0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views28 pagesUnderstanding Protein Translation Process
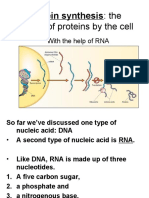
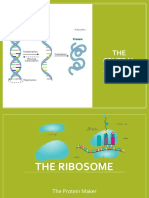
The document describes the process of translation, which involves mRNA carrying protein instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where ribosomes use tRNA to translate mRNA codons into a polypeptide chain of amino acids. The three steps of translation are initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves a ribosome assembling around mRNA and the first tRNA. Elongation adds new amino acids one by one. Termination releases the finished protein when a stop codon is reached.
Uploaded by
Daryl FCCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views28 pagesUnderstanding Protein Translation Process
The document describes the process of translation, which involves mRNA carrying protein instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where ribosomes use tRNA to translate mRNA codons into a polypeptide chain of amino acids. The three steps of translation are initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves a ribosome assembling around mRNA and the first tRNA. Elongation adds new amino acids one by one. Termination releases the finished protein when a stop codon is reached.
Uploaded by
Daryl FCCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd