Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microbiology Lec 2 - Clinical Bacteriology - Gram Positive Cocci
Uploaded by
Rochelle Joyce AradoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microbiology Lec 2 - Clinical Bacteriology - Gram Positive Cocci
Uploaded by
Rochelle Joyce AradoCopyright:
Available Formats
COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW
OF MEDICAL
MICROBIOLOGY
Martin Miguel I. Amor, MD
UP College of Medicine
Class 2009
Topnotch Board Prep
CLINICAL BACTERIOLOGY
GRAM POSITIVE COCCI
Staphylococci
Topnotch Board Prep
Topnotch Board Prep
STAPHYLOCOCCI
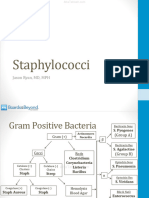
Coagulase Typical Important
Species
Production Hemolysis Features
Protein A on
S. aureus + Beta
surface
Sensitive to
S. epidermidis – None
novobiocin
Resistant to
S. saprophyticus – None
novobiocin
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
CHARACTERISTICS
• Gram-positive cocci in clusters
• -hemolytic yellow or golden
colonies on blood agar
• Catalase-positive
• Coagulase-positive
• Salt-tolerant on MSA
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
• HABITAT
– human nose (ANTERIOR
NARES) and skin
• TRANSMISSION
– direct contact (hands)
– fomites
– contaminated food
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
VIRULENCE FACTORS: Immunomodulators
• Protein A: prevents complement activation
• Coagulase: builds an insoluble fibrin capsule
• Hemolysins (cytotoxins): toxic to
hematopoietic cells
• Leukocidin: specific for white blood cells
• Catalase: detoxifies hydrogen peroxide
• Penicillinase: inactivates penicillin derivatives
Topnotch Board Prep
PRETEST REVIEW
Which virulence enzyme of Staphyloccus aureus
prevents complement activation?
A. Protein A***
B. Coagulase
C. Catalase
D. Leukocidin
E. Penicillinase
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
VIRULENCE FACTORS: Tissue Penetrance
• Hyaluronidase: hydrolyzes hyaluronic acid
• Fibrinolysin (staphylokinase): dissolves fibrin
clots
• Lipase: spread in fat-containing areas of the
body
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
VIRULENCE FACTORS: Toxins
• Exfoliatin: causes epidermal separation
• Enterotoxins (heat-stable): superantigens
causing food poisoning
• Toxic shock syndrome toxin (TSST-1):
superantigen leading to toxic shock syndrome
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Pyogenic
• SKIN and SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONS
– folliculitis, furuncles, carbuncles, cellulitis,
hidradenitis suppurativa, mastitis, surgical site
infections
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Pyogenic
• ACUTE ENDOCARDITIS
– most common cause of acute endocarditis
– native valve (tricuspid valve) in IV drug abusers
Topnotch Board Prep
PRETEST REVIEW
Staphyloccus aureus is the most common cause of
which type of endocarditis?
A. subacute endocarditis
B. acute endocarditis***
C. culture-negative endocarditis
D. prosthetic valve endocarditis
E. native valve endocardits
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Pyogenic
• PNEUMONIA
– nosocomial pneumonia, necrotizing pneumonia,
complicated by empyema, abscess or
pneumatocele
– post-viral pneumonia
Topnotch Board Prep
PRETEST REVIEW
Necrotizing pneumonia with empyema and
pneumatocoele formation is most likely caused by?
A. Klebsiella pneumoniae
B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
C. Staphyloccus aureus***
D. Bacillus anthracis
E. Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Pyogenic
• OSTEOMYELITIS and SEPTIC ARTHRITIS
– from hematogenous spread or local introduction at
wound site
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Toxigenic
• GASTROENTERITIS
– acute onset (4 hrs) of vomiting and
diarrhea due to ingestion of
preformed heat-stable enterotoxin
– source: salad made with mayonnaise
(potato or tuna salad)
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Toxigenic
• SCALDED SKIN SYNDROME
– exfoliatin cleaves desmoglein in
desmosomes
• separation of epidermis at zona
granulosa
– characterized by fever, large
bullae, and an erythematous
macular rash
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Toxigenic
• TOXIC SHOCK SYNDROME
– due to TSST-1
– fever, hypotension, strawberry
tongue, desquamating rash and
multi-organ involvement (>3)
– usually no site of pyogenic
inflammation; blood CS negative
– usual scenario: tampon-using
menstruating women or in patients
with nasal packing for epistaxis
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus aureus
TREATMENT
• methicillin-sensitive SA (MSSA)
– Penicillinase-resistant penicillins (nafcillin, oxacillin,
and dicloxacillin)
• methicillin-resistant SA (MRSA)
– contain altered PBP; DOC is vancomycin
• vancomycin-resistant SA (VRSA)
– DOC is linezolid
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus epidermidis
CHARACTERISTICS
• Gram-positive cocci in clusters
• Catalase-positive
• Coagulase-negative
• Novobiocin-sensitive
• Whitish, non-hemolytic colonies
on blood agar
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus epidermidis
• HABITAT
– normal skin flora
• TRANSMISSION
– autoinfection
– direct contact (hands)
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus epidermidis
PATHOGENESIS
• low-virulence organism
• glycocalyx adheres well to foreign bodies
– prosthetic heart valves
– prosthetic joints
– ventriculoperitoneal shunts
– indwelling catheters
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus epidermidis
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE
• most common cause of
– prosthetic valve endocarditis
– septic arthritis in prosthetic joints
– ventriculoperitoneal shunt infections
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus epidermidis
TREATMENT
• removal of prosthetic device
• over 50% are methicillin-resistant and thus
require vancomycin
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
CHARACTERISTICS
• Gram-positive cocci in clusters
• Catalase-positive
• Coagulase-negative
• Novobiocin-resistant
• Whitish, non-hemolytic colonies
on blood agar
Topnotch Board Prep
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE
• epidemiology
– 2nd most common cause of UTIs in
sexually active women
• clinical findings
– dysuria, pyuria, and bacteriuria
• treatment
– TMP-SMX, quinolones
Topnotch Board Prep
CLINICAL BACTERIOLOGY
GRAM POSITIVE COCCI
Streptococci
Topnotch Board Prep
Topnotch Board Prep
STREPTOCOCCI
Lancefield Typical
Species Diagnostic Features
Group Hemolysis
S. pyogenes A Beta Bacitracin-sensitive
Bacitracin-resistant; hippurate
S. agalactiae B Beta
hydrolyzed
Alpha or beta
E. faecalis D Growth in 6.5% NaCl
or none
Alpha or
S. bovis D No growth in 6.5% NaCl
none
S. pneumoniae NA Alpha Bile-soluble; inhibited by optochin
Not bile-soluble; not inhibited by
Viridans group NA Alpha
optochin
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
CHARACTERISTICS
• Gram-positive cocci in chains
• Catalase-negative
• Beta-hemolytic
• Bacitracin-sensitive
• Lancefield group A
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
• HABITAT
– human throat (oropharynx)
– skin
• TRANSMISSION
– respiratory droplets
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
PATHOGENESIS: Virulence Enzymes
• Hyaluronidase
– degrades hyaluronic acid (spreading factor)
• Streptokinase (fibrinolysin)
– activates plasminogen
• DNase (streptodornase)
– degrades DNA in exudates or necrotic tissue
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
PATHOGENESIS: Toxins
• Erythrogenic toxin
– produces scarlet fever
• Streptolysin O (oxygen-labile)
– highly antigenic, causes AB formation
• Streptolysin S (oxygen-stable)
• Pyogenic exotoxin A
– superantigen similar to TSST
• Exotoxin B
– protease that rapidly destroys tissue
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Pyogenic
• SKIN and SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONS
– Impetigo: perioral vesicular/blistered lesions with
honey-colored crust
Topnotch Board Prep
PRETEST REVIEW
Which among the following diseases caused by GABHS
has a pyogenic etiology?
A. impetigo***
B. rheumatic fever
C. glomerulonephritis
D. necrotizing fasciitis
E. toxic shock syndrome
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Pyogenic
• SKIN and SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONS
– Erysipelas: superficial infection extending into
dermal lymphatics
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Pyogenic
• SKIN and SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONS
– Cellulitis: deeper infection involving
subcutaneous/dermal tissues
• facilitated by hyaluronidase (spreading factor)
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Toxigenic
• SKIN and SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONS
– Necrotizing fasciitis: rapidly progressive infection
of deep subcutaneous tissues
• facilitated by exotoxin B
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Toxigenic
• streptococcal toxic shock
syndrome
– clinically similar but milder
than S. aureus TSS
– due to pyogenic exotoxin A
– recognizable site of pyogenic
inflammation
– blood cultures are often
positive
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Pyogenic
• PHARYNGITIS
– most common bacterial
cause of sore throat
– inflammation, exudate,
fever, leukocytosis, and
tender CLAD
– pyogenic complications:
abscess, otitis, sinusitis,
meningitis
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Toxigenic
• SCARLET FEVER
– postpharyngitic
– due to erythrogenic toxin, seen
in lysogenized strains
– fever, strawberry tongue,
centrifugal rash (sandpaper-
like), Pastia’s lines,
desquamation
– Dick test for susceptibility
Topnotch Board Prep
PRETEST REVIEW
Which test evaluates for susceptibility to scarlet fever?
A. Elek test
B. Dick test***
C. Frei test
D. Pastia test
E. PPD test
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Immunologic
• ACUTE RHEUMATIC FEVER
– postpharyngitic
– cross-reacting antibodies to M
proteins and antigens of joint,
heart, and brain tissue
– JONES CRITERIA:
• migratory polyarthritis
• pancarditis
• erythema marginatum
• Sydenham chorea
• subcutaneous nodules
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Immunologic
• GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
– post-impetigo OR
postpharyngitic
– M protein incites immune
complex deposition on the
glomerular basement membrane
– ssx: hypertension, periorbital
edema, hematuria
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pyogenes
TREATMENT
• Penicillin G
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus agalactiae
CHARACTERISTICS
• Gram-positive cocci in chains
• Catalase-negative
• Beta-hemolytic
• Bacitracin-resistant
• Lancefield group B
• hydrolyze hippurate
• CAMP test–positive
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus agalactiae
HABITAT and TRANSMISSION
• HABITAT
– Vagina
• TRANSMISSION
– Transvaginal
– Transplacental
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus agalactiae
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE: Pyogenic
• urinary tract infection in pregnant women
• neonatal pneumonia, sepsis and meningitis
– most common cause
• endometritis
Topnotch Board Prep
PRETEST REVIEW
What is the most common cause of neonatal
pneumonia?
A. GABHS
B. C. trachomatis
C. S. pneumoniae
D. S. pyogenes
E. S. agalactiae***
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus agalactiae
TREATMENT
• Penicillin G
Topnotch Board Prep
group D streptococci
CHARACTERISTICS
• Gram-positive cocci in chains
• Catalase-negative
• Gamma hemolytic colonies
• Lancefield group D
• Grows in 6.5% NaCl
• hydrolyzes esculin in BEA
• positive pyrazine amidase (PYR)
test
Topnotch Board Prep
group D streptococci
HABITAT and TRANSMISSION
• HABITAT
– human colon
– urethra and female genital tract
can be colonized
• TRANSMISSION
– may enter bloodstream during
GIT or GUT surgery
Topnotch Board Prep
group D streptococci
SPECTRUM OF DISEASES
• UTIs due to indwelling urinary catheters and
urinary tract instrumentation
• biliary tract infections
• endocarditis in patients who underwent GIT
surgery due to E. faecalis
• marantic endocarditis in patients with
abdominal malignancy due to S. bovis
Topnotch Board Prep
PRETEST REVIEW
A 54/M with colon cancer develops subacute onset of
fever with rigors and chills. Auscultation reveals a
holosystolic murmur. What is the most likely etiology of
infective endocarditis in this patient?
A. Enterococcus faecalis
B. viridans streptococci
C. Streptococcus bovis***
D. Staphylococcus aureus
E. Kingella kingae
Topnotch Board Prep
group D Streptococci
TREATMENT
• Penicillin or vancomycin plus gentamicin
• Linezolid for vancomycin-resistant strains
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pneumoniae
CHARACTERISTICS
• Gram-positive "lancet-shaped"
cocci in pairs or chains
• Catalase-negative
• Alpha-hemolytic
• Bile and optochin-sensitive
• positive Quellung reaction
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pneumoniae
HABITAT and TRANSMISSION
• habitat is upper respiratory tract
• transmission via respiratory droplets
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pneumoniae
PATHOGENESIS
• capsule retards phagocytosis
– encapsulated bacteria:
• S. pneumoniae
• H. influenzae
• N. meningitidis
• K. pneumoniae
• IgA protease for colonization
• c-substance reacts with CRP
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pneumoniae
SPECTRUM OF DISEASES: Pyogenic
• PNEUMONIA
– most common cause of CAP
– sudden chill, fever, productive
cough, and pleuritic chest pain
– lobar pattern
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pneumoniae
SPECTRUM OF DISEASES: Pyogenic
• otitis media, sinusitis,
meningitis
– most common cause
– skull fracture with spinal fluid
leakage from nose
predisposes to meningitis
• septic shock
– splenectomy predisposes to
sepsis
Topnotch Board Prep
Streptococcus pneumoniae
TREATMENT and PREVENTION
• TREATMENT
– Penicillin G
• PREVENTION
– polyvalent (23-type) polysaccharide vaccine
– conjugated vaccine: pneumococcal polysaccharide
coupled with carrier protein (diphtheria toxoid)
Topnotch Board Prep
Viridans streptococci
CHARACTERISTICS
• Gram-positive cocci in chains
• Catalase-negative
• Alpha-hemolytic
• Bile and optochin-resistant
Topnotch Board Prep
Viridans streptococci
HABITAT and TRANSMISSION
• habitat is oropharynx
• enters bloodstream during dental procedures
Topnotch Board Prep
Viridans streptococci
PATHOGENESIS
• glycocalyx enhances adhesion to damaged
heart valves
• protected from host defenses within
vegetations
Topnotch Board Prep
Viridans streptococci
SPECTRUM OF DISEASE
• S. mutans, for dental caries
• S. sanguis, for subacute
bacterial endocarditis (SBE)
– most common cause of
subacute and native valve
endocarditis
• S. intermedius, for brain
abscesses
Topnotch Board Prep
Viridans streptococci
TREATMENT
• Penicillin G with or without an aminoglycoside
Topnotch Board Prep
END OF SECTION 2
Topnotch Board Prep
You might also like
- Skills Checklist-Critical CareDocument3 pagesSkills Checklist-Critical CareRom Anog100% (4)
- The Six Killer DiseaseDocument26 pagesThe Six Killer DiseaseFrancis Luke63% (8)
- Systemic BacteriologyDocument495 pagesSystemic BacteriologyAkash KaranwalNo ratings yet
- Tests of Hypothesis Single MeanDocument5 pagesTests of Hypothesis Single MeanMhar G-i SalalilaNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy for Pediatric Weight ManagementDocument7 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy for Pediatric Weight Managementdakota100% (1)
- Strepto ClassDocument34 pagesStrepto ClassAbcdefg HijklNo ratings yet
- Chapter15 StreptococciDocument66 pagesChapter15 StreptococciNursheda Abangon AzisNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae Staphylococci Faculty: Dr. Alvin FoxDocument32 pagesStreptococcus Pneumoniae Staphylococci Faculty: Dr. Alvin Foxdanish sultan100% (1)
- 2) BacteriologyDocument94 pages2) BacteriologyMadhulikaNo ratings yet
- Streptococci: Zainab Abdul Jabar AldhaherDocument32 pagesStreptococci: Zainab Abdul Jabar Aldhaherمروه عماد عيسىNo ratings yet
- Identification of S. pneumoniae and Differentiation from Other StreptococciDocument21 pagesIdentification of S. pneumoniae and Differentiation from Other Streptococciavnish5203sdNo ratings yet
- MicroPara Compre Review 2021 - Dr. HemedezDocument65 pagesMicroPara Compre Review 2021 - Dr. HemedezStephenMontoyaNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Bacteria Types and DiseasesDocument51 pagesGram Positive Bacteria Types and DiseasesDzachary13100% (1)
- Bacteria Charts - ComprehensiveDocument6 pagesBacteria Charts - ComprehensiveDiMa Marsh100% (1)
- Micro CDBDocument9 pagesMicro CDBLicensed to HealNo ratings yet
- CoryneformDocument38 pagesCoryneformتجربة أولىNo ratings yet
- Gram + ve cocci in pairs or chains, causes variety of infectionsDocument46 pagesGram + ve cocci in pairs or chains, causes variety of infectionsmulatumeleseNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci Sem 1 1Document45 pagesGram Positive Cocci Sem 1 1Charmaine Corpuz Granil100% (1)
- Gram Positive - Cocci PDFDocument4 pagesGram Positive - Cocci PDFJasmine BunaoNo ratings yet
- 1 StaphylococciDocument26 pages1 StaphylococciAyeshaNo ratings yet
- StreptococciDocument43 pagesStreptococciAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus pneumoniae and other streptococciDocument24 pagesStreptococcus pneumoniae and other streptococciPearl NoconNo ratings yet
- StaphylococcusDocument28 pagesStaphylococcusBasma MohamedNo ratings yet
- Common Skin and Soft Tissue InfectionsDocument8 pagesCommon Skin and Soft Tissue InfectionsAdel mohammadNo ratings yet
- Family of StreptococcaceaeDocument10 pagesFamily of StreptococcaceaeLovely B. AlipatNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci Identification and DifferentiationDocument45 pagesGram Positive Cocci Identification and DifferentiationCharmaine Corpuz GranilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 StaphylococcusDocument40 pagesChapter 21 Staphylococcusyixecix709No ratings yet
- 1-Pyogenic CocciDocument77 pages1-Pyogenic CocciMooNy LibyaNo ratings yet
- Staphylococci & MicrococciDocument52 pagesStaphylococci & Micrococcihoneylemon.coNo ratings yet
- Streptococci and Enterococci and OthersDocument11 pagesStreptococci and Enterococci and OthersthedarkwingNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Special Report: General Template for Characterizing Important MicrobesDocument68 pagesMicrobiology Special Report: General Template for Characterizing Important MicrobesrefuapalackyNo ratings yet
- Salmonella: DR - Vasanthi .R Professor Dept Microbiology ChriDocument52 pagesSalmonella: DR - Vasanthi .R Professor Dept Microbiology ChrividhyashreeNo ratings yet
- Medically Important Bacteria - PPTX Filename UTF-8 Medically Important BacDocument77 pagesMedically Important Bacteria - PPTX Filename UTF-8 Medically Important Bacjethreel diosoNo ratings yet
- Bacillus and Clostridium Species: Spore-Forming Gram Positive BacilliDocument13 pagesBacillus and Clostridium Species: Spore-Forming Gram Positive BacilliDennis ValdezNo ratings yet
- Anubhav Rai StaphylococcusDocument34 pagesAnubhav Rai StaphylococcusHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Report PathoDocument70 pagesReport PathoRgm UyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Pathogenic Gram Positive CocciDocument76 pagesChapter 2 Pathogenic Gram Positive CocciMubaarįk ÝãřeNo ratings yet
- Streptococci: S. Pyogenes S. AgalactiaeDocument9 pagesStreptococci: S. Pyogenes S. AgalactiaeChristine BuenNo ratings yet
- STAPHYLOCOCCIDocument26 pagesSTAPHYLOCOCCIDaud Rehman KhanNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive CocciDocument55 pagesGram Positive CocciAyat MostafaNo ratings yet
- StreptococciDocument10 pagesStreptococciGea MarieNo ratings yet
- Staphylococci AtfDocument22 pagesStaphylococci Atftahaijaz89No ratings yet
- Streptococcus and EnterococcusDocument7 pagesStreptococcus and EnterococcusSharmaine TrangiaNo ratings yet
- Gram Stains and Characteristics of Major Anaerobic BacteriaDocument73 pagesGram Stains and Characteristics of Major Anaerobic BacteriaMaria ClaraNo ratings yet
- 11 - Anaerobic BacteriaDocument68 pages11 - Anaerobic BacteriaJohanna Kate DiestroNo ratings yet
- DR Jimoh - Enterobacteriaceae - LectureDocument42 pagesDR Jimoh - Enterobacteriaceae - LectureSUfyan RaZiNo ratings yet
- Lecture PP5&6 StaphylococcusDocument44 pagesLecture PP5&6 StaphylococcusVera AkmiliaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Gram Positive CocciDocument9 pages1.1 Gram Positive CocciJustine Mel Concepcion IlardeNo ratings yet
- Gram +/-Cocci: Thao Nguyen, PHD Thao - Nguyen@Ttu - Edu.VnDocument98 pagesGram +/-Cocci: Thao Nguyen, PHD Thao - Nguyen@Ttu - Edu.VnNguyen Phan TrongNo ratings yet
- Coagulase +ve Coagulase - VeDocument41 pagesCoagulase +ve Coagulase - Veshrutik91No ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Aureus: Ali Somily MD, FRCPCDocument32 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus: Ali Somily MD, FRCPCraanja2No ratings yet
- S. Aureus, Cons: S.Epidermidis, Cons: S.SaprophyticusDocument14 pagesS. Aureus, Cons: S.Epidermidis, Cons: S.SaprophyticusMugiNo ratings yet
- CB Part 3Document76 pagesCB Part 3Mohammad MambuayNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument62 pagesFinalChristian AriasNo ratings yet
- GIT ProblemDocument104 pagesGIT Problemfelixhalim39No ratings yet
- ANAEROBES - Narayan Parajul - MMIHS III RD YearDocument42 pagesANAEROBES - Narayan Parajul - MMIHS III RD YearRajkishor YadavNo ratings yet
- StaphylococcusDocument4 pagesStaphylococcusipad backupNo ratings yet
- StreptococciDocument40 pagesStreptococciGjfyigyivNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus, Entrococcus and Other Catalayse Negative GramDocument15 pagesStreptococcus, Entrococcus and Other Catalayse Negative GramKeen ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus, Enterococcus, and Other Catalase-Negative, Gram - Positive CocciDocument75 pagesStreptococcus, Enterococcus, and Other Catalase-Negative, Gram - Positive CocciJhenille SalasNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Gram Negative SPPDocument9 pagesMiscellaneous Gram Negative SPPTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Non-Spore Forming Gram-Positive BacilliDocument31 pagesAerobic Non-Spore Forming Gram-Positive BacilliCagar Irwin TaufanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lec 1 - Basic BacteriologyDocument88 pagesMicrobiology Lec 1 - Basic BacteriologyRochelle Joyce AradoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 9485Document7 pagesRepublic Act 9485Rochelle Joyce AradoNo ratings yet
- Topnotch Parasitology Super Table by DR - Yns PereyraDocument50 pagesTopnotch Parasitology Super Table by DR - Yns PereyraRochelle Joyce AradoNo ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGYDocument1 pagePARASITOLOGYRochelle Joyce AradoNo ratings yet
- Physiology FinalADocument18 pagesPhysiology FinalAvaegmundig100% (1)
- Biochemistry FinalDocument60 pagesBiochemistry FinalAndrassy Twinkle Alinea100% (2)
- Chapter 1 PathoDocument37 pagesChapter 1 PathoRochelle Joyce AradoNo ratings yet
- Planchon 1994Document10 pagesPlanchon 1994Rochelle Joyce AradoNo ratings yet
- The History of Grandmothers in The African American Community - Jillian JimenezDocument30 pagesThe History of Grandmothers in The African American Community - Jillian JimenezClemente PennaNo ratings yet
- 22-23 Pan Sloan Canyon Student Parent HandbookDocument81 pages22-23 Pan Sloan Canyon Student Parent Handbookapi-470026636No ratings yet
- JMP 2023 Wash HouseholdsDocument172 pagesJMP 2023 Wash Householdsmadiha.arch24No ratings yet
- Disclosure of Research InformationDocument64 pagesDisclosure of Research InformationThe Hastings CenterNo ratings yet
- Flow rate uniformity of TARAL 200 PITON TURBO sprayer for pest controlDocument4 pagesFlow rate uniformity of TARAL 200 PITON TURBO sprayer for pest controlAndreea DiaconuNo ratings yet
- RASA BooksDocument57 pagesRASA BooksArathy Krishna100% (1)
- Adjuvant Analgesics (2015) PDFDocument177 pagesAdjuvant Analgesics (2015) PDFsatriomega100% (1)
- OCP - 15 - GrindingDocument2 pagesOCP - 15 - GrindingNagendra Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cam CMD 2022 Presentation SepDocument156 pagesCam CMD 2022 Presentation SepLeBron JamesNo ratings yet
- Reducing AgeismDocument2 pagesReducing AgeismAntónio LealNo ratings yet
- Report On Riverside County Coroner's OfficeDocument15 pagesReport On Riverside County Coroner's OfficeThe Press-Enterprise / pressenterprise.comNo ratings yet
- Food and Beverages Shoes and Clothes Beauty Products Services EntertainmentDocument5 pagesFood and Beverages Shoes and Clothes Beauty Products Services EntertainmentRonibeMalinginNo ratings yet
- 서초구 고교기출 4회차Document7 pages서초구 고교기출 4회차ᄋᄋNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY: Lidocaine, Methocarbamol, MetaxaloneDocument28 pagesDRUG STUDY: Lidocaine, Methocarbamol, MetaxaloneLucas, Darah Angelica A.No ratings yet
- FdarDocument4 pagesFdarCecile DavantesNo ratings yet
- CUSTOM - LETTER - RPT - Custom Tailored Email - REV C - v5Document2 pagesCUSTOM - LETTER - RPT - Custom Tailored Email - REV C - v5Aaron De VeraNo ratings yet
- The Tiger King PDFDocument52 pagesThe Tiger King PDFAnonymous OITciJmAJ4100% (2)
- Thesis PPT For VivaDocument62 pagesThesis PPT For VivaNamrata DahakeNo ratings yet
- CPSP Dissertation Data SheetDocument8 pagesCPSP Dissertation Data SheetPayToWritePaperSingapore100% (1)
- GuideMia Sample Report - EnglishDocument9 pagesGuideMia Sample Report - Englishzhiao liuNo ratings yet
- Sip InformationDocument111 pagesSip InformationakashNo ratings yet
- Quick RemapDocument32 pagesQuick RemapmollitonyNo ratings yet
- And Netflix Show, Ask The Storybots, Now Star in Their Own Board Books!Document2 pagesAnd Netflix Show, Ask The Storybots, Now Star in Their Own Board Books!kagnejukkeNo ratings yet
- Revision 2Document7 pagesRevision 2Maina JonnNo ratings yet
- Neurodegenerative Disease Among Male Elite Football (Soccer) Players in Sweden: A Cohort Study - TheDocument3 pagesNeurodegenerative Disease Among Male Elite Football (Soccer) Players in Sweden: A Cohort Study - Thepitufi11No ratings yet
- What Is MindfulnessDocument4 pagesWhat Is MindfulnessPongal PunithaNo ratings yet