Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fatigue
Fatigue
Uploaded by
Ayush Ravi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pagesFatigue is a feeling of tiredness and lack of energy that can be physical, mental, or both. It has many potential causes including lack of sleep, medical conditions, stress, medications, poor diet or hydration, and sedentary lifestyle. Fatigue can range from temporary tiredness to chronic long-term fatigue lasting over six months. Management involves treating any underlying causes, getting adequate sleep, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and considering medical evaluation for persistent fatigue.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFatigue is a feeling of tiredness and lack of energy that can be physical, mental, or both. It has many potential causes including lack of sleep, medical conditions, stress, medications, poor diet or hydration, and sedentary lifestyle. Fatigue can range from temporary tiredness to chronic long-term fatigue lasting over six months. Management involves treating any underlying causes, getting adequate sleep, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and considering medical evaluation for persistent fatigue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pagesFatigue
Fatigue
Uploaded by
Ayush RaviFatigue is a feeling of tiredness and lack of energy that can be physical, mental, or both. It has many potential causes including lack of sleep, medical conditions, stress, medications, poor diet or hydration, and sedentary lifestyle. Fatigue can range from temporary tiredness to chronic long-term fatigue lasting over six months. Management involves treating any underlying causes, getting adequate sleep, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and considering medical evaluation for persistent fatigue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
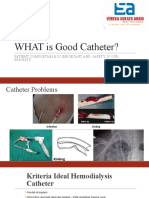
FATIGUE
• Fatigue is a common and complex symptom characterized by
a persistent feeling of tiredness, weakness, and a lack of
energy. It can be physical, mental, or a combination of both.
Fatigue can vary in intensity and duration and may result from
various underlying causes. Here's a detailed explanation of
fatigue
TYPES
• Physical Fatigue: This is the most common type of fatigue and is
characterized by a sense of physical tiredness or weakness. It can
result from strenuous physical activity, lack of sleep, or other
physical factors.
• Mental Fatigue: Mental fatigue, also known as cognitive fatigue,
involves a feeling of mental exhaustion. It can result from prolonged
mental effort, such as studying for exams, working long hours on
mentally demanding tasks, or emotional stress.
• Chronic Fatigue: Chronic fatigue is a long-term, persistent fatigue
that lasts for six months or more and is not relieved by rest. Chronic
fatigue syndrome (CFS), also known as myalgic encephalomyelitis
(ME), is a condition characterized by severe, unexplained fatigue
that often worsens with physical or mental exertion.
CAUSES OF FATIGUE
• Lack of Sleep: Insufficient or poor-quality sleep is a common
cause of fatigue. Sleep disorders like insomnia, sleep apnea,
and restless legs syndrome can also contribute.
• Physical Health Conditions:
• Anemia: Low red blood cell count can lead to reduced oxygen transport
to tissues, causing fatigue.
• Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) can result in
fatigue.
• Chronic Illness: Conditions like diabetes, cancer, fibromyalgia, and
autoimmune diseases can cause chronic fatigue.
• Infections: Viral and bacterial infections, such as mononucleosis or flu,
can lead to fatigue.
• Heart and Lung Problems: Heart failure, chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease (COPD), and other cardiovascular or respiratory
issues can cause fatigue.
• Psychological Factors:
• Stress: Chronic stress can lead to mental and physical fatigue.
• Depression and Anxiety: Mood disorders often involve fatigue as a
prominent symptom.
• Bipolar Disorder: Both depressive and manic phases can be associated
with fatigue.
• Medications: Some medications, including antihistamines,
antidepressants, and certain blood pressure drugs, can cause
fatigue as a side effect.
• Poor Diet and Hydration: Inadequate nutrition and
dehydration can lead to low energy levels.
• Lifestyle Factors: Sedentary lifestyles, lack of regular
physical activity, and excessive use of electronic devices can
contribute to fatigue.
• Environmental Factors: Exposure to extreme temperatures,
pollution, or high altitudes can lead to fatigue.
SYMPTOMS OF FATIGUE
• Persistent tiredness or lack of energy
• Muscle weakness
• Difficulty concentrating
• Memory problems
• Irritability
• Decreased motivation
• Sleep disturbances
• Headaches
• Gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea or diarrhea
MANAGING FATIGUE
• The management of fatigue depends on its underlying cause,
and treatment may involve addressing the specific condition or
factors contributing to fatigue. Here are some general
strategies for managing fatigue:
• Get Adequate Sleep: Ensure you have a regular sleep
schedule and practice good sleep hygiene.
• Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, stay
hydrated, and engage in regular physical activity.
• Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques,
such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga.
• Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Excessive consumption of these
substances can disrupt sleep and contribute to fatigue.
• Medical Evaluation: If fatigue is persistent or severe, consult
a healthcare provider to identify and address any underlying
medical conditions.
• Medication Review: If medications are causing fatigue,
discuss potential alternatives or adjustments with your
healthcare provider.
• Psychological Support: In cases of mental fatigue, consider
therapy or counseling to address underlying emotional issues
• It's essential to address fatigue as it can significantly impact a
person's quality of life and overall well-being. Identifying the
underlying cause is crucial for effective management and
treatment.
You might also like
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome 2010 Caoe CodDocument65 pagesChronic Fatigue Syndrome 2010 Caoe CodDavid_Waltos_2571No ratings yet
- Panna Dhai Maa Subharti Nursing College: Amritanshu Chanchal M.SC Nursing 2 Year Bipolar DisorderDocument24 pagesPanna Dhai Maa Subharti Nursing College: Amritanshu Chanchal M.SC Nursing 2 Year Bipolar DisorderamritanshuNo ratings yet
- Chronic Fatigue SyndromeDocument1 pageChronic Fatigue Syndromeshailesh284No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Immune Diseases (Part I) (Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease)Document6 pagesChapter 6 - Immune Diseases (Part I) (Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease)Ernie G. Bautista II, RN, MD90% (21)
- Radiology Quiz Medical Students Workbook: Author: DR Aussami Abbas SPR RadiologyDocument11 pagesRadiology Quiz Medical Students Workbook: Author: DR Aussami Abbas SPR RadiologyMădălina Ciobotariu100% (1)
- Patterns of Maladaptive BehaviorDocument49 pagesPatterns of Maladaptive BehaviorArrelee MangasparNo ratings yet
- Somatoform DisordersDocument40 pagesSomatoform Disordersamal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Zuku Visual Flashnotes Distemper ExtendedDocument4 pagesZuku Visual Flashnotes Distemper ExtendedShubham HarishNo ratings yet
- Approach To FatigueDocument27 pagesApproach To FatigueBasil HussamNo ratings yet
- Symptom Management in Palliative CareDocument56 pagesSymptom Management in Palliative CareDisala RanaweeraNo ratings yet
- OET 2.0 Speaking and Writing (G & P) PDFDocument222 pagesOET 2.0 Speaking and Writing (G & P) PDFRyu Tse100% (5)
- Depression PowerpointDocument17 pagesDepression PowerpointAlbert Kenneth Lupase UcangNo ratings yet
- D1D2 DietDocument5 pagesD1D2 DietSengupta SuryaNo ratings yet
- 04 Format Manual UpdatedDocument83 pages04 Format Manual UpdatedBurhan Wagh WaghNo ratings yet
- 01 - Fatigue - ExplainedDocument4 pages01 - Fatigue - ExplainedYuni BongNo ratings yet
- Altered Mood States DepressionDocument22 pagesAltered Mood States Depressionmushahida khatoonNo ratings yet
- Mood DisorderDocument19 pagesMood DisorderUmar KhanNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument9 pagesAnxiety DisordersGEETA MOHANNo ratings yet
- Fatigue: Systems, Causes and TreatmentDocument23 pagesFatigue: Systems, Causes and TreatmentMelford BernardNo ratings yet
- Causes and Treatment of DepressionDocument12 pagesCauses and Treatment of DepressionGEETA MOHANNo ratings yet
- Symptoms and Consequences of DepressionDocument5 pagesSymptoms and Consequences of Depressionkeniacastroa12No ratings yet
- DepressionDocument50 pagesDepressionAshutosh MishraNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 - (PART 5) - Learners With Socio Emotional DisorderDocument17 pagesUNIT 3 - (PART 5) - Learners With Socio Emotional DisorderDarlene Joy CambayNo ratings yet
- What Is A Mood Disorder?Document4 pagesWhat Is A Mood Disorder?miit yadavNo ratings yet
- Vinyasa Flow Yoga: Annexure 1Document30 pagesVinyasa Flow Yoga: Annexure 1Manash PratimNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Presentation Sem7Document17 pagesGroup 3 Presentation Sem7super star videos SPsNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Kerja 8Document21 pagesFisiologi Kerja 8Kemal GunawanNo ratings yet
- DEPRESSION (Anaya Singh)Document16 pagesDEPRESSION (Anaya Singh)Arasshjit SandhuNo ratings yet
- Somatoform DisorderDocument30 pagesSomatoform DisorderRujuta BaramateNo ratings yet
- Stress ManagementDocument25 pagesStress ManagementShubham BokoliaNo ratings yet
- Module-4 Mood DisorderDocument4 pagesModule-4 Mood Disordermiit yadavNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document9 pagesModule 3Monu LunaychNo ratings yet
- Accumulated StressDocument1 pageAccumulated Stresshitter.acute0nNo ratings yet
- Lecture INST-100091 2023 10 17 18 42 57Document22 pagesLecture INST-100091 2023 10 17 18 42 57Stuti PatelNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1Itsmeh WaitiNo ratings yet
- Anorexia Nervosa 1Document15 pagesAnorexia Nervosa 1Adilriazkhanachkzai AdilriazkhanachkzaiNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument2 pagesAnxiety DisordersDaniel Sánchez PovedaNo ratings yet
- Muscle FatigueDocument1 pageMuscle FatigueViennie C'nutNo ratings yet
- Name:-Group 1 Class:-ADCP 1 Subject:-Abnormalpsychology Instructor:-Samia Sarwar Topic:-Mood DisordersDocument22 pagesName:-Group 1 Class:-ADCP 1 Subject:-Abnormalpsychology Instructor:-Samia Sarwar Topic:-Mood DisordersSana Zahra GillaniNo ratings yet
- Depression: Brought To You By: Alexandru David-Mihai & Dănilă Gabriela CristinaDocument14 pagesDepression: Brought To You By: Alexandru David-Mihai & Dănilă Gabriela CristinaGabriela DănilăNo ratings yet
- Alcoholism: Alcohol Withdrawal SymptomsDocument8 pagesAlcoholism: Alcohol Withdrawal SymptomsMonnesJNo ratings yet
- Depressio N: Shri Shankaracharya College of Nursing Hudco BhilaiDocument18 pagesDepressio N: Shri Shankaracharya College of Nursing Hudco Bhilaisurbhi thakkarNo ratings yet
- Depressive DisorderDocument54 pagesDepressive DisordersirshakNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Giant Kelompok Taufiq Beri Nia ErikaDocument123 pagesGeriatric Giant Kelompok Taufiq Beri Nia ErikaNurrahmanita AzizaNo ratings yet
- FibromyalgiaDocument5 pagesFibromyalgiadrnareshNo ratings yet
- How To Deal Stress ?: Wi THDocument14 pagesHow To Deal Stress ?: Wi THMalek MokbliNo ratings yet
- Affective Bipolar Disorder Episodes Kini ManiaDocument16 pagesAffective Bipolar Disorder Episodes Kini ManiaDeasy Arindi PutriNo ratings yet
- Copy Somatic Illness ADocument25 pagesCopy Somatic Illness AKriscia NakpilNo ratings yet
- DepressionDocument9 pagesDepressionirene deiparineNo ratings yet
- DepressionDocument23 pagesDepressionDavid FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Depression: Pembimbing: Dr. Iwan Sys. SPKJDocument30 pagesUnderstanding Depression: Pembimbing: Dr. Iwan Sys. SPKJIrene Natalie MamesahNo ratings yet
- Understanding DepressionDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Depressionnic jNo ratings yet
- Fatigue & Tiredness: Done By: Mohammed Z. SharadqahDocument29 pagesFatigue & Tiredness: Done By: Mohammed Z. SharadqahMohammed SharadqahNo ratings yet
- How Can We Know If We Have Depression?Document3 pagesHow Can We Know If We Have Depression?Edgar GilNo ratings yet
- Mental FitnessDocument23 pagesMental FitnessSajida Bibi NoonariNo ratings yet
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)Document11 pagesSeasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)Tahseen MukhtyarNo ratings yet
- Eating DisordersDocument8 pagesEating Disordersاسماء نبيل حسن غريبNo ratings yet
- Coping With Excessive SleepinessDocument6 pagesCoping With Excessive Sleepinessyyfan98No ratings yet
- Lifestyle Diseases and ManagementDocument45 pagesLifestyle Diseases and ManagementSooraj S ChembakasseryNo ratings yet
- CLIN PHAR ACT. No. 13Document85 pagesCLIN PHAR ACT. No. 13Jeyma DacumosNo ratings yet
- Fibromyalgia: by AdamDocument17 pagesFibromyalgia: by AdamMioara HorbaniucNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Issues in StudentsDocument10 pagesMental Health Issues in StudentsJo MalaluanNo ratings yet
- FATIGUE 03012023 093103pmDocument25 pagesFATIGUE 03012023 093103pmNasreen BegumNo ratings yet
- Management of Chronic PainDocument9 pagesManagement of Chronic Pain22SUPS01 ASWIN KNo ratings yet
- Depression: by William, Devon and MishaDocument6 pagesDepression: by William, Devon and MishaMongeko SharinganNo ratings yet
- Mkravatz - Burns Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesMkravatz - Burns Cheat SheetMika ReyesNo ratings yet
- Investigación Artículo. Los Factores de Riesgo para El Consumo de Metanfetamina Entre Los Jóvenes: Una Revisión SistemáticaDocument10 pagesInvestigación Artículo. Los Factores de Riesgo para El Consumo de Metanfetamina Entre Los Jóvenes: Una Revisión SistemáticaCarlos RoqueNo ratings yet
- Kolon CancerDocument14 pagesKolon CancerzalinaNo ratings yet
- Tes Psikotes BUMN - 10 - Bahasa InggrisDocument20 pagesTes Psikotes BUMN - 10 - Bahasa InggrisPrsty 12No ratings yet
- CF Exemplar NURS-FPX4020 Assessment 4Document13 pagesCF Exemplar NURS-FPX4020 Assessment 4Sabahat BashirNo ratings yet
- Defend A Stand On The Issue Day 1Document28 pagesDefend A Stand On The Issue Day 1Lea CabarNo ratings yet
- PERDEVASSL4Document5 pagesPERDEVASSL4Joanna Carla LlorenteNo ratings yet
- Product Presentation BAIHE HDC-CVC-CVC-AMDocument13 pagesProduct Presentation BAIHE HDC-CVC-CVC-AMwahyudi pangestuNo ratings yet
- J.B. Family Case Presentation Group 1Document67 pagesJ.B. Family Case Presentation Group 1Jeno Luis AcubNo ratings yet
- Therapy HypoalbuminemiaDocument10 pagesTherapy HypoalbuminemiaFeny GoenNo ratings yet
- Epithelix FlyersDocument2 pagesEpithelix Flyerskrishgen biosystemsNo ratings yet
- Fall Prevention and OTDocument31 pagesFall Prevention and OTMaya JohnsonNo ratings yet
- High-Flow Nasal Cannula-Protocol For Initiation, Titration and WeaningDocument3 pagesHigh-Flow Nasal Cannula-Protocol For Initiation, Titration and WeaningMahmoud khedrNo ratings yet
- Fluitest Glu HK: Glucose Hexokinase 100+1Document4 pagesFluitest Glu HK: Glucose Hexokinase 100+1akaweadeNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Sanitasi 2Document9 pagesJurnal Sanitasi 2herlianiNo ratings yet
- Seminar 6Document7 pagesSeminar 6Miha Şi AtâtNo ratings yet
- Effects of Raw Vegan Diet On Periodontal and Dental ParametersDocument6 pagesEffects of Raw Vegan Diet On Periodontal and Dental ParametersKarolis KNo ratings yet
- Using Photovoice Methodology To Give Voice To The Health Care Needs of Homeless FamiliesDocument14 pagesUsing Photovoice Methodology To Give Voice To The Health Care Needs of Homeless FamiliesCarlos YeboahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Clinical RadiologyDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Clinical RadiologyMUBIRU SAMUEL EDWARDNo ratings yet
- Asthma PrioDocument2 pagesAsthma PrioHugh Klied ItuhatNo ratings yet
- The Different Perspectives of DisasterDocument3 pagesThe Different Perspectives of DisasterJuliane Rebecca PitlongayNo ratings yet
- The GRE Issue EssayDocument5 pagesThe GRE Issue EssayAlizeh ANo ratings yet
- Lilienfeld1978 PDFDocument4 pagesLilienfeld1978 PDFLis RibeiroNo ratings yet
- KIFHP - CARE - First Interim Narrative ReportDocument39 pagesKIFHP - CARE - First Interim Narrative ReportEliNo ratings yet