Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Heart - Lesson Notes CIE
Uploaded by
Jamaila NateCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Heart - Lesson Notes CIE
Uploaded by
Jamaila NateCopyright:
Available Formats
THE HEART
GRADE 11 BLUE BIOLOGY - CIE
Education for the Real World
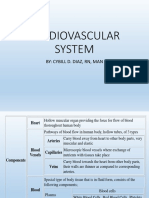
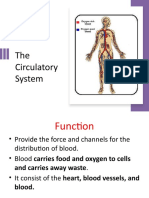
Heart Structure: Basics
• The heart is labelled as if it was in the chest so what is your left on a diagram is
actually the right hand side and vice versa
• The right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps
it to the lungs
• The left side of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to
the body
• Blood is pumped towards the heart in veins and away from the heart in arteries
• The two sides of the heart are separated by a muscle wall called the septum
• The heart is made of muscle tissue which are supplied with blood by the coronary
arteries
Education for the Real World
Education for the Real World
Heart Structure
• The ventricles have thicker muscle walls than the atria as they are pumping blood
out of the heart and so need to generate a higher pressure
• The left ventricle has a thicker muscle wall than the right ventricle as it has to
pump blood at high pressure around the entire body, whereas the right ventricle is
pumping blood at lower pressure to the lungs
• The septum separates the two sides of the heart and so prevents mixing of
oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
Education for the Real World
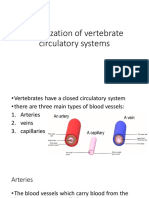
Structure of the heart showing the different valves
Education for the Real World
The Function of Valves
• The basic function of all valves is to prevent blood flowing backwards
• There are two sets of valves in the heart:
• The atrioventricular valves separate the atria from the ventricles
• The valve in the right side of the heart is called the TRICUSPID and the valve
in the left side is called the BICUSPID
• These valves are pushed open when the atria contract but when the ventricles
contract they are pushed shut to prevent blood flowing back into the atria
• The semilunar valves are found in the two blood arteries that come out of the
top of the heart
• They are unusual in that they are the only two arteries in the body that
contain valves
• These valves open when the ventricles contract so blood squeezes past them
out of the heart, but then shut to avoid blood flowing back into the heart
Education for the Real World
You might also like
- Cardio NewDocument204 pagesCardio NewHaleema SaadiaNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument81 pagesTransport in AnimalsIbrahim NOORZADNo ratings yet
- Chapter VIII CardiovascularDocument7 pagesChapter VIII CardiovascularTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of HeartDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of HeartSANJAY SNo ratings yet
- PHA618 Ex 31 Revised PDFDocument20 pagesPHA618 Ex 31 Revised PDFPATRICIA ROSE SORIANONo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument18 pagesCardiovascular SystemDeep RoyNo ratings yet
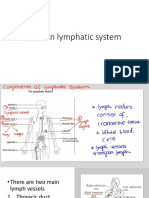
- Lymphatic SystemDocument30 pagesLymphatic SystemWijesiri D WNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument12 pagesHeartRebar photographyNo ratings yet
- Hear Structure NotesDocument27 pagesHear Structure NotesRaifa FathimaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Heart ModuleDocument19 pagesCardiovascular System Heart Modulebadodong700No ratings yet
- Transport System in AnimalsDocument21 pagesTransport System in Animalssonia sonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument26 pagesCardiovascular SystemGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: - HeartDocument58 pagesCardiovascular System: - HeartFaraz AhmedNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Transport in Animals NotesDocument62 pagesIGCSE Biology Transport in Animals NotesSir AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Heart of The MatterDocument27 pagesThe Heart of The MatterSumit JangraNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System P2Document17 pagesThe Circulatory System P2Kristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Heart & DiseasesDocument9 pages1.5 Heart & DiseasesRayonesh RayanaNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument33 pagesTransport in AnimalssamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Structureo of HeartDocument23 pages6.4 Structureo of HeartFathimaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 CH 4.05 The HeartDocument12 pagesGrade 7 CH 4.05 The HeartMunmun AfnanNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document43 pagesModule 3Sharanya BasakNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument99 pagesCardiovascular Physiologyredhat56964No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)Document89 pagesCardiovascular System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)DiazNo ratings yet
- CVS Up To Cardiac Output-1Document198 pagesCVS Up To Cardiac Output-1mokshachapaneriNo ratings yet
- Life Processes: Class 10 BiologyDocument8 pagesLife Processes: Class 10 BiologyHEMALAH SNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy 5.thoracic Cavity (Intro To Cardivascular and Respiratory)Document49 pagesGeneral Anatomy 5.thoracic Cavity (Intro To Cardivascular and Respiratory)amrokhalefa21No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Shoaib AlamDocument28 pagesCardiovascular System: Shoaib AlamUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Cardiovascular SystemDocument49 pages2.2 Cardiovascular SystemPratham ChopraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CVSDocument24 pagesIntroduction To CVSKjoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument103 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular SystemChristina GonezNo ratings yet
- Full Notes - Transport in AnimalsDocument39 pagesFull Notes - Transport in Animalsmiriam odonkorNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: A. KabweDocument117 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: A. KabwePeter ChipatelaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System REVISEDDocument11 pagesCirculatory System REVISEDKim GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Biology Chapter 6 Term 1 ST 1Document27 pagesCirculatory System: Biology Chapter 6 Term 1 ST 1Pranati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Structure of HeartDocument66 pagesCardiovascular System - Structure of HeartsureshNo ratings yet
- Stern Chap 15Document16 pagesStern Chap 15evansternhgpNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular To MhsDocument25 pagesThe Cardiovascular To MhsikuwageNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of CVS: 2. The HeartDocument68 pagesAnatomy of CVS: 2. The Heartsultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Human Body Circulatory SystemDocument41 pagesHuman Body Circulatory SystemFrancis MacasioNo ratings yet
- CSEC The Heart & CirculationDocument28 pagesCSEC The Heart & CirculationDondre HibbertNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Normal Cardiac Structure and FunctionDocument9 pagesWeek 1 Normal Cardiac Structure and FunctionJames ParkNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument18 pagesCardiovascular SystemBinta Elsa JohnNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With Othe Organs in The SystemDocument29 pagesThe Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With Othe Organs in The SystemAngela VirayNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andDocument62 pagesCirculatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andBlister CountNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System: EpicardiumDocument17 pagesThe Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System: Epicardiumlourd nabNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andDocument62 pagesCirculatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andBlister Count100% (1)
- Circulatory SystemDocument96 pagesCirculatory SystemuzumakiyashNo ratings yet
- Notes Grade: 9 Subject: Biology Chapter No: 9 Chapter Name: Transport in Animals ObjectivesDocument36 pagesNotes Grade: 9 Subject: Biology Chapter No: 9 Chapter Name: Transport in Animals Objectivespraneeth satishNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument77 pagesCardiovascular System - The HeartZiraili VidalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Cardiovascular SystemDocument89 pagesChapter 15 - Cardiovascular SystemOliver Namyalo100% (1)
- Circulatory System - Chapter 9Document4 pagesCirculatory System - Chapter 9Viviana PlacentinoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument53 pagesCardiovascular SystemPelin OktayNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System SDDocument16 pagesCardiovascular System SDJosh DeeNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System PDFDocument149 pagesCardiovascular System PDFGayathri SNo ratings yet
- Life Processes, Class XDocument31 pagesLife Processes, Class XPiyushNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument15 pagesCardiovascular SystemTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System S in VertebratesDocument24 pagesCirculatory System S in VertebratesWijesiri D WNo ratings yet
- CVS/ The Blood Vessels: by DR - Ahmed Avdel MandaniDocument27 pagesCVS/ The Blood Vessels: by DR - Ahmed Avdel MandaniSerwan J AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Intro To Circulation 2014 2Document51 pagesTissues and Intro To Circulation 2014 2Chantae JulienNo ratings yet
- Ecology 2 - Lesson NotesDocument9 pagesEcology 2 - Lesson NotesJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- ECOLOGY - NotesDocument18 pagesECOLOGY - NotesJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument14 pagesBiotechnologyJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- Shunt VesselsDocument7 pagesShunt VesselsJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- Ventilation of The Lungs - Lesson Notes CIEDocument9 pagesVentilation of The Lungs - Lesson Notes CIEJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange - Lesson NotesDocument5 pagesGaseous Exchange - Lesson NotesJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Cbmec StratmgtDocument2 pagesCourse Outline Cbmec StratmgtskyieNo ratings yet
- PMDG 737NGX Tutorial 2 PDFDocument148 pagesPMDG 737NGX Tutorial 2 PDFMatt HenryNo ratings yet
- Approved College List: Select University Select College Type Select MediumDocument3 pagesApproved College List: Select University Select College Type Select MediumDinesh GadkariNo ratings yet
- Combining Wavelet and Kalman Filters For Financial Time Series PredictionDocument17 pagesCombining Wavelet and Kalman Filters For Financial Time Series PredictionLuis OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Context in TranslationDocument23 pagesContext in TranslationRaluca FloreaNo ratings yet
- Technical DescriptionDocument2 pagesTechnical Descriptioncocis_alexandru04995No ratings yet
- B.e.eeeDocument76 pagesB.e.eeeGOPINATH.MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Depreciation - Sum of The Years Digit MethodPart 4Document8 pagesChapter 3 Depreciation - Sum of The Years Digit MethodPart 4Tor GineNo ratings yet
- Issue15 - Chirag JiyaniDocument6 pagesIssue15 - Chirag JiyaniDipankar SâháNo ratings yet
- Eaai S 23 02045 PDFDocument28 pagesEaai S 23 02045 PDFAnjali JainNo ratings yet
- MBA-7002-20169108-68 MarksDocument17 pagesMBA-7002-20169108-68 MarksN GNo ratings yet
- Sidomuncul20190313064235169 1 PDFDocument298 pagesSidomuncul20190313064235169 1 PDFDian AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Newcastle University Dissertation FormatDocument6 pagesNewcastle University Dissertation FormatWriteMyEnglishPaperForMeSterlingHeights100% (1)
- Load Schedule: DescriptionDocument1 pageLoad Schedule: Descriptionkurt james alorroNo ratings yet
- Early Christian ArchitectureDocument38 pagesEarly Christian ArchitectureInspirations & ArchitectureNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions: Lecture 7 To 9 Hydraulic PumpsDocument5 pagesFrequently Asked Questions: Lecture 7 To 9 Hydraulic PumpsJatadhara GSNo ratings yet
- OMM 618 Final PaperDocument14 pagesOMM 618 Final PaperTerri Mumma100% (1)
- Wps For Carbon Steel THK 7.11 GtawDocument1 pageWps For Carbon Steel THK 7.11 GtawAli MoosaviNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Preliminary DiscussionDocument2 pagesPurposive Communication Preliminary DiscussionJohn Mark100% (1)
- Market EquilibriumDocument36 pagesMarket EquilibriumLiraOhNo ratings yet
- OM Part B - Rev1Document45 pagesOM Part B - Rev1Redouane BelaassiriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Brief: ScenarioDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Brief: ScenarioChâu TrầnNo ratings yet
- Studies - Number and Algebra P1Document45 pagesStudies - Number and Algebra P1nathan.kimNo ratings yet
- Subject: PSCP (15-10-19) : Syllabus ContentDocument4 pagesSubject: PSCP (15-10-19) : Syllabus ContentNikunjBhattNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs TalkDocument3 pagesSteve Jobs TalkDave CNo ratings yet
- King Saud UniversityDocument10 pagesKing Saud UniversitypganoelNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesKlaribelle VillaceranNo ratings yet
- Geopolymer Book Chapter1 PDFDocument37 pagesGeopolymer Book Chapter1 PDFDick ManNo ratings yet
- MMB & DFT 2012 Workshop ProceedingsDocument44 pagesMMB & DFT 2012 Workshop ProceedingsFelipe ToroNo ratings yet
- دور أخلاقيات الأعمال في تحسين أداء المنظماتDocument14 pagesدور أخلاقيات الأعمال في تحسين أداء المنظماتChaima LaifaNo ratings yet