Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Clotting
Uploaded by
Jamaila Nate0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesPlatelets play a key role in blood clotting by forming scabs over wounds to prevent further blood loss. When skin is broken, platelets arrive at the wound and release chemicals that trigger a series of reactions, converting fibrinogen proteins into an insoluble fibrin mesh. This fibrin mesh forms a clot that traps red blood cells and eventually dries to create a scab, sealing the wound and protecting it from bacterial infection as new skin grows underneath.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPlatelets play a key role in blood clotting by forming scabs over wounds to prevent further blood loss. When skin is broken, platelets arrive at the wound and release chemicals that trigger a series of reactions, converting fibrinogen proteins into an insoluble fibrin mesh. This fibrin mesh forms a clot that traps red blood cells and eventually dries to create a scab, sealing the wound and protecting it from bacterial infection as new skin grows underneath.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesBlood Clotting
Uploaded by
Jamaila NatePlatelets play a key role in blood clotting by forming scabs over wounds to prevent further blood loss. When skin is broken, platelets arrive at the wound and release chemicals that trigger a series of reactions, converting fibrinogen proteins into an insoluble fibrin mesh. This fibrin mesh forms a clot that traps red blood cells and eventually dries to create a scab, sealing the wound and protecting it from bacterial infection as new skin grows underneath.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
BLOOD CLOTTING
GRADE 11 BLUE BIOLOGY - CIE
Education for the Real World
Blood Clotting
• Platelets are fragments of cells which are involved in blood clotting and
forming scabs where skin has been cut or punctured
• Blood clotting prevents continued / significant blood loss from wounds
• Scab formation seals the wound with an insoluble patch that prevents entry of
microorganisms that could cause infection
• It remains in place until new skin has grown underneath it, sealing the skin again
Education for the Real World
Blood Clotting
Education for the Real World
Blood Clotting
Education for the Real World
Blood Clotting
Education for the Real World
How the blood clots
• When the skin is broken (i.e. there is a wound) platelets arrive to stop the bleeding
• A series of reactions occur within the blood plasma
• Platelets release chemicals that cause soluble fibrinogen proteins to convert
into insoluble fibrin and form an insoluble mesh across the wound, trapping red
blood cells and therefore forming a clot
• The clot eventually dries and develops into a scab to protect the wound from
bacteria entering
Education for the Real World
You might also like
- Tissue RepairDocument9 pagesTissue RepairSakidu LegionNo ratings yet
- Ulcer: DR - Sunil Kumar Asst - Professor Dept - of Gen - Surgery MNR Medical College Sangareddy 01-05-2019Document83 pagesUlcer: DR - Sunil Kumar Asst - Professor Dept - of Gen - Surgery MNR Medical College Sangareddy 01-05-2019Aashmi ChandrikaaNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Tissue Repair: Kristine Krafts, M.D. - September 13, 2010Document59 pagesTissue Repair: Kristine Krafts, M.D. - September 13, 2010Antonino CassottaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Hemorrhage FinalDocument6 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage Finalvarshasharma05No ratings yet
- Hemostasis and ThrombosisDocument23 pagesHemostasis and ThrombosisFiqrotul Umam100% (1)
- Defense Against Infectious Disease: Skin As A Barrier To InfectionDocument8 pagesDefense Against Infectious Disease: Skin As A Barrier To InfectionFranchesca Rosabel BudimanNo ratings yet
- WoundDocument31 pagesWoundEnos ErastusNo ratings yet
- Black White Fashion Boutique Simple Open Closed Sign Poster LandscapeDocument6 pagesBlack White Fashion Boutique Simple Open Closed Sign Poster LandscapeDobby ElfNo ratings yet
- Platelet Count by Haemocytometer 2nd Year NotesDocument21 pagesPlatelet Count by Haemocytometer 2nd Year Notesrajanti904No ratings yet
- Blood Clotting For TeensDocument7 pagesBlood Clotting For TeensMbabazi TheosNo ratings yet
- A Hand Book On Clinical Chemistry in IVD IndustryDocument41 pagesA Hand Book On Clinical Chemistry in IVD Industryvikasverma90No ratings yet
- Formation of Bilaminar Germ DiscsDocument32 pagesFormation of Bilaminar Germ DiscsVincent OkoroNo ratings yet
- Surgery Assignment: Name: Venugopal Asbeliin IMD 14/15/16 TutorialDocument7 pagesSurgery Assignment: Name: Venugopal Asbeliin IMD 14/15/16 TutorialAsbelNo ratings yet
- Radicular CystDocument28 pagesRadicular CystDr. Deepanshi SutariaNo ratings yet
- AbscessDocument4 pagesAbscessShivBalakChauhanNo ratings yet
- Wound Healing and ScarDocument35 pagesWound Healing and ScarLayla CabduqaadirNo ratings yet
- Formation of Bilaminar Germ DiscsDocument32 pagesFormation of Bilaminar Germ DiscsStanley OdiraNo ratings yet
- Fetal and Embryonic DevelopmentDocument29 pagesFetal and Embryonic Developmentshan mackNo ratings yet
- Components of BloodDocument8 pagesComponents of BloodMaame ForsonNo ratings yet
- Hydatidcyst 180609173228 PDFDocument60 pagesHydatidcyst 180609173228 PDFKarem MaaliNo ratings yet
- Abscess, Cyst & HaematomaDocument36 pagesAbscess, Cyst & HaematomaAqsa Zahoor Ahmad NadeemNo ratings yet
- White Blood Cells: Each White Blood Cell Type Is Named According To Its Appearance in Stained PreparationsDocument12 pagesWhite Blood Cells: Each White Blood Cell Type Is Named According To Its Appearance in Stained PreparationsBeah Marie AlisosoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - 3 Placenta and Umbilical Cord: Group 4 MED 114 PresentationDocument69 pagesWeek 1 - 3 Placenta and Umbilical Cord: Group 4 MED 114 PresentationVidur S SinghNo ratings yet
- 2ND WeekDocument21 pages2ND WeekUti SolomonNo ratings yet
- 4 Tissue-PhysiologyDocument34 pages4 Tissue-PhysiologyMhykhaela CaparasNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System PhysioDocument53 pagesIntegumentary System PhysioMhykhaela CaparasNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Pathology Unit 3Document14 pagesFundamentals of Pathology Unit 3Sujoy TontubayNo ratings yet
- Unit 1msn Last PartDocument11 pagesUnit 1msn Last PartSusmita BeheraNo ratings yet
- 1.3 The Mechanism of Blood ClottingDocument10 pages1.3 The Mechanism of Blood ClottingReakhd Bt KhdNo ratings yet
- Circulation 23.13-23.17Document6 pagesCirculation 23.13-23.17Melanie ZelayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Bilaminar Germ DiscDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Bilaminar Germ DiscJustine Ivan CapiralNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Patologi Gangguan Metabolisme 2017Document89 pagesKuliah Patologi Gangguan Metabolisme 2017Oman SetiyantoNo ratings yet
- Blood Lec 4Document18 pagesBlood Lec 4islamtareqa121No ratings yet
- Backup of Homeostatic ImbalancesDocument5 pagesBackup of Homeostatic ImbalancesDwi N.No ratings yet
- 6.3 Defence Against Infectious DiseaseDocument43 pages6.3 Defence Against Infectious DiseaseAlacrity Xenoion SpadesNo ratings yet
- Biology - MYP 3 - 30th SeptemberDocument3 pagesBiology - MYP 3 - 30th Septemberarchit.kulkarni7756No ratings yet
- Regeneration. Wound Healing: October 10, 2006Document47 pagesRegeneration. Wound Healing: October 10, 2006Komang Tri Adi SuparwatiNo ratings yet
- Good Morning..: Free Powerpoint Templates Free Powerpoint TemplatesDocument36 pagesGood Morning..: Free Powerpoint Templates Free Powerpoint TemplatesRoopa PatilNo ratings yet
- A 5-Year-Old Boy Consulted You For A Wound Which He Incurred A Few Minutes Ago While Playing BasketballDocument5 pagesA 5-Year-Old Boy Consulted You For A Wound Which He Incurred A Few Minutes Ago While Playing BasketballAl IbsNo ratings yet
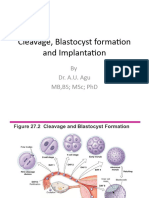
- Cleavage, Blastocyte Formation and ImplantationDocument23 pagesCleavage, Blastocyte Formation and Implantationobianujuonyeka6No ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders - DR RashaDocument95 pagesBleeding Disorders - DR RashaRasha TelebNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument24 pagesPlacentaNibedita 2015No ratings yet
- تجميعات Surgical Physiology Dr Matary 2013-2014Document23 pagesتجميعات Surgical Physiology Dr Matary 2013-2014Abdallah GamalNo ratings yet
- Wound Classification and Its Management: Presented By: Dr. Dhiren B. BhoiDocument48 pagesWound Classification and Its Management: Presented By: Dr. Dhiren B. BhoiBenita Janet AppajiNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument59 pagesPlacentaEdna Jenkins100% (9)
- BloodDocument82 pagesBloodptrcksx.jNo ratings yet
- Mon Surgical Infections Boils, Abscess, Ulcer, Cellulitis, Curbuncle, Gangrene, Sinus, Fistula CDocument48 pagesMon Surgical Infections Boils, Abscess, Ulcer, Cellulitis, Curbuncle, Gangrene, Sinus, Fistula CPanna SahaNo ratings yet
- Oral 5Document236 pagesOral 5Iodeh1985 OdehNo ratings yet
- Stages of Wound HealingDocument9 pagesStages of Wound HealingIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaeDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placentaeeugeniamaranan.06No ratings yet
- OralsDocument278 pagesOralsDr-Mohammad Ali-Fayiz Al TamimiNo ratings yet
- Wound Healing-1Document63 pagesWound Healing-1sunday danielNo ratings yet
- L10 Wound HealingDocument26 pagesL10 Wound HealingAnggi HimranNo ratings yet
- Session 08 Acute InflammationDocument40 pagesSession 08 Acute Inflammationkasper mkNo ratings yet
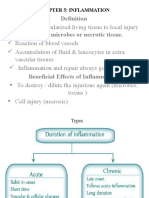
- CHAPTER 5 InflammationDocument51 pagesCHAPTER 5 Inflammationyeshita yonasNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument7 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationSunaina AdhikariNo ratings yet
- CRPC AssignmentDocument2 pagesCRPC Assignmentjyotitated.170No ratings yet
- The Mechanism of BloodDocument8 pagesThe Mechanism of BloodSafwan ZulfazliNo ratings yet
- Blood Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument28 pagesBlood Anatomy and PhysiologyPORTRAIT OF A NURSENo ratings yet
- Ecology 2 - Lesson NotesDocument9 pagesEcology 2 - Lesson NotesJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- ECOLOGY - NotesDocument18 pagesECOLOGY - NotesJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument14 pagesBiotechnologyJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- Preventing & Treating CHDDocument6 pagesPreventing & Treating CHDJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Metals - ChemistryDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Metals - ChemistryJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- Shunt VesselsDocument7 pagesShunt VesselsJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration - Lesson Notes CIE (Autosaved)Document10 pagesAerobic Respiration - Lesson Notes CIE (Autosaved)Jamaila NateNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SytemDocument4 pagesThe Lymphatic SytemJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- Ventilation of The Lungs - Lesson Notes CIEDocument9 pagesVentilation of The Lungs - Lesson Notes CIEJamaila NateNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange - Lesson NotesDocument5 pagesGaseous Exchange - Lesson NotesJamaila NateNo ratings yet