receiver, the transactional model which views communication as generating social realities within contexts, and the interactive model where participants alternate as sender and receiver to generate meaning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views19 pagesModels of Communication
Models of Communication
Uploaded by
Prin CeCommunication involves sending and receiving verbal and non-verbal messages between individuals to build understanding. Several models of communication are described, including the linear model involving a one-way message from sender to receiver, the transactional model which views communication as generating social realities within contexts, and the interactive model where participants alternate as sender and receiver to generate meaning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Communication
Communication is a process that involves sending
and receiving messages through the verbal and
non-verbal methods. Communication is a two-
way means of communicating information in the
form of thoughts, opinions, and ideas between
two or more individuals with the purpose of
building an understanding.
Linear Model of
Communication
The way in which a message, the content of
information being sent, is transmitted from a
sender to a receiver. It is the type of
communication that only occurs one way
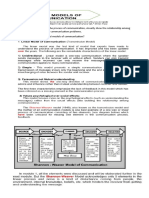
Transactional Model of Communication
The Transaction Model of communication
describes communication as a process in
which communicators generate social realities
within social, relational, and cultural contexts.
Interactive Model of
Communication
The Interaction Model of communication
describes communication as a process in
which participants alternate positions as
sender and receiver and generate meaning by
sending messages and receiving feedback
within physical and psychological contexts.
Lasswell’s Model
It analyzes communication in terms of five
basic questions: "Who", "Says What", "In
What Channel", "To Whom", and "With What
Effect“.
Aristotle’s Model
It is mainly a speaker centred model where
the speaker and speech are very important.
Berlo’s Model
It is outlined into six stages: the
communications source, the encoding of the
message, the message, the delivery method of
the message, the decoding of the message,
and the message receiver.
Barlund’s Model
It explains how each person only gives
attention to certain cues by decoding them
while they encode and produce behavioural
cues in response.
Shannon-Weaver’s Model
It explains communication in terms of five
basic components: a source, a transmitter, a
channel, a receiver, and a destination.
Schramm’s Model
Based on three fundamental components: a
source, a destination, and a message.
White's model of
Communication
Eugene White's model recognizes feedback as
a part of the communication process.
Barriers to Communication
• Physical
• Linguistic
• Interpersonal
• Intrapersonal
• Cultural
• Organizational
You might also like
- Communication ModelsDocument3 pagesCommunication ModelsMary Yvonne AresNo ratings yet
- Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument13 pagesNature and Elements of CommunicationPhilip Jayson L. Lestojas100% (12)
- Models of Communication, ExplainedDocument7 pagesModels of Communication, ExplainedKVVenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Models of CommunicationDocument29 pagesLesson 2 Models of CommunicationIah BelaleNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument7 pagesModels of CommunicationВіка СобчукNo ratings yet
- Different Models of CommunicationDocument9 pagesDifferent Models of CommunicationBhosz Leo Lee100% (1)
- Orlcom1 ReviewerDocument16 pagesOrlcom1 ReviewerAlyanna ManaloNo ratings yet
- Models CommunicationDocument6 pagesModels CommunicationJames Robert CanlasNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 2 Oral ComDocument5 pages02 Handout 2 Oral ComEnzo PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Communication 1Document16 pagesUnderstanding Human Communication 1ilantamizh RNo ratings yet
- 8 Models of Communication by ProponentsDocument8 pages8 Models of Communication by ProponentsRea TorneaNo ratings yet
- Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument28 pagesNature and Elements of CommunicationJerwin LualhatiNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument33 pagesModels of CommunicationSaiza JeonNo ratings yet
- Purpose Communication Group5 Bsab 1bDocument12 pagesPurpose Communication Group5 Bsab 1bRegine Magsayo SingzonNo ratings yet
- Teaching ON Communication: Presented By:Rekha Kumari, Assistant ProfessorDocument69 pagesTeaching ON Communication: Presented By:Rekha Kumari, Assistant ProfessorT. Lamnunnem HaokipNo ratings yet
- Three Models of Communication .Document4 pagesThree Models of Communication .russianescoNo ratings yet
- Intro To Mass Com Models 5 6th Week 15022024 090621pmDocument11 pagesIntro To Mass Com Models 5 6th Week 15022024 090621pmarbab6654No ratings yet
- Oral 2 1Document13 pagesOral 2 1Dobby The elfNo ratings yet
- Linear Models of CommunicationDocument3 pagesLinear Models of CommunicationRay CahayagNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument2 pagesModels of CommunicationZarah CaloNo ratings yet
- Communication Processes, Principles, and EthicsDocument19 pagesCommunication Processes, Principles, and EthicsYanna DerpoNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelDocument19 pagesCommunication ModelApoorva RaviNo ratings yet
- MCTP CombinedDocument231 pagesMCTP CombinedAnmol ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Reading MaterialDocument12 pagesReading MaterialAnmol ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 1-Model of CommunicationDocument4 pages1-Model of CommunicationÂdriân ViloriâNo ratings yet
- Models of Communication: Communication Theory - M2 Assignment No: 01Document12 pagesModels of Communication: Communication Theory - M2 Assignment No: 01Zargham AliNo ratings yet
- ToleraDocument11 pagesToleraRegasa GutemaNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument13 pagesModels of CommunicationleonwaypNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelsDocument4 pagesCommunication ModelsCamille AdarnaNo ratings yet
- (Model Communication) Caole, Aron Joel 11-Abm - ADocument3 pages(Model Communication) Caole, Aron Joel 11-Abm - AAron Joel CaoleNo ratings yet
- 1 Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument13 pages1 Nature and Elements of CommunicationKyle TadifaNo ratings yet
- Communication: Hidaya Ismail MA Student School of Letters MG UniversityDocument25 pagesCommunication: Hidaya Ismail MA Student School of Letters MG UniversityHidayaNo ratings yet
- Escobido, Norberto J. BSTM202Document2 pagesEscobido, Norberto J. BSTM202Kyl CajesNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Task 1 DIOQUINODocument5 pagesAsynchronous Task 1 DIOQUINORm DioquinoNo ratings yet
- Media and Information M1Document39 pagesMedia and Information M1Nazame NayukiNo ratings yet
- Communication ArtsDocument1 pageCommunication ArtsmunchkinniivyNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelDocument6 pagesCommunication ModelHailu TamirNo ratings yet
- Communication Models Describe The Process of CommunicationDocument4 pagesCommunication Models Describe The Process of CommunicationMaria GraceNo ratings yet
- Lesson-1the Basics-Of CommunicationDocument6 pagesLesson-1the Basics-Of CommunicationMagtvna TambayanNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument9 pagesBusiness CommunicationBELENGA GEOFREYNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy ReviewerDocument12 pagesMedia and Information Literacy ReviewerMa. Fe BadilloNo ratings yet
- Sds TRC and Rgicd College of Nursing Bengaluru-29.: Seminar: Communication ModelDocument27 pagesSds TRC and Rgicd College of Nursing Bengaluru-29.: Seminar: Communication ModelREVATHI H KNo ratings yet
- Midterm ModuleDocument42 pagesMidterm ModuleKoolet GalNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelDocument23 pagesCommunication ModelVenny Rose LmstNo ratings yet
- Media Information and LiteracyDocument38 pagesMedia Information and Literacyvankirbylucero123No ratings yet
- Communication Intro1Document5 pagesCommunication Intro1Carlo Jhan LolongNo ratings yet
- Chapter I Communication ModelsDocument8 pagesChapter I Communication ModelsodysonNo ratings yet
- The Communication Model ShaiDocument9 pagesThe Communication Model ShaiShainna PanopioNo ratings yet
- Group 2 PPT PresentationDocument15 pagesGroup 2 PPT PresentationGio MagayonNo ratings yet
- Report On Models of CommunicationDocument38 pagesReport On Models of CommunicationShawn Henry CepedaNo ratings yet
- 8 Models of CommunicationDocument9 pages8 Models of CommunicationLornaNo ratings yet
- Teacher: Dr. Ayesha Riaz Mam Humera Hina Mr. Faisal Ihsan EDU-504 - 3 (3-0)Document16 pagesTeacher: Dr. Ayesha Riaz Mam Humera Hina Mr. Faisal Ihsan EDU-504 - 3 (3-0)Nabeel TahirNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument13 pagesPurposive CommunicationKate Rose SantosNo ratings yet
- Communication (From Latin "Communis", Meaning To Share) Is TheDocument2 pagesCommunication (From Latin "Communis", Meaning To Share) Is TheRonelly EscaladaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Long ExamDocument2 pagesReviewer For Long ExamTrisha EnilNo ratings yet
- What Is A Communication ModelDocument39 pagesWhat Is A Communication ModelDanica CabelloNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument74 pagesBusiness CommunicationHardik SNo ratings yet
- 1 2 MergedDocument8 pages1 2 MergedAira CorderoNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONDocument4 pagesCOMMUNICATIONRoisa JoyNo ratings yet