0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views25 pagesMotion Graph
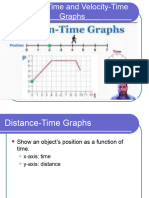
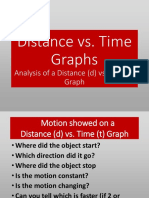
The document discusses different types of graphs that can be used to represent the motion of objects, including position-time graphs where the slope represents speed, speed-time graphs where changes in slope indicate changes in acceleration or deceleration, and ticker tape diagrams that show the position of an object over time through a series of snapshots. These various motion graphs provide visual ways to describe and understand how the speed and position of an object changes throughout its movement.
Uploaded by
Joanne Gaviola GodezanoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views25 pagesMotion Graph
The document discusses different types of graphs that can be used to represent the motion of objects, including position-time graphs where the slope represents speed, speed-time graphs where changes in slope indicate changes in acceleration or deceleration, and ticker tape diagrams that show the position of an object over time through a series of snapshots. These various motion graphs provide visual ways to describe and understand how the speed and position of an object changes throughout its movement.
Uploaded by
Joanne Gaviola GodezanoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd