0% found this document useful (0 votes)
305 views35 pagesReflection of Light
- Light travels in straight lines and at a very high speed in a vacuum.
- Light is emitted from luminous sources like the sun, stars, candles, and lamps.
- White light is a mixture of the colors in the visible light spectrum.
- A ray is the path that light energy travels along, represented by a straight line with an arrow showing direction.
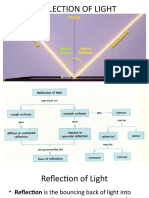
- When light rays change direction abruptly at the boundary between different mediums, it is called reflection. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
- Images formed by plane mirrors are virtual, upright, and laterally inverted with the same size as the object.
Uploaded by
charlesferrer718Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
305 views35 pagesReflection of Light
- Light travels in straight lines and at a very high speed in a vacuum.
- Light is emitted from luminous sources like the sun, stars, candles, and lamps.
- White light is a mixture of the colors in the visible light spectrum.
- A ray is the path that light energy travels along, represented by a straight line with an arrow showing direction.
- When light rays change direction abruptly at the boundary between different mediums, it is called reflection. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
- Images formed by plane mirrors are virtual, upright, and laterally inverted with the same size as the object.
Uploaded by
charlesferrer718Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd