Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DC Ac
Uploaded by
Dr.K.Krishna Veni Professor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views41 pagesOriginal Title
DC-AC
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views41 pagesDC Ac
Uploaded by
Dr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 41
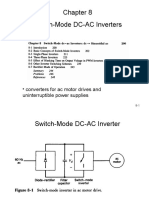
Chapter 8
Switch-Mode DC-AC Inverters
• converters for ac motor drives and
uninterruptible power supplies
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-1
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Switch-Mode DC-AC Inverter
• Block diagram of a motor drive where the power
flow is unidirectional
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-2
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Switch-Mode DC-AC Inverter
• Block diagram of a motor drive where the power
flow can be bi-directional
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-3
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Switch-Mode DC-AC Inverter
• Four quadrants of operation
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-4
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
One Leg of a Switch-Mode DC-AC Inverter
• The mid-point shown is fictitious
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-5
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Synthesis of a Sinusoidal Output by PWM
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-6
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Details of a Switching Time Period
• Control voltage can be assumed constant during
a switching time-period
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-7
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Harmonics in the DC-AC Inverter Output
Voltage
• Harmonics appear around the carrier frequency
and its multiples
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-8
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Harmonics due to Over-modulation
• These are harmonics of the fundamental
frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-9
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Output voltage Fundamental as a Function
of the Modulation Index
• Shows the linear and the over-modulation
regions; square-wave operation in the limit
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-10
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Square-Wave Mode of Operation
• Harmonics are of the fundamental frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-11
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Half-Bridge Inverter
• Capacitors provide the mid-point
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-12
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Single-Phase Full-Bridge DC-AC Inverter
• Consists of two inverter legs
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-13
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
PWM to Synthesize Sinusoidal Output
• The dotted curve is the desired output; also the
fundamental frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-14
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Analysis assuming Fictitious Filters
• Small fictitious filters eliminate the switching-
frequency related ripple
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-15
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
DC-Side Current
• Bi-Polar Voltage switching
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-16
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Output Waveforms:
Uni-polar Voltage
Switching
• Harmonic
components around
the switching
frequency are absent
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-17
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
DC-Side Current in a Single-Phase Inverter
• Uni-polar voltage switching
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-18
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Sinusoidal Synthesis by Voltage Shift
• Phase shift allows voltage cancellation to
synthesize a 1-Phase sinusoidal output
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-19
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Single-Phase Inverter
• Analysis at the fundamental frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-20
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Square-Wave and PWM Operation
• PWM results in much smaller ripple current
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-21
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Push-Pull Inverter
• Low Voltage to higher output using square-wave
operation
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-22
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Three-Phase Inverter
• Three inverter legs; capacitor mid-point is
fictitious
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-23
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Three-
Phase
PWM
Waveforms
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-24
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Three-Phase Inverter Harmonics
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-25
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Three-Phase Inverter Output
• Linear and over-modulation ranges
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-26
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Three-Phase Inverter: Square-Wave Mode
• Harmonics are of the fundamental frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-27
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Three-Phase Inverter: Fundamental
Frequency
• Analysis at the fundamental frequency can be
done using phasors
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-28
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Square-Wave and PWM Operation
• PWM results in much smaller ripple current
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-29
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
DC-Side Current in a Three-Phase Inverter
• The current consists of a dc component and the
switching-frequency related harmonics
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-30
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Square-Wave Operation
• devices conducting are indicated
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-31
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
PWM Operation
• devices conducting are indicated
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-32
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Short-Circuit States in PWM Operation
• top group or the bottom group results in short
circuiting three terminals
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-33
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Effect of Blanking
Time
• Results in
nonlinearity
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-34
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Effect of Blanking Time
• Voltage jump when the current reverses direction
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-35
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Effect of Blanking Time
• Effect on the output voltage
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-36
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Programmed Harmonic Elimination
• Angles based on the desired output
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-37
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Tolerance-Band Current Control
• Results in a variable frequency operation
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-38
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Fixed-Frequency Operation
• Better control is possible using dq analysis
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-39
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Transition from Inverter to Rectifier Mode
• Can analyze based on the fundamental-
frequency components
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-40
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
Summary of DC-AC Inverters
• Functional representation in a block-diagram form
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 8 Switch-Mode DC- 8-41
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Sinusoidal AC Inverters
You might also like
- Gojek Take Home Test Assessment - Achmad RamlanDocument10 pagesGojek Take Home Test Assessment - Achmad RamlanAnonym AnonNo ratings yet
- Mohan - Power Electronics Converters Applications and Design 3rd - EditionDocument736 pagesMohan - Power Electronics Converters Applications and Design 3rd - EditionDan Alexandru Neagu100% (1)
- Article 147-148 of The Family CodeDocument2 pagesArticle 147-148 of The Family CodeJona Addatu100% (2)
- Four Quadrant Operation of DC Drives: - Dual ConvertersDocument12 pagesFour Quadrant Operation of DC Drives: - Dual ConvertersDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Machine Manual - TPSys - 2.4Document276 pagesMachine Manual - TPSys - 2.4Денис ФроловNo ratings yet
- Chap 8 Mohan (Laminas) PDFDocument41 pagesChap 8 Mohan (Laminas) PDFfer6669993No ratings yet
- 1LN InvertersDocument49 pages1LN Invertersankit.chandra.eee21No ratings yet
- Ch6 PDFDocument39 pagesCh6 PDFanasNo ratings yet
- Ch7 DC-DC Switch Mode ConvertersDocument34 pagesCh7 DC-DC Switch Mode ConvertersjimyaoNo ratings yet
- DC DCDocument34 pagesDC DCDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converters For Switch-Mode DC Power Supplies and Dc-Motor DrivesDocument34 pagesDC-DC Converters For Switch-Mode DC Power Supplies and Dc-Motor DrivesDina GaranNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: P.Karthikeyan, BE (EEE), SmecDocument19 pagesPower Electronics: P.Karthikeyan, BE (EEE), SmecKrishnamoorthy AyyasamiNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document38 pagesCH 10anasNo ratings yet
- CH 8Document41 pagesCH 8Dina GaranNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 EDDocument22 pagesUnit - 3 EDMayank GoyalNo ratings yet
- Switch-Mode DC-AC Inverters: Converters For Ac Motor Drives and Uninterruptible Power SuppliesDocument19 pagesSwitch-Mode DC-AC Inverters: Converters For Ac Motor Drives and Uninterruptible Power SuppliesnandhakumarmeNo ratings yet
- How Does A Power Inverter Work?: Inverters Can Also Be Used With Transformers To Change A Certain DC Input Voltage IntoDocument15 pagesHow Does A Power Inverter Work?: Inverters Can Also Be Used With Transformers To Change A Certain DC Input Voltage Intoshubham choudharyNo ratings yet
- Power InverterDocument11 pagesPower Inverterriz2010No ratings yet
- ELG4139L1PEDocument30 pagesELG4139L1PERudra MishraNo ratings yet
- DC Drives: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 2-1Document20 pagesDC Drives: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 2-1Engr Umar AshrafNo ratings yet
- Power Presentation On Design of InverterDocument18 pagesPower Presentation On Design of Inverteraa bbNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Converters, Applications, and DesignDocument736 pagesPower Electronics Converters, Applications, and Designaaaravin100% (7)
- DC Motor Drives: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 2-1Document21 pagesDC Motor Drives: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 2-1Abir LovesickNo ratings yet
- Switch-Mode DC-AC Inverters: Converters For Ac Motor Drives and Uninterruptible Power SuppliesDocument19 pagesSwitch-Mode DC-AC Inverters: Converters For Ac Motor Drives and Uninterruptible Power SuppliesHartoyo MpNo ratings yet
- Lecture Three - Review of DC-AC InvertersDocument87 pagesLecture Three - Review of DC-AC InvertersShimelisNo ratings yet
- Electrical MotorDocument30 pagesElectrical Motordayat_ridersNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document45 pagesCH 9api-3705260No ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument59 pagesPower ElectronicsbojjasaigowthamiNo ratings yet
- VP Electronics Winter Training Presentation: Report By: Urvashi KhandelwalDocument25 pagesVP Electronics Winter Training Presentation: Report By: Urvashi KhandelwalLenowahira DillemanowaryNo ratings yet
- SUBTOPIC 1 - Power ElectronicsDocument29 pagesSUBTOPIC 1 - Power ElectronicsJasperNo ratings yet
- Ideal and Practical Inverter Have Sinusoidal and No-Sinusoidal Waveforms at Output RespectivelyDocument16 pagesIdeal and Practical Inverter Have Sinusoidal and No-Sinusoidal Waveforms at Output RespectivelyThanksNo ratings yet
- InvertersDocument21 pagesInvertersjorgenovachrolloNo ratings yet
- Guest Lecture: DC and AC Motor DrivesDocument38 pagesGuest Lecture: DC and AC Motor DrivesveenaNo ratings yet
- Rotary Converter - WikipediaDocument8 pagesRotary Converter - Wikipediasonu kumarNo ratings yet
- DC and AC Motor Drives: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 2-1Document11 pagesDC and AC Motor Drives: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 2-1Aslam MohammadNo ratings yet
- Inverters: Inverters Take DC From A Battery (Etc) and Convert It Electronically To Ac PowerDocument13 pagesInverters: Inverters Take DC From A Battery (Etc) and Convert It Electronically To Ac PowerAbu-Abdullah SameerNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Chapter 4: Switch-Mode Dc-Ac InvertersDocument71 pagesPower Electronics: Chapter 4: Switch-Mode Dc-Ac InvertersAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Electric Drives Part 2Document18 pagesElectric Drives Part 2Srujana TallaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2Jay EyNo ratings yet
- Ned Mohan Power Electronics CH5 SlidesDocument40 pagesNed Mohan Power Electronics CH5 SlidesTayyab Hussain100% (1)
- Ch17 PDFDocument18 pagesCh17 PDFjoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument68 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsLovely CastilloNo ratings yet
- 15EC73Document307 pages15EC73KN DEEPSHINo ratings yet
- PSD..UNIT 3..motor DrivesDocument38 pagesPSD..UNIT 3..motor Drivessatish reddyNo ratings yet
- Power Semi Conductor DrivesDocument38 pagesPower Semi Conductor Drivesdeepu4303No ratings yet
- AC Generator: Group 3 - CE-2109Document47 pagesAC Generator: Group 3 - CE-2109Krizelle ManaloNo ratings yet
- Nueva Vida Rectificadores D PotenciaDocument10 pagesNueva Vida Rectificadores D PotenciaprimekronosNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Chapter 2 (BRB)Document3 pages2.1 Chapter 2 (BRB)Anil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- DC and AC Motor Drives: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 2-1Document38 pagesDC and AC Motor Drives: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 2-1nightfurryify0% (1)
- Input Voltage: High Voltage Direct CurrentDocument2 pagesInput Voltage: High Voltage Direct CurrentKarteekNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Boost Converter Applied For DC Motor DriveDocument51 pagesImplementation of Boost Converter Applied For DC Motor DriveLeri FirdianNo ratings yet
- Lab Presentation: Electrical Drive Systems Presenter: Azmat Ali Matriculation Num: 441430 Topics: AC Motor & Full Wave RectifierDocument22 pagesLab Presentation: Electrical Drive Systems Presenter: Azmat Ali Matriculation Num: 441430 Topics: AC Motor & Full Wave RectifierAhmed IshaqNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsFrom EverandHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsNo ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Analog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignFrom EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNo ratings yet
- Digital Power Electronics and ApplicationsFrom EverandDigital Power Electronics and ApplicationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- SMPSDocument59 pagesSMPSDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of BrakingDocument19 pages3 Types of BrakingDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Chopper: Class-C or Type-CDocument42 pagesChopper: Class-C or Type-CDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorNo ratings yet
- 1.course File - POWER SEMICONDUCTOR DRIVESDocument14 pages1.course File - POWER SEMICONDUCTOR DRIVESDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Chopper Fed Drives Updated18-10-2021Document44 pagesChopper Fed Drives Updated18-10-2021Dr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Control NewDocument47 pagesClosed Loop Control NewDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorNo ratings yet
- BEE Unit-IDocument25 pagesBEE Unit-IDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Security Awareness TrainingDocument25 pagesSecurity Awareness TrainingMehul dubey100% (1)
- APFU Deputation NotificationDocument7 pagesAPFU Deputation Notificationteja prasadNo ratings yet
- Gonzales V Atty CabucanaDocument2 pagesGonzales V Atty CabucanaButch Sui Generis100% (1)
- Sheronne Blasi Calls On Marty Heyen To ResignDocument1 pageSheronne Blasi Calls On Marty Heyen To ResignStatesman JournalNo ratings yet
- Mobilization and Empowerment of Marginalized Women in South AsiaDocument32 pagesMobilization and Empowerment of Marginalized Women in South AsiaaalsNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment Report On: Corrugated Galvanized Steel Sheet, Steel Profile and Insulated Panel Production ProjectDocument80 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment Report On: Corrugated Galvanized Steel Sheet, Steel Profile and Insulated Panel Production ProjectMekon-Engineering Mke100% (1)
- Affidavit of Change Color - EmeperadorDocument2 pagesAffidavit of Change Color - Emeperadorjoonee09No ratings yet
- BIR - Remittance of CWT (Form 1606) Should Be in The Name of The Buyer - JUAN PATAG REAL ESTATEDocument2 pagesBIR - Remittance of CWT (Form 1606) Should Be in The Name of The Buyer - JUAN PATAG REAL ESTATERoy RitagaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance in IndiaDocument29 pagesCorporate Governance in IndiaMH PHOTO CREATIVENo ratings yet
- Causes of The RevoltDocument9 pagesCauses of The RevoltSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Medicare To Eliminate Appeals Backlog Within 4 Years, HHS Tells JudgeDocument30 pagesMedicare To Eliminate Appeals Backlog Within 4 Years, HHS Tells JudgeHLMeditNo ratings yet
- BnwasDocument3 pagesBnwasClifford DmelloNo ratings yet
- The History of Rome - Volume 1 (Theodor Mommsen) PDFDocument649 pagesThe History of Rome - Volume 1 (Theodor Mommsen) PDFJ ValeriusNo ratings yet
- Reynard Prather Govt Sentencing MemoDocument8 pagesReynard Prather Govt Sentencing MemoEmily BabayNo ratings yet
- Biography of Hazrat Sahwi Shah Sahib HyderabadDocument6 pagesBiography of Hazrat Sahwi Shah Sahib HyderabadMohammed Abdul Hafeez, B.Com., Hyderabad, IndiaNo ratings yet
- TAX Cases - General Principles - Tax EvasionDocument65 pagesTAX Cases - General Principles - Tax EvasionJunRobotboiNo ratings yet
- Randall - Gender Politics and The State PDFDocument6 pagesRandall - Gender Politics and The State PDFMarco NavarroNo ratings yet
- LBP Vs TapuladoDocument3 pagesLBP Vs Tapuladojun junNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines vs. Kerry Lao OngDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines vs. Kerry Lao OnglearningNo ratings yet
- Account SettingsDocument19 pagesAccount SettingsPatrick Brillante DE Leon0% (5)
- E PaymentsDocument33 pagesE PaymentskenNo ratings yet
- Gonzales v. KatigbakDocument2 pagesGonzales v. KatigbakdelayinggratificationNo ratings yet
- Mcdo RatiosDocument3 pagesMcdo RatiosMykaNo ratings yet
- Data On The UndocumentedDocument4 pagesData On The UndocumentedChris SmithNo ratings yet
- A. Unlawful Detention or ImprisonmentDocument2 pagesA. Unlawful Detention or ImprisonmentzurianimNo ratings yet
- The Cagayan Railway Extension ProjectDocument8 pagesThe Cagayan Railway Extension ProjectDeus NobiscumNo ratings yet
- IRDocument18 pagesIRMALAVIKA JAYAKRISHNAN P T 1827039No ratings yet