Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L1. Sup Mimicry
L1. Sup Mimicry
Uploaded by
Cedric Hastings0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views8 pagesThis document summarizes an experiment that tested Batesian mimicry between poisonous coral snakes and non-poisonous scarlet kingsnakes. Researchers hypothesized that kingsnakes have evolved to mimic coral snakes' color patterns to reduce predation. They placed artificial kingsnake and brown snake models in areas with and without coral snakes, and found kingsnake models were attacked less often where coral snakes lived, supporting the mimicry hypothesis.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes an experiment that tested Batesian mimicry between poisonous coral snakes and non-poisonous scarlet kingsnakes. Researchers hypothesized that kingsnakes have evolved to mimic coral snakes' color patterns to reduce predation. They placed artificial kingsnake and brown snake models in areas with and without coral snakes, and found kingsnake models were attacked less often where coral snakes lived, supporting the mimicry hypothesis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views8 pagesL1. Sup Mimicry
L1. Sup Mimicry
Uploaded by
Cedric HastingsThis document summarizes an experiment that tested Batesian mimicry between poisonous coral snakes and non-poisonous scarlet kingsnakes. Researchers hypothesized that kingsnakes have evolved to mimic coral snakes' color patterns to reduce predation. They placed artificial kingsnake and brown snake models in areas with and without coral snakes, and found kingsnake models were attacked less often where coral snakes lived, supporting the mimicry hypothesis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
READ THE Case Study:
Investigating Mimicry in Snake Populations
• Many poisonous species are brightly colored, which warns
potential predators
• Mimics are harmless species that closely resemble poisonous
species
• Henry Bates hypothesized that this mimicry evolved in
harmless species as an evolutionary adaptation that reduces
their chances of being eaten
Hypothesis Testing
• Hypothesis tested with poisonous eastern coral snake
and its mimic, the non-poisonous scarlet kingsnake
• Both live in the Carolinas, but the scarlet kingsnake is
also found in regions without poisonous coral snakes
• If …. Then statement of hyspothesis testing
– If predators inherit an avoidance of the coral snake’s
coloration, then the colorful scarlet kingsnake will be
attacked less often in the regions where coral snakes are
present
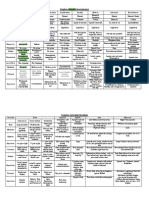
Fig. 1-25
Scarlet kingsnake (nonpoisonous)
Key
Range of scarlet
kingsnake only
Overlapping ranges of
scarlet kingsnake and
eastern coral snake
North
Carolina
Eastern coral snake
(poisonous)
South
Carolina
Scarlet kingsnake (nonpoisonous)
Field Experiments with Artificial Snakes
• To test this mimicry hypothesis, researchers made
hundreds of artificial snakes:
– An experimental group resembling kingsnakes
– A control group resembling plain brown snakes
• Equal numbers of both types were placed at field
sites, including areas without poisonous coral snakes
Designing Controlled Experiments
• A controlled experiment compares an experimental group
(artificial kingsnakes) with a control group (the artificial
brown snakes)
• Ideally, only the variable of interest (the color pattern of
the artificial snakes) differs between the control and
experimental groups
• A controlled experiment means that control groups are
used to cancel the effects of unwanted variables
• A controlled experiment does not mean that all unwanted
variables are kept constant
Question, Hypothesis, & Prediction…
• Question
– Does the scarlet kingsnake benefit from its mimicry of the
eastern coral snake?
• Hypothesis
– The scarlet kingsnake avoids predation due to its mimicry of
the eastern coral snake.
• Predictions
– In areas with both species, predators will avoid scarlet king
snakes; in areas with only scarlet kingsnakes, their pattern
will have no protective effect.
Testing…
• Place artificial snakes in the environment
and measure “predation” – how frequently
the models are attacked:
– Experimental group: artificial scarlet
kingsnakes
– Control group: artificial brown snakes
• Ideally, the control group differs from the
experimental group by the variable of
interest - the variable under study
– What was the variable in this case?
– Reproducibility: place hundreds of each kind
of “snake”.
Results…
• After four weeks, the scientists
retrieved the artificial snakes
and counted the bite or claw
marks
• Data fit the predictions of the
mimicry hypothesis (not
falsifiable): Ringed snakes
were attacked less frequently in
the geographic region where
coral snakes were found
You might also like
- The Book of Snakes: A Life-Size Guide to Six Hundred Species from Around the WorldFrom EverandThe Book of Snakes: A Life-Size Guide to Six Hundred Species from Around the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lords of Gossamer & ShadowDocument17 pagesLords of Gossamer & ShadowValerio CriniNo ratings yet
- Snakes Myths & Facts in English by Santosh TakaleDocument47 pagesSnakes Myths & Facts in English by Santosh TakaleSantosh Takale100% (26)
- Cot 1 Science 6Document2 pagesCot 1 Science 6HAMPASLUPA TRAVELS75% (4)
- Tracing and Coloring Worksheet For KidsDocument12 pagesTracing and Coloring Worksheet For KidsanandpanoliNo ratings yet
- Snake Bite: Abhija Babuji. Crri. Department of Pediatrics. SmimsDocument76 pagesSnake Bite: Abhija Babuji. Crri. Department of Pediatrics. SmimsMeliani FranzNo ratings yet
- Snakes: 101 Super Fun Facts And Amazing Pictures (Featuring The World's Top 10 Snakes With Coloring Pages)From EverandSnakes: 101 Super Fun Facts And Amazing Pictures (Featuring The World's Top 10 Snakes With Coloring Pages)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Venomous Snake TrainingDocument8 pagesVenomous Snake TrainingFirdaus BillyNo ratings yet
- Snakes: 101 Super Fun Facts And Amazing Pictures (Featuring The World's Top 10 Snakes)From EverandSnakes: 101 Super Fun Facts And Amazing Pictures (Featuring The World's Top 10 Snakes)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Yowie Rarity Chart A4 PDFDocument6 pagesYowie Rarity Chart A4 PDFrudiNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and SuperlativesDocument67 pagesComparatives and SuperlativesDIANA CAROLINA CAMACHO AVILANo ratings yet
- Snakes, Venom, Effects, AntivenomDocument5 pagesSnakes, Venom, Effects, AntivenomLakshya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Types of Snakes: By: Consorcio K. Bongabong JRDocument7 pagesTypes of Snakes: By: Consorcio K. Bongabong JRMr. JAMESNo ratings yet
- Animal Toxins Zootoxins Snake VenomDocument96 pagesAnimal Toxins Zootoxins Snake VenomSRINIVASAN GnanasabapathyNo ratings yet
- Venomous Snake Bites: Iswarya Obilineni Assistant Professor Nirmala College of PharmacyDocument13 pagesVenomous Snake Bites: Iswarya Obilineni Assistant Professor Nirmala College of Pharmacykolipakula venkatNo ratings yet
- Snake PoisoningDocument47 pagesSnake Poisoning126.NishkaraniNo ratings yet
- Snakes - Identification of Poisonous & Non-Poisonous Snakes, Poison Apparatus, Venom & Its EffectDocument6 pagesSnakes - Identification of Poisonous & Non-Poisonous Snakes, Poison Apparatus, Venom & Its EffectAakash VNo ratings yet
- Snake Bite & ManagementDocument88 pagesSnake Bite & ManagementWesley KasmirNo ratings yet
- About SnakesDocument2 pagesAbout SnakesqutywamicahNo ratings yet
- Pine DesignDocument12 pagesPine Designpranavnath.granetgspsNo ratings yet
- Deepak Rawal Assistant Professor Mohanlal Sukhadia University Udaipur IndiaDocument28 pagesDeepak Rawal Assistant Professor Mohanlal Sukhadia University Udaipur IndiaKargboNo ratings yet
- Snakes: General Biology Damage and Damage IdentificationDocument4 pagesSnakes: General Biology Damage and Damage IdentificationPratyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Classification of Venomous SnakesDocument22 pagesClassification of Venomous SnakesAthulya VjNo ratings yet
- SnakesDocument13 pagesSnakesMAXOSNo ratings yet
- Burning Sands - Animals and MountsDocument8 pagesBurning Sands - Animals and Mountspatrick menezesNo ratings yet
- Kangaroos The Ultimate Kangaroo Book for Kids: 100+ Amazing Kangaroo Facts, Photos, Quiz and MoreFrom EverandKangaroos The Ultimate Kangaroo Book for Kids: 100+ Amazing Kangaroo Facts, Photos, Quiz and MoreNo ratings yet
- CT Nature SpidersDocument1 pageCT Nature SpidersHartford CourantNo ratings yet
- What Are Rare Plants and Animals?Document11 pagesWhat Are Rare Plants and Animals?Saurya PandeyNo ratings yet
- King Cobra SnakeDocument3 pagesKing Cobra SnakeVeri YuliantoNo ratings yet
- Ppt6 Intro To Living Primates Onlinecomp RevSP16Document66 pagesPpt6 Intro To Living Primates Onlinecomp RevSP16Dylan OfriasNo ratings yet
- The Cast of SHARKS: Educator'S GuideDocument20 pagesThe Cast of SHARKS: Educator'S GuideAnxo Martinez CalvoNo ratings yet
- Rhinoceroses For Kids Amazing Animal Books For Young ReadersFrom EverandRhinoceroses For Kids Amazing Animal Books For Young ReadersNo ratings yet
- Bio 110 Prelim Lec 4 Chap 2Document85 pagesBio 110 Prelim Lec 4 Chap 2Sherly MAKIJINo ratings yet
- Chordata (Vertebrates) Scorpionfishes (Scorpaenidae)Document8 pagesChordata (Vertebrates) Scorpionfishes (Scorpaenidae)AnonimousNo ratings yet
- SnakesDocument71 pagesSnakeskf9tqpnkrzNo ratings yet
- Attempted Experimental Transfer ofDocument6 pagesAttempted Experimental Transfer ofLarissa AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Cobra EscupidoraDocument7 pagesCobra EscupidorachristianNo ratings yet
- SharksDocument1 pageSharksHartford CourantNo ratings yet
- Lab Animals PDFDocument98 pagesLab Animals PDFdahiphale1No ratings yet
- Barnacles On TurtlesDocument10 pagesBarnacles On TurtlesRajas ShrikoliNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Name For The Asian Silver Carp Is Hypophthalmichthys MolitrixDocument1 pageThe Scientific Name For The Asian Silver Carp Is Hypophthalmichthys MolitrixShayan UzzamanNo ratings yet
- SNAKES AND SNAKE VENOM NewDocument85 pagesSNAKES AND SNAKE VENOM NewDheerajNo ratings yet
- Mantis ShrimpDocument9 pagesMantis Shrimpapi-459203108No ratings yet
- Jump To Navigationjump To Search: For Other Uses, See - "Foxes" and "Vixen" Redirect Here. For Other Uses, See andDocument4 pagesJump To Navigationjump To Search: For Other Uses, See - "Foxes" and "Vixen" Redirect Here. For Other Uses, See andFrances camille TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On AnimalsDocument50 pagesLesson Plan On AnimalsanimoniNo ratings yet
- MMM 24 Research SlidesDocument2 pagesMMM 24 Research Slidesasfia.elias6No ratings yet
- Piner High School Ste A M Certificate Level 1 Orca DynastyDocument3 pagesPiner High School Ste A M Certificate Level 1 Orca Dynastyapi-738384895No ratings yet
- Green Organic Exploring The Animal Kingdom Presentation-1Document23 pagesGreen Organic Exploring The Animal Kingdom Presentation-1keerthigaganeshamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Emperor Penguins Are Birds That Live in Antarctica. They Are The Largest Species of PenguinDocument8 pagesEmperor Penguins Are Birds That Live in Antarctica. They Are The Largest Species of PenguinThe Children's NurturyNo ratings yet
- Barclay1985 PDFDocument9 pagesBarclay1985 PDFAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Animal PresentationDocument14 pagesAnimal PresentationDavey PhillipsNo ratings yet
- TigerDocument5 pagesTigerAhmad Leong SengNo ratings yet
- Utah DWR RattlesnakeDocument4 pagesUtah DWR RattlesnakeLarryDCurtisNo ratings yet
- Marine Mammal of BCDocument51 pagesMarine Mammal of BCCelia KoellschNo ratings yet
- SnakesDocument49 pagesSnakesAnees PmNo ratings yet
- Classification of MammalsDocument56 pagesClassification of MammalsDr. Girish PandeyNo ratings yet
- King Cobra: DescriptionDocument4 pagesKing Cobra: DescriptionRoopes RsNo ratings yet
- Scorpions: Stuff You Never Knew About ScorpionsDocument37 pagesScorpions: Stuff You Never Knew About ScorpionsSara FatimaNo ratings yet
- Rose SemiDocument11 pagesRose SemiJINGKY HUMAMOYNo ratings yet
- Hiss, Spit and Bite - Deadly Snakes | Snakes for Kids | Children's Reptile & Amphibian BooksFrom EverandHiss, Spit and Bite - Deadly Snakes | Snakes for Kids | Children's Reptile & Amphibian BooksNo ratings yet
- Inggris 10 2021Document5 pagesInggris 10 2021Aan SaputraNo ratings yet
- Studying Mammals A Winning Design PrintableDocument35 pagesStudying Mammals A Winning Design PrintableAmanda RutllantNo ratings yet
- Sci 8 4TH Quarter Module 6Document35 pagesSci 8 4TH Quarter Module 6Diosa BakingNo ratings yet
- LBOBI12 XB1 Group7 Lab-Activity19 Solidum TanDocument16 pagesLBOBI12 XB1 Group7 Lab-Activity19 Solidum TanFernando Martin BarbaNo ratings yet
- Interaksi Varanus Salvator (Interaction of Varanus Salvator) : Prey, Predator, Atau DETRIVORE? (Varanus Salvato..Document12 pagesInteraksi Varanus Salvator (Interaction of Varanus Salvator) : Prey, Predator, Atau DETRIVORE? (Varanus Salvato..Anggi jayadi RiwuNo ratings yet
- Flinders Ranges Scorpion: (Urodacus Elongatus)Document2 pagesFlinders Ranges Scorpion: (Urodacus Elongatus)RickNo ratings yet
- Life Stages of A Toad: Stage 1: The TadpoleDocument2 pagesLife Stages of A Toad: Stage 1: The TadpoleMary Grace Yañez100% (1)
- Relationship - Cards On SymbiosisDocument2 pagesRelationship - Cards On SymbiosisERICKA NEUDANo ratings yet
- 6027b81960a78Class-8-Lesson Plan For 14th-18th Feb, 2021tDocument2 pages6027b81960a78Class-8-Lesson Plan For 14th-18th Feb, 2021tmibsamNo ratings yet
- Single Sheet DungeonDocument2 pagesSingle Sheet DungeonleonNo ratings yet
- The Vertebrates: 500 Million Years AgoDocument100 pagesThe Vertebrates: 500 Million Years AgoShawa DabaNo ratings yet
- Pokédex: Lilian Besson January 12, 2018Document159 pagesPokédex: Lilian Besson January 12, 2018Justine DominicNo ratings yet
- PTS Kelas 9 SoalDocument6 pagesPTS Kelas 9 SoalErris SetiyoNo ratings yet
- Dragons: by WillDocument16 pagesDragons: by WillMatthew FletcherNo ratings yet
- Intelligence: Comparing That One of Humans' and Animals': Human V. Animal IntelligenceDocument2 pagesIntelligence: Comparing That One of Humans' and Animals': Human V. Animal IntelligenceCharla BriceNo ratings yet
- Name That AnimalDocument4 pagesName That AnimalMikee MercadoNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Animals' UniqenessDocument28 pagesUnit 7 - Animals' UniqenessMonica SelvianaNo ratings yet
- Axolotl Zoology Creative FinalDocument2 pagesAxolotl Zoology Creative Finalapi-643479863No ratings yet
- Collecta 2019 PDFDocument131 pagesCollecta 2019 PDFJorge Garcia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan: Love Your Animals at HomeDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan: Love Your Animals at Homemailyn ParejaNo ratings yet
- Jatim Park 2Document2 pagesJatim Park 2Alexander PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Main Idea and Supporting DetailsDocument3 pagesMain Idea and Supporting DetailsLeyra BonillaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia SummaryDocument2 pagesKingdom Animalia Summaryaqeel abdullahNo ratings yet
- Thousands and The Presence Are Classified Into Two Inv T RatesDocument7 pagesThousands and The Presence Are Classified Into Two Inv T RatesVedansh SinghNo ratings yet
- The Shape of The Cross-Section and The Strength of The Long BonesDocument36 pagesThe Shape of The Cross-Section and The Strength of The Long BonesLuděk SpíchalNo ratings yet
- 10 Endangered Animals in Malaysia - RS Eco Palm SDN BHDDocument8 pages10 Endangered Animals in Malaysia - RS Eco Palm SDN BHDNUR IZZATINo ratings yet