Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Upload 2
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views12 pagesThe document discusses different types of transducers. A transducer is defined as a device that converts one form of energy into another, especially for measurement or control purposes. Transducers can be classified based on their principle of transduction, whether they are primary/secondary, active/passive, analog/digital, normal/inverse, and whether they are smart or intelligent. Common principles of transduction include thermoelectric, magnetoresistive, electrokinetic, and optical effects. Transducers find applications in industry automation, process control, and embedded systems in automobiles, medical devices, aircraft, and consumer electronics.
Original Description:
Original Title
upload2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of transducers. A transducer is defined as a device that converts one form of energy into another, especially for measurement or control purposes. Transducers can be classified based on their principle of transduction, whether they are primary/secondary, active/passive, analog/digital, normal/inverse, and whether they are smart or intelligent. Common principles of transduction include thermoelectric, magnetoresistive, electrokinetic, and optical effects. Transducers find applications in industry automation, process control, and embedded systems in automobiles, medical devices, aircraft, and consumer electronics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views12 pagesUpload 2
The document discusses different types of transducers. A transducer is defined as a device that converts one form of energy into another, especially for measurement or control purposes. Transducers can be classified based on their principle of transduction, whether they are primary/secondary, active/passive, analog/digital, normal/inverse, and whether they are smart or intelligent. Common principles of transduction include thermoelectric, magnetoresistive, electrokinetic, and optical effects. Transducers find applications in industry automation, process control, and embedded systems in automobiles, medical devices, aircraft, and consumer electronics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Transducer
VSSUT, Measurement and Instrumentation Dr. Gyan Ranjan
• Sensor / Transducer (Instrument Society of America): A device which
provides a usable output in response to a specified measurand.
• Output: defined as an Electrical Quantity (finally).
• Measurand: as a Physical quantity / property / condition which is
measured.
Physical quantity – pressure, heat, flow rate, liquid level,
flow, position, humidity etc.
Output - measured in terms of parametric change or electrical signal.
VSSUT, Measurement and Instrumentation Dr. Gyan Ranjan
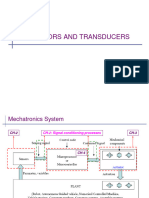
• Transducer: which converts one form of energy into
device form for the purpose of measurement / control.
another
•Sensor : Transducer (physical into electrical) + electrodes and
I/O mechanisms.
•SensorI/P Transducer
•Actuator O/P Transducer
VSSUT, Measurement and Instrumentation Dr. Gyan Ranjan
Classification of Transducers
1. Based on principle of transduction
2. Primary and secondary
3. Active & passive
4. Analog & digital
5. Transducer and Inverse transducer
6. Smart / Intelligent (latest one)
VSSUT, Measurement and Instrumentation Dr. Gyan Ranjan
Based on principle used
Thermo electric
Magneto resistive
Electro kinetic
Optical
VSSUT, Measurement and Instrumentation Dr. Gyan Ranjan
Based on Applications
Industry Automation / Process Control
Embedded Control: Automobiles; Medical; Aircraft; Consumer
Electronics
VSSUT, Measurement and Instrumentation Dr. Gyan Ranjan
Passive Transducer
Device which derive power reqd. for transduction
from
auxiliary power source
externally powered
Examples : resistive, inductive, capacitive
Without power they will not work
VSSUT, Measurement and Instrumentation Dr. Gyan Ranjan
Active Transducer
No extra power reqd. to produce I/P
Self generating
Draw power from input applied
Examples: Smart accelerometer or vibration sensor ; Piezo-
resistive Si-type Diaphragm Pressure sensor (with the strain gauge
and a thin film resistor network) ; Piezo-electric type
accelerometer
VSSUT, Measurement and Instrumentation Dr. Gyan Ranjan
Analog Transducer
Convert I/P quantity into an analog O/P
Analog O/P - a continuous function of ‘amplitude and
time’
Examples: Strain gauge, LVDT, thermocouple, manometer
VSSUT, Measurement and Instrumentation Dr. Gyan Ranjan
Digital Transducer
Converts I/P into an electrical O/P in the form of pulses (quasi-
digital O/P) or a discrete function of ‘amplitude and time’
Examples: Smart and Intelligent transducers
VSSUT, Measurement and Instrumentation Dr. Gyan Ranjan
Inverse Transducer
Converts electrical signal to physical quantity, typically, known as
Actuator’.
Accepts a data sample (samples) and converts them into physical
action.
VSSUT, Measurement and Instrumentation Dr. Gyan Ranjan
Smart Sensor
• Smart Sensor: A module containing sensor element(s) suitably
integrated with necessary electronics such that the O/P is truly or
easily compatible with the intended end device, and the module is
usually takes the form of a single IC chip.
• Intelligent Sensor: Smart sensor + Digital Processor (DPU)
VSSUT, Measurement and Instrumentation Dr. Gyan Ranjan
You might also like
- No No NanetteDocument110 pagesNo No NanetteFrank Raso100% (4)
- CARDIOPULMONARY BYPASS - CompressedDocument117 pagesCARDIOPULMONARY BYPASS - CompressedBayan TahaNo ratings yet
- Roosendaal Study of Vaccinated vs. Unvaccinated Children in The Netherlands: Results SurveyDocument4 pagesRoosendaal Study of Vaccinated vs. Unvaccinated Children in The Netherlands: Results Surveythomas_austin_189% (9)
- Opical Tranducer MaualDocument40 pagesOpical Tranducer MaualhemantecNo ratings yet
- Transducers and Data Aquisition SystemsDocument176 pagesTransducers and Data Aquisition SystemsSHINYNo ratings yet
- Transducers 1Document40 pagesTransducers 1SagarNo ratings yet
- Sensorandtransducerslect1 160623152141Document80 pagesSensorandtransducerslect1 160623152141pushpanarayanan100% (1)
- Sensors and TransducersDocument118 pagesSensors and TransducersDhaval PatelNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageNo ratings yet
- Process Instrumentation Basic DefinitionsDocument49 pagesProcess Instrumentation Basic DefinitionsMantuomNo ratings yet
- Dr. H. S. Kalsi Dept. of Physics Guru Nanak Khalsa College Matunga, MumbaiDocument100 pagesDr. H. S. Kalsi Dept. of Physics Guru Nanak Khalsa College Matunga, MumbaiGAURI AGROTECH100% (1)
- Fabrication of 2 X 1000 MT Capacity Mounded LPG Storage VesselsDocument84 pagesFabrication of 2 X 1000 MT Capacity Mounded LPG Storage VesselsMilan DjumicNo ratings yet
- Transducer and Their ClassificationDocument2 pagesTransducer and Their ClassificationPujaChaudhuryNo ratings yet
- Sensors and TransducersDocument79 pagesSensors and TransducersMohdQasim0% (1)
- Sensors and TransducersDocument118 pagesSensors and TransducersAhmad HamoudaNo ratings yet
- Emi Unit 5Document28 pagesEmi Unit 5neha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Slide NoteDocument35 pagesWeek 10 Slide NoteJunsyaNo ratings yet
- Introductiontosensorstransducers 140830045447 Phpapp02Document17 pagesIntroductiontosensorstransducers 140830045447 Phpapp02Karim NazefNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument9 pagesSeminar ReportNk Kushal0% (1)
- Measurement Concepts and Classification of SensorsDocument26 pagesMeasurement Concepts and Classification of SensorsArvind kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Instrumentation SystemDocument17 pagesUnit 1 Instrumentation SystemAnuj NikamNo ratings yet
- Process Control & InstrumentationDocument49 pagesProcess Control & InstrumentationMantuomNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - General Principles of MeasurementDocument53 pagesChapter - 1 - General Principles of MeasurementmarNo ratings yet
- Shahbaz 85 Lab1Document4 pagesShahbaz 85 Lab1Shahbaz ZafarNo ratings yet
- EE413 Module IDocument162 pagesEE413 Module IVeena MundaNo ratings yet
- Semester I, 2022 A.Y. Ieng-4161: Mechatronics Introduction To InstrumentationDocument63 pagesSemester I, 2022 A.Y. Ieng-4161: Mechatronics Introduction To InstrumentationDenamo BekeleNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document22 pagesLec 2mgeneralworkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transducers Hand Written Class NotesDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Transducers Hand Written Class NotesBhushan SoniNo ratings yet
- Lec1 3 TransducesDocument15 pagesLec1 3 Transduceshossain1821054No ratings yet
- 4thunitemi PDFDocument33 pages4thunitemi PDFSrirangam RajeshNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Transducers Real Time Computing and Programming - SensorsDocument80 pagesSensors and Transducers Real Time Computing and Programming - SensorsNon ArtistsNo ratings yet
- 2.introduction Sensors TransducerDocument15 pages2.introduction Sensors TransducerRaunaq SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 1 Sensor and TransducersDocument48 pagesChapter 3 Part 1 Sensor and TransducersFikadu Eshetu100% (1)
- 01 Basic Concept in Measurement SystemDocument95 pages01 Basic Concept in Measurement SystemWong Kai YiNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and Measurements - MaterialDocument150 pagesInstrumentation and Measurements - MaterialYAVANA BNo ratings yet
- Transducer Instrumentation & ControlDocument8 pagesTransducer Instrumentation & Control401-Arsh AlamNo ratings yet
- 1 CO4 Inst Sys Till Cap TransDocument78 pages1 CO4 Inst Sys Till Cap TransRashmika MurugeshanNo ratings yet
- Lec1.0 - Introduction To Instrumentation & Its ApplicationsDocument54 pagesLec1.0 - Introduction To Instrumentation & Its ApplicationsMuhammad Naufal RamzNo ratings yet
- Measurement: Measuring InstrumentsDocument6 pagesMeasurement: Measuring InstrumentsSubhransu MohapatraNo ratings yet
- SensorDocument100 pagesSensorZaki nouiNo ratings yet
- CH-2 SensorsDocument55 pagesCH-2 Sensorsdagimawgchew777No ratings yet
- Clo 3-TransducerDocument42 pagesClo 3-TransducerPoovarashan ManimaranNo ratings yet
- Electronic MeasurementsDocument66 pagesElectronic MeasurementsBenson Mansingh P MNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - Transducer and Sensors PDFDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Transducer and Sensors PDFROYALNEWSS100% (1)
- Instrumentation and Measurements: Engr. Muhammad Usman Sardar Lecturer, EEDocument29 pagesInstrumentation and Measurements: Engr. Muhammad Usman Sardar Lecturer, EEMuhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - ASVDocument24 pagesUnit 1 - ASVAnup S. Vibhute DITNo ratings yet
- Assignment With AnswersDocument19 pagesAssignment With AnswersMythily VedhagiriNo ratings yet
- Tranducers 2Document10 pagesTranducers 2Preston JerryNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4: Basics of Measurement and InstrumentationDocument34 pagesUnit - 4: Basics of Measurement and InstrumentationZim ShahNo ratings yet
- Transducers and Signal ConditionersDocument157 pagesTransducers and Signal Conditionersrohit pooniaNo ratings yet
- Sensors and TransducersDocument17 pagesSensors and TransducersLeeNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation EnglishDocument49 pagesInstrumentation EnglishSara N'driNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 TransducerDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 3 TransducerDegaga KebedeNo ratings yet
- SAITDocument2 pagesSAITAnum ShamshadNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document9 pagesAssignment 1Alimin AnniNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Medical InstrumentationDocument16 pagesBasic Concepts of Medical InstrumentationLove Gupta100% (1)
- Introduction To Measurements: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Measurements: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringKavitha A KNo ratings yet
- Oa1-Two MarksDocument28 pagesOa1-Two MarksMEIVELJ 19EE025No ratings yet
- TESCA-52051 ManualDocument4 pagesTESCA-52051 ManualGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Biosensors and Transducers 1 ManojDocument25 pagesBiosensors and Transducers 1 ManojaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Transducers - Characteristics, Classification, Applications PDFDocument18 pagesDifferent Types of Transducers - Characteristics, Classification, Applications PDFAAKASHNo ratings yet
- Alsalama College of Sciences &technology Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument40 pagesAlsalama College of Sciences &technology Electrical Engineering DepartmentAlamin IbrahimNo ratings yet
- SensoreDocument53 pagesSensorenunuNo ratings yet
- Us-Conversion CycleDocument3 pagesUs-Conversion CycleThessaloe B. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Epson C82 Service ManualDocument48 pagesEpson C82 Service ManualPablo RothNo ratings yet
- Served POsDocument21 pagesServed POsYay DumaliNo ratings yet
- (GHS SDS-en) - TAT - SOL-32 - 201901Document5 pages(GHS SDS-en) - TAT - SOL-32 - 201901Ian PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Booklet Course 8 Chapter 5Document18 pagesBooklet Course 8 Chapter 5PaolaNo ratings yet
- Green Gram CultivationDocument7 pagesGreen Gram CultivationSudhakar JayNo ratings yet
- Abstract CV: Maharani Retna Duhita, M.SC.,PHD - Med.ScDocument39 pagesAbstract CV: Maharani Retna Duhita, M.SC.,PHD - Med.ScnanaNo ratings yet
- Digital Photography in OrthodonDocument48 pagesDigital Photography in OrthodonSrinivasan BoovaraghavanNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Module 14 - Multiplication and Division of Fractions - November 20 and 21, 2020Document4 pagesQuarter 1 Module 14 - Multiplication and Division of Fractions - November 20 and 21, 2020MJ FabNo ratings yet
- Vatusa-Vatnz-Vatpac: Oceanic PartnershipDocument10 pagesVatusa-Vatnz-Vatpac: Oceanic PartnershipJerome Cardenas TablacNo ratings yet
- Literature Review and Case StudyDocument4 pagesLiterature Review and Case StudyNimNo ratings yet
- 2010 Skema Pat SBPDocument17 pages2010 Skema Pat SBPAfiqah RoshidiNo ratings yet
- My Two Week Meal Plan: Day Date Breakfast Lunch Dinner SignatureDocument1 pageMy Two Week Meal Plan: Day Date Breakfast Lunch Dinner SignatureIan Nathaniel Versoza AmadorNo ratings yet
- ECE-Class TT 21-22 EVEN-28.01.22Document13 pagesECE-Class TT 21-22 EVEN-28.01.22Sivakumar PothirajNo ratings yet
- At22 ElectricalDocument19 pagesAt22 ElectricalfabuleukalengaNo ratings yet
- Air Bag BleizerDocument88 pagesAir Bag BleizerEnrique Felipe Reveco BahamondesNo ratings yet
- Costing of Sea Water RO Plant KPT Manora Design at 100,000 IGPD at 35,000 PPMDocument3 pagesCosting of Sea Water RO Plant KPT Manora Design at 100,000 IGPD at 35,000 PPMMohtashim KazmiNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: LCI-100/200 Illumination and Imaging SystemDocument69 pagesService Manual: LCI-100/200 Illumination and Imaging SystemfugarisaNo ratings yet
- The Beauty of HolinessDocument5 pagesThe Beauty of HolinessGrace Church Modesto100% (1)
- Transportation Research Part E: Ángel Felipe, M. Teresa Ortuño, Giovanni Righini, Gregorio TiradoDocument18 pagesTransportation Research Part E: Ángel Felipe, M. Teresa Ortuño, Giovanni Righini, Gregorio TiradoAngélica MoralesNo ratings yet
- Worksheet of EDC - 2018Document2 pagesWorksheet of EDC - 2018pranavmurthyNo ratings yet
- III 12copernicus (RRL)Document4 pagesIII 12copernicus (RRL)Ricci MikaelaNo ratings yet
- Layer 3 48-Port 10G SFP+ + 2-Port 40G QSFP+ + 4-Port 100G QSFP28 Managed SwitchDocument10 pagesLayer 3 48-Port 10G SFP+ + 2-Port 40G QSFP+ + 4-Port 100G QSFP28 Managed Switchbader eddine khezamiNo ratings yet
- Dee Mandala InfoMemoDocument27 pagesDee Mandala InfoMemoSheetalkumarNo ratings yet
- Gec-Tcw Prelims GlobalizationDocument4 pagesGec-Tcw Prelims GlobalizationClarynce MojadoNo ratings yet
- Classified Coordinate Geometry Further Maths ExercisesDocument24 pagesClassified Coordinate Geometry Further Maths ExercisesAbrar RahmanNo ratings yet