Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hand and Wrist Disorders
Uploaded by
2020033390 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views25 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views25 pagesHand and Wrist Disorders
Uploaded by
202003339Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
By
Dr. Mahmoud Yasser, MD
Alex University
Bony anatomy of the wrist
Wrist arthritis
• Causes
-Degenerative OA (primary)
-Post traumatic due to carpal
instability.
-inflammatory as Rh arthritis.
-secondary to congenital anomalis
- Idiopathic
Diagnosis
• Symptoms and signs • Investigations
Pain Plain x rays
Tenderness CT scan
Limitation of movement MRI
Deformity (in advanced) Wrist arthroscopy
Treatment
• Conservative (Mild to moderate)
Non steroidal anti inflammatory
Steroid injection
Wrist support
Work modification
Physical therapy
• surgical
Limited fusion
Wrist arthrodesis
kienbock’s disease
• Avascular necrosis of the lunate • Symtoms
Pain in wrist
bone leading to abnormal
Tenderness
carpal motion and wrist
Limitation of movement
osteoarthritis. Joint effusion
• Cause is unknown but history of Deformity in advanced arthritis
trauma may be a risk factor. • Invistigation
-Plain x ray in advanced stage reveled collapse of
• Progressive and potentially the lunate, carpal instability and arthritis.
debilitating condition if -CT scan if collapse has already occured
unrecognized and untreated. -MRI in early stage
-bone scan in early stage (very sensitive).
Early stage
Untreated and advanced stages
• Surgical management
Treatment Before collapse -----vascularized
bone grafting for revascularization
• Conservative in
-Old age
-Younger than 15y
-In very early stage and mostly will
need surgical intervention.
Non steroidal anti inflammatory
Steroid injection
Wrist support
Work modification
Physical therapy
After collapse and before advanced arthritis
• Proximal row carpectomy
-The best results
-Removal of 3 (scaphoid, lunate
triquetrum) bones of proximal row
- Articulation of capitate to radius
- Aims to delay wrist fusion
- Will end in the future by wrist
arthrodesis
In late and advanced arthritis
• Wrist fusion (standard) • Total wrist arthroplasty (very bad
results)
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)
• The most common compressive neuropathy
• Pathologic inflamed synovium the most
common cause of idiopathic CTS.
• Risk factors
- Females
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Hypothyrodism
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Smoking
- Alcoholism
- Advanced age
- Repetitive motion activities
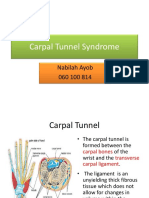
Anatomy of the carpal tunnel
Clinical picture
Symptoms • Signs
-Inspection may show thenar muscle
- Numbness and tingling in radial atrophy.
3and 1\2 fingers. - Carpal tunnel compression test (Durkan’s
test) is the most sensitive test to diagnose
- Pain and paresthesias that CTS
awaken the patient at night. - Performed by pressing thumbs over the
carpal tunnel and holding pressure for 30
seconds.
Onset of pain or paresthesia in the median
nerve distribution within 30 seconds is a
positive result.
Diagnosis is clinical
• Invistigations
-EMG and NCV to confirm the
diagnosis
-plain x rays and MRI in young
patients for diagnosis secondry
CTS (Mass, bony tumors.
treatment
• Conservative • Surgical
- Non steroidal - Carpal tunnel release
- Night splint opened or endoscopic release.
- Activity modification (avoid
aggravating activity
- Steroid injection (especially in
pregnancy)
• Symptoms
Rheumatoid arthritis - Morning stiffness and polyarthropathy.
- All joints of the hand affected except
distal interphalangeal joint (DIJ) usually
• A chronic systemic autoimmune spared.
disease with genetic • Diagnostic criteria
predisposition -morning stiffness
• More in female -Swelling of more than 3 joints
-Rheumatoid nodules
- Radiological changes in hand
- Systemic arthritis
- + Rheumatoid factor
- Arthritis of the hand joints
- 4 criteria or more = Rh arthritis
Hand and wrist in Rheumatoid arthritis
• 1- Rheumatoid nodules in aggressive disease • Treatment
over the IP joints (never in the DIP joint).
• 2- arthritis in wrist and all joints of hand except • 1- medical
DIP joint.
• 3- ulnar deviation of the fingers at MCP joint
• 2- physical therapy early as
due to extensor tendons rupture at the wrist possible before deformities
• 4- mallet finger due to rupture of extensor long life
expansion
• 5- Swan neck deformity due to rupture of • 3- surgical according to
terminal tendon deformity and arthritis
• 6- Boutonniere deformity due to silding of
extensor tendon at the site of middle inter
phalangeal joint
• Carpal tunnel syndrome.
Deformities of the hand in Rh arthritis
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis
• A stenosing tenosynovial inflammation • Symptoms
of the 1st dorsal compartment which - Gradual onset of radial sided wrist pain
include
- Pain exacerbated by gripping and
-abductor pollicis longus
raising objects with wrist in neutral
- Extensor polishis brevis
• Physical examination
• Women more than men
-Tenderness over the 1st dorsal
• 30-50 y compartment at the level of the radial
• Thickening and swelling of the styloid.
retinaculum including 2 tendons causes - Pain with resisted radial deviation .
increase tendon friction
- Normal motion and neurological
• Most of the cases resolve with non
operative treatment.
examination
Management
• Diagnosis mainly clinical • Treatment
• x ray to exclude mass or • Conservative
calcification NSAID
Physical therapy
Local injection
• Surgical
surgical release of 1st dorsal
compartment in severe and
resistant cases
You might also like
- JSA of Glass FixingDocument5 pagesJSA of Glass FixingPAVANKUMAR50% (2)
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument39 pagesCarpal Tunnel SyndromeNindyNo ratings yet
- Neuromusculosklatal Disorders FK UnayaDocument62 pagesNeuromusculosklatal Disorders FK UnayaSuci MayveraNo ratings yet
- Wrist Pain: Pramono Ari Wibowo, MDDocument46 pagesWrist Pain: Pramono Ari Wibowo, MDIwan Wonodihardjo100% (1)
- Shoulder Pain TreatmentDocument36 pagesShoulder Pain Treatmentpocadew100% (1)
- Joint and Back Pain: Myriam I. Garcia Gonzalez, MD Internal Medicine Board CertifiedDocument39 pagesJoint and Back Pain: Myriam I. Garcia Gonzalez, MD Internal Medicine Board CertifiedStephanie RiveraNo ratings yet
- الفصل الثاني محاضرات PDFDocument20 pagesالفصل الثاني محاضرات PDFAZOZ 19No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Pain Syndromes ExplainedDocument50 pagesMusculoskeletal Pain Syndromes ExplainedIkhsan Amadea9969No ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument38 pagesCarpal Tunnel Syndromereza prayogaNo ratings yet
- Trigger Finger and Ganglion Cyct - Seminar Ortho Year 5Document63 pagesTrigger Finger and Ganglion Cyct - Seminar Ortho Year 5Sh Zahra100% (1)
- Journal Reading CTSDocument27 pagesJournal Reading CTSwillie hardysonNo ratings yet
- Nerve Compression (Entrapment) SyndromeDocument23 pagesNerve Compression (Entrapment) SyndromeTrending razeNo ratings yet
- RheumatoidDocument35 pagesRheumatoidDeva LekshmiNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument45 pagesArthritisFadlu ManafNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome-AbiDocument34 pagesCarpal Tunnel Syndrome-AbiSri MahadhanaNo ratings yet
- Red Flag: MSK Services Pathway - Elbow PathologyDocument7 pagesRed Flag: MSK Services Pathway - Elbow PathologyMuhammed ElgasimNo ratings yet
- Handout Lat Elbow Pain PDFDocument47 pagesHandout Lat Elbow Pain PDFgemichan26No ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Emergencies AndreDocument49 pagesOrthopaedic Emergencies AndreLusi MunawarohNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrom Rustam 2024Document42 pagesCarpal Tunnel Syndrom Rustam 2024white.bear251102No ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve Disorders (Dr. Ken)Document72 pagesPeripheral Nerve Disorders (Dr. Ken)Nurindha Shimelia M ZNo ratings yet
- Arthritis OsteoarthritisDocument43 pagesArthritis OsteoarthritisMYMANo ratings yet
- Compressive Neuropathy of Upper LimbDocument49 pagesCompressive Neuropathy of Upper LimbYamunaVaaneeSivalingamNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Fracture of Distal of Right Radius Fracture of Styloid of Right UlnaDocument23 pagesCase Report: Fracture of Distal of Right Radius Fracture of Styloid of Right Ulna-'Rhya Rhyemma James Potter'-No ratings yet
- Test biceps reflex by tapping the biceps tendon with reflex hammer while arm is supinated.- C6 – Brachioradialis reflexDocument74 pagesTest biceps reflex by tapping the biceps tendon with reflex hammer while arm is supinated.- C6 – Brachioradialis reflexBushra EjazNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument26 pagesCarpal Tunnel Syndrome Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentWong RakatNo ratings yet
- Common Sports Injuries: Ukris Gunadham, MD, FRCOST Department of Orthopaedics Trang HospitalDocument71 pagesCommon Sports Injuries: Ukris Gunadham, MD, FRCOST Department of Orthopaedics Trang HospitalMohammed SaqoorNo ratings yet
- Hand and Upper Extremity Review for NBCOT ExamDocument59 pagesHand and Upper Extremity Review for NBCOT ExamJenny RajanNo ratings yet
- 2 2-ArthritidesDocument76 pages2 2-ArthritidesAvinash KaushikNo ratings yet
- Lower Back Pain: DR Robert Ramcharan MBBS, Frcsed, DM (Neurosurgery) NeurosurgeonDocument69 pagesLower Back Pain: DR Robert Ramcharan MBBS, Frcsed, DM (Neurosurgery) NeurosurgeonShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve Disorders ReviewDocument66 pagesPeripheral Nerve Disorders ReviewReno Andri0% (1)
- Hand & WristDocument56 pagesHand & WristAbdallah Samir Mostafa٢٠١٩٠٢١٥٩No ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument22 pagesCarpal Tunnel SyndromePinimNo ratings yet
- Wrist DropDocument38 pagesWrist DropFardan AnsarNo ratings yet
- De Quervain's TendinosisDocument19 pagesDe Quervain's TendinosisSze Wing LeeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3Document52 pagesAnatomy 3Balsam TeineNo ratings yet
- ICA - Limbs Upper Limb Focus 10-17-17Document108 pagesICA - Limbs Upper Limb Focus 10-17-17Mark CubillanNo ratings yet
- Modul KFR Peripheral NeuropathyDocument68 pagesModul KFR Peripheral NeuropathyHasna Diyani SalamahNo ratings yet
- Red Flag: MSK Services Pathway - Shoulder PathologyDocument11 pagesRed Flag: MSK Services Pathway - Shoulder PathologyMuhammed ElgasimNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedics EmergenciesDocument63 pagesOrthopaedics EmergencieszzooooeeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic and Traumatology: Dr. Sukry Asdar Putra Hasibuan, SP - OTDocument37 pagesOrthopaedic and Traumatology: Dr. Sukry Asdar Putra Hasibuan, SP - OTNiaUlfaAngreiniTambunanNo ratings yet
- Problem of SpineDocument99 pagesProblem of SpineSashwini Dhevi100% (1)
- Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDocument16 pagesThoracic Outlet SyndromeDeepak RajNo ratings yet
- De Quervain's TendinosisDocument19 pagesDe Quervain's TendinosisSze Wing LeeNo ratings yet
- CTS-Boy - CtsDocument10 pagesCTS-Boy - CtsFahmi RizqiNo ratings yet
- 6 DR NarsimuluDocument67 pages6 DR Narsimulushirish gundalaNo ratings yet
- ARTHRITIS-by Ayesigwa GeraldDocument38 pagesARTHRITIS-by Ayesigwa GeraldAyesigwa Gerald96No ratings yet
- Presentasi Radiologi: Dita Ayu Pertiwi FAA 114 016Document88 pagesPresentasi Radiologi: Dita Ayu Pertiwi FAA 114 016dita ayuNo ratings yet
- Osteonecrosis of The Femoral Head: Kriangk BenjawongsathianDocument65 pagesOsteonecrosis of The Femoral Head: Kriangk Benjawongsathianryc0% (1)
- Presentasi Kasus Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument25 pagesPresentasi Kasus Carpal Tunnel SyndromeIhsanNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Assignment On Posterior Wrist PalpationDocument11 pagesIntroduction: Assignment On Posterior Wrist PalpationRashi SinghNo ratings yet
- Pengayaan Koass Ortho - Update 5 VersionDocument122 pagesPengayaan Koass Ortho - Update 5 Versionanon_967171484No ratings yet
- Red Flag: MSK Services Pathway - Hand PathologyDocument10 pagesRed Flag: MSK Services Pathway - Hand PathologyMuhammed ElgasimNo ratings yet
- Seminar-Quadripplegia, Paraplegia, MNDDocument107 pagesSeminar-Quadripplegia, Paraplegia, MNDSalsabila Al-BasheerNo ratings yet
- Ra and Osteoarthritis R IfDocument43 pagesRa and Osteoarthritis R IfsnfhanNo ratings yet
- WEEK Orthopedics DR JohnDocument16 pagesWEEK Orthopedics DR JohnnoorgianilestariNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome AntyDocument22 pagesCarpal Tunnel Syndrome Antyamel015No ratings yet
- Low Back Pain - 1-07Document39 pagesLow Back Pain - 1-07Nur Sabriany LihawaNo ratings yet
- CBD Spinal Infection: by Neoh Zhong NingDocument26 pagesCBD Spinal Infection: by Neoh Zhong NingJoni NeohNo ratings yet
- Bone Tuberculosis (Smu)Document31 pagesBone Tuberculosis (Smu)Andre F SusantioNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCarpal Tunnel Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Laboratory 1. Anatomical Position and TerminologiesDocument2 pagesLaboratory 1. Anatomical Position and TerminologiesAANo ratings yet
- LiftAire II Elevator Air ConditionerDocument13 pagesLiftAire II Elevator Air ConditionerMohammed HussenNo ratings yet
- Anterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaDocument24 pagesAnterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaSky StoneNo ratings yet
- Phlebitis and ThrombophlebitisDocument27 pagesPhlebitis and ThrombophlebitisMaría Fernanda Ríos100% (1)
- 2017 Domestic Violence FatalitiesDocument28 pages2017 Domestic Violence FatalitiesAlyssa Roberts100% (1)
- ZXSDR BTS& Node B Maintenance Guide v1.0Document93 pagesZXSDR BTS& Node B Maintenance Guide v1.0danesh_ieee100% (1)
- Stranger Things DraftDocument45 pagesStranger Things Draftpearlie_vNo ratings yet
- LG LED TV ManualDocument36 pagesLG LED TV Manualmph_88No ratings yet
- Paintball Release of LiabilityDocument2 pagesPaintball Release of LiabilityitargetingNo ratings yet
- Standard Treatment ProtocolsDocument663 pagesStandard Treatment Protocolsdrvins1No ratings yet
- EFT Choice Method Basic StatementsDocument3 pagesEFT Choice Method Basic StatementsmichingonNo ratings yet
- Quasi-Delict vs Breach of Contract in Awarding DamagesDocument2 pagesQuasi-Delict vs Breach of Contract in Awarding DamagesAngela Louise SabaoanNo ratings yet
- Pertamina Geothermal Medical Emergency PlanDocument10 pagesPertamina Geothermal Medical Emergency PlanNur Azima AhmadNo ratings yet
- Filing an NHRC complaint for custodial tortureDocument4 pagesFiling an NHRC complaint for custodial tortureVara Prasad NeelamsettiNo ratings yet
- Hamstring Weakness After Surgery For Anterior Cruciate InjuryDocument4 pagesHamstring Weakness After Surgery For Anterior Cruciate InjuryAdrien VaillatNo ratings yet
- 9 - PE7PF Id 30Document2 pages9 - PE7PF Id 30Metchie PalisNo ratings yet
- Laceration Repair: A Practical Approach: Randall T. Forsch, MD, MPH Sahoko H. Little, MD, PHD and Christa Williams, MDDocument10 pagesLaceration Repair: A Practical Approach: Randall T. Forsch, MD, MPH Sahoko H. Little, MD, PHD and Christa Williams, MDLeonardoCampanelliNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - Manual HandlingDocument1 pageRisk Assessment - Manual HandlingGenerdheil Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- (06012023 0716) Efae23302 AnsDocument4 pages(06012023 0716) Efae23302 AnsBhargaviNo ratings yet
- Foot Anatomy: Muhammad AzamDocument30 pagesFoot Anatomy: Muhammad AzamMuhammad AzamNo ratings yet
- Workload Management BasicsDocument24 pagesWorkload Management BasicsFilardi Anindito50% (2)
- SCOLIOSIS CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENTDocument20 pagesSCOLIOSIS CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENTSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Corrective Exercise Guide PDFDocument13 pagesCorrective Exercise Guide PDFRui Cunha100% (2)
- Ob - Operative ObstetricsDocument224 pagesOb - Operative Obstetricsapi-385605133% (3)
- Fatigue Failure Analysis and Design Methods for Variable LoadingDocument113 pagesFatigue Failure Analysis and Design Methods for Variable LoadingZaher ZaherNo ratings yet
- Supracondylar Fracture and Elbow Injuries in ChildrenDocument33 pagesSupracondylar Fracture and Elbow Injuries in Childrenirfanzukri100% (3)
- HOUSE OF LORDS DECISION ON SHIP CHARTER DAMAGESDocument40 pagesHOUSE OF LORDS DECISION ON SHIP CHARTER DAMAGESKikoy IlaganNo ratings yet
- Burn ManagementDocument19 pagesBurn ManagementKavimathy SukumaranNo ratings yet
- Kelli Smith Edt 321 Resume UpdateDocument2 pagesKelli Smith Edt 321 Resume Updateapi-283093639No ratings yet