Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ali Hassan
Uploaded by
aimenshahzad5550 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views13 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views13 pagesAli Hassan
Uploaded by
aimenshahzad555Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
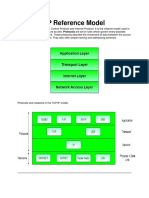
Network protocl
A network protocol is a set of rules and conventions that
define how data is transmitted and received over a network.
These protocols enable communication between devices in a
network, ensuring that information is exchanged accurately
and efficiently. Network protocols operate at different layers
of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, which is a
conceptual framework that standardizes the functions of a
telecommunication or computing system into seven
abstraction layers.
• Here are some key points about network protocols:
1.Layered Structure: The OSI model divides network functionality
into seven layers, each responsible for specific tasks. Different
protocols operate at different layers to provide various services.
• Common Protocols:
• Application Layer: Protocols such as HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol),
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), and FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
operate at this layer, handling high-level communication tasks.
• Transport Layer: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User
Datagram Protocol) are commonly used at this layer, managing end-to-end
communication and data flow control.
• Network Layer: IP (Internet Protocol) is a fundamental protocol in this
layer, handling routing and addressing.
• Link Layer: Ethernet and Wi-Fi protocols are examples of link layer
protocols, responsible for local network communication.
• TCP/IP Protocol Suite:
• The TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) suite is
the foundation of the Internet and includes protocols like TCP, IP,
UDP, ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), and others.
• Connection-Oriented vs. Connectionless Protocols:
Connection-Oriented: Protocols like TCP establish a connection
between devices before transmitting data, ensuring reliable and ordered
delivery.
Connectionless: Protocols like UDP do not establish a connection
beforehand and provide a faster, but potentially less reliable, means of
communication.
Packet Switching:
Most modern networks use packet-switching, where data is divided into
packets for transmission. Each packet contains information such as the
destination address, allowing it to traverse the network independently.
• Security Protocols: Protocols like SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets
Layer/Transport Layer Security) provide secure communication over
the Internet, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
Examples of Protocols:
• HTTP/HTTPS: Used for web browsing.
• SMTP/POP/IMAP: Used for email communication.
• TCP/UDP: Transport layer protocols.
• IP: Network layer protocol.
You might also like
- Network Protocol and TCPDocument5 pagesNetwork Protocol and TCPJoshua SantillanaNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & NetworkingDocument71 pagesData Communication & NetworkingShabanaNo ratings yet
- CCN Note First Module - CompressedDocument21 pagesCCN Note First Module - CompressedsbaleemaNo ratings yet
- The OSI and TCPDocument8 pagesThe OSI and TCPSreejith VaneryNo ratings yet
- TCP CharacteristicsDocument38 pagesTCP CharacteristicsgidumafayeraNo ratings yet
- Presentation Topic: Tcp/Ip Presented By: Iftakhar Hussain Roll No: 2019-BSIT-043 Department: Cs & ItDocument14 pagesPresentation Topic: Tcp/Ip Presented By: Iftakhar Hussain Roll No: 2019-BSIT-043 Department: Cs & ItIftakhar HussainNo ratings yet
- 19-203-0802 Computer Commu-Nication and Net - Working: Professional Elective - IV SEM-8Document45 pages19-203-0802 Computer Commu-Nication and Net - Working: Professional Elective - IV SEM-8Ťèjùźź ȚèjùNo ratings yet
- The TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument4 pagesThe TCP/IP Reference ModelJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- 9IP ModelDocument4 pages9IP ModelJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- 9IP Model-1Document4 pages9IP Model-1Jawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- TCP:IP Reference ModelDocument12 pagesTCP:IP Reference Modelsocekay372No ratings yet
- Protocols Invovled in TcipDocument23 pagesProtocols Invovled in TcipFiremandeheavenly InamenNo ratings yet
- Network TRWDocument7 pagesNetwork TRWT024KOUSTAV CHATTERJEENo ratings yet
- Secure Communication ProtocolsDocument33 pagesSecure Communication Protocolsdrrana.alshabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Network ModelsDocument21 pagesChapter 02 Network ModelsFarhan TamzidNo ratings yet
- Work Protocols and ArchitecturesDocument51 pagesWork Protocols and ArchitecturesSaleih GeroNo ratings yet
- Network Protocol ArchitecturesDocument17 pagesNetwork Protocol Architecturesamash.emillyNo ratings yet
- TCP-IP and OSIDocument49 pagesTCP-IP and OSIacme bombNo ratings yet
- Techtarget TCPIPDocument3 pagesTechtarget TCPIPyashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Internetworking-1Document91 pagesChapter 4 - Internetworking-1Goitom HaileNo ratings yet
- Overview of TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument3 pagesOverview of TCP/IP Reference ModelReign Earl B. Gup-ayNo ratings yet
- A Brief Summary On TCP/IPDocument30 pagesA Brief Summary On TCP/IPShubham VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- The Network LayerDocument14 pagesThe Network Layerpeter_joonNo ratings yet
- Osimodel 170406162300 PDFDocument42 pagesOsimodel 170406162300 PDFPvkkiy EceNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Module 1 Lesson 1 NotesDocument11 pagesCyber Security Module 1 Lesson 1 NotesAnshpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Linux Unit 5Document22 pagesLinux Unit 5Adeefa AnsariNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument5 pagesPDF DocumentBritney PitttersonNo ratings yet
- 98-366 MVA Slides Lesson 2Document29 pages98-366 MVA Slides Lesson 2cvigaNo ratings yet
- Network NotesDocument24 pagesNetwork Notesmayank barsenaNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument82 pagesNetworkDavidoffNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document32 pagesChapter 1Abdirazak ImanNo ratings yet
- CcnaDocument17 pagesCcnaajinkyaNo ratings yet
- Protocols and The Tcp/Ip Protocol SuiteDocument19 pagesProtocols and The Tcp/Ip Protocol SuiteGeetansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Networking Protocols: Submitted byDocument26 pagesNetworking Protocols: Submitted byvasupahujaNo ratings yet
- 2 Osi-TcpipDocument62 pages2 Osi-TcpipTutun Juhana100% (1)
- CN Basics 5-6-7Document51 pagesCN Basics 5-6-7F. B. I.No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: TCP/IP and OSI: Business Data Communications, 5eDocument40 pagesChapter 5: TCP/IP and OSI: Business Data Communications, 5eGargi Chatterjee MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - 6 Data Communication and Networking: BY Muhammad AfzalDocument36 pagesLecture 5 - 6 Data Communication and Networking: BY Muhammad AfzalHamzah AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Is 103 Module 9 w1112 NvcfiDocument5 pagesIs 103 Module 9 w1112 NvcfiKim Razon SemblanteNo ratings yet
- Defining Networks With The OSI ModelDocument29 pagesDefining Networks With The OSI ModelPradeep ManralNo ratings yet
- Computer FundamentalDocument3 pagesComputer FundamentalabidullahkhanNo ratings yet
- OSI and TCP IP MODELDocument29 pagesOSI and TCP IP MODELHarsh IsamaliaNo ratings yet
- ISS331 Lecture Note 1Document17 pagesISS331 Lecture Note 1RANTSHADI ELIJAHNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document10 pagesAssignment 4anil rajputNo ratings yet
- Protocols and The TCP/IP Suite: Thanks To Prof. William StalingsDocument31 pagesProtocols and The TCP/IP Suite: Thanks To Prof. William StalingsJosé Victor Zaconeta FloresNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 TCP, OSIDocument36 pagesLecture 2 TCP, OSImubeen naeemNo ratings yet
- Network Interface LayerDocument3 pagesNetwork Interface LayerdhasalswapnilNo ratings yet
- #17 TCP-IP ModelDocument11 pages#17 TCP-IP ModelPatel NayakNo ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip: Understanding The Function of ProtocolsDocument10 pagesTcp/Ip: Understanding The Function of Protocolsapurb tewaryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document7 pagesLecture 1owronrawan74No ratings yet
- Chapter One Physical and Data Link Layer OverviewDocument68 pagesChapter One Physical and Data Link Layer Overviewabrham tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Communicating Over The NetworkDocument34 pagesChapter 2 Communicating Over The Networkelaine grace lariosaNo ratings yet
- Network Chapter ThreeDocument46 pagesNetwork Chapter ThreeDaniel AshagrieNo ratings yet
- Osi Model: Network LayeringDocument13 pagesOsi Model: Network LayeringМилош Недић100% (1)
- The Best Guide To Understand What Is TCP (03.01.2024)Document8 pagesThe Best Guide To Understand What Is TCP (03.01.2024)aloishp36No ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument6 pagesTCP Ipkannanperu123No ratings yet
- Deltastar Power Project Services PVT - LTD:: EngineersDocument25 pagesDeltastar Power Project Services PVT - LTD:: EngineerskailasamvvNo ratings yet
- DCCN TplgyDocument40 pagesDCCN TplgyANANYANo ratings yet
- Packet Switching: GROUP 2: Understanding Network Protocols I. Definition of Network ProtocolsDocument18 pagesPacket Switching: GROUP 2: Understanding Network Protocols I. Definition of Network ProtocolsLiezl LagrimasNo ratings yet
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisFrom EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 7th Semester 48 PDFDocument27 pagesLab Report 7th Semester 48 PDFaimenshahzad555No ratings yet
- Presentation On Components of Programming-1Document2 pagesPresentation On Components of Programming-1aimenshahzad555No ratings yet
- Quantum ComputingDocument11 pagesQuantum Computingaimenshahzad555No ratings yet
- Traditional Process ModelsDocument23 pagesTraditional Process Modelsaimenshahzad555No ratings yet
- Present-Simple-Revision-Doc June10Document1 pagePresent-Simple-Revision-Doc June10Sonia AñonNo ratings yet
- Aint It Fun - Guns N RosesDocument4 pagesAint It Fun - Guns N RosesRadio ParamoNo ratings yet
- 00040000001B5000Document3 pages00040000001B5000leonhartani06No ratings yet
- When To Go en PointeDocument4 pagesWhen To Go en PointeBarouni PeggyNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic System Schematic 914-g PDFDocument2 pagesHydraulic System Schematic 914-g PDFpupoz100% (7)
- Footnote To YouthDocument1 pageFootnote To YouthMila Casandra CastañedaNo ratings yet
- DEVIALET ID PRICELIST 28062023Document2 pagesDEVIALET ID PRICELIST 28062023M farhan alfariziNo ratings yet
- Night Ranger - Best of PDFDocument115 pagesNight Ranger - Best of PDFSzabolcs Juhász100% (4)
- NarrativeDocument10 pagesNarrativez26a3100% (1)
- Taller 2° Periodo 28 de Abril-AlexandraDocument4 pagesTaller 2° Periodo 28 de Abril-AlexandraTatiana MurallasNo ratings yet
- Winchester Uke Jam Songbook Vol 2 Ipad Version Rev 01Document62 pagesWinchester Uke Jam Songbook Vol 2 Ipad Version Rev 01Rejane RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Anki DroidDocument88 pagesAnki DroidNestor Manuel Castillo BurgosNo ratings yet
- Past Sins Ereader by Maximillianveers-D40me3jDocument553 pagesPast Sins Ereader by Maximillianveers-D40me3jTobi Nicole GaillardNo ratings yet
- Stairway To Heaven SoloDocument2 pagesStairway To Heaven SoloJakob FrandsenNo ratings yet
- Dim Sum King MenuDocument5 pagesDim Sum King MenuthingsofaugustNo ratings yet
- How ComeDocument24 pagesHow ComeGreenNo ratings yet
- PricelistDocument2,276 pagesPricelistadilcmsNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choices: Encircle The Correct Answer.: Short Service LineDocument3 pagesMultiple Choices: Encircle The Correct Answer.: Short Service LineLester LabitoriaNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - Task Assignment - Old Vs ModernDocument16 pagesWeek 11 - Task Assignment - Old Vs ModernAneli Reza VilcasNo ratings yet
- Manage Your Booking Online - Etihad AirwaysDocument7 pagesManage Your Booking Online - Etihad AirwaysarunrajsNo ratings yet
- Miso Hungry Japanese RecipesDocument27 pagesMiso Hungry Japanese Recipesgojanmajkovic0% (1)
- ZXUR 9000 UR13 UMTS Dimension PricipleDocument22 pagesZXUR 9000 UR13 UMTS Dimension PricipleMokbelNo ratings yet
- 19th Century SculptureDocument444 pages19th Century SculptureHéctor Cayuela Pedreño100% (1)
- Ingles ExamenesDocument4 pagesIngles ExamenesLalo SptNo ratings yet
- False PretenseDocument5 pagesFalse Pretenseapi-25898532No ratings yet
- Film Review - First Man - ARNOLDDocument7 pagesFilm Review - First Man - ARNOLDNaruto UzumakiNo ratings yet
- Honor Honor Unto The Dying - AmbDocument5 pagesHonor Honor Unto The Dying - AmbEveryman EleanyaNo ratings yet
- The Story of Theseus and The MinotaurDocument4 pagesThe Story of Theseus and The MinotaurLeonardo BessaNo ratings yet
- Computerized Embroidery MachineDocument27 pagesComputerized Embroidery Machinevibhav100% (2)
- Test Satzbau de LoesungDocument3 pagesTest Satzbau de LoesungcacbuNo ratings yet