Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 4
Uploaded by
g-ipgp213012270 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views22 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views22 pagesTopic 4
Uploaded by
g-ipgp21301227Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
THEORY AND PRACTICE IN PRIMARY ENGLISH LANGUAGE TEACHING II
Lecture – Week 12- Assessment and Feedback for Primary ESL
Classroom
(1) Classroom-based Assessment (CBA)
Assessment is a fundamental attribute of pupils' learning. An
assessment provides students and teachers with knowledge and
information about student learning outcomes, strengths, and
weaknesses (Mansor et al., 2020).
• In 2011, SBA which consists of both assessments, formative and
summative has been implemented formally on the Year One
students.
• The school-based assessment (SBA) system is a holistic assessment
system conducted in school by subject teachers to assess the
students’ cognitive (intellect), affective (emotional and spiritual)
and psychomotor (physical) aspects.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
SBA, in the Malaysian educational context consists of two main
components known as the academic components (school and
central assessment) and the non-academic components (physical
activities, sports, co-curricular assessment and psychometric
assessment)
It is a form of assessment which is planned, administered, scored
and reported by the subject teachers following the guidelines from
the Malaysian Examination Syndicate (Lembaga Peperiksaan
Malaysia)
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
CBA used to be known as School Based Assessment (SBA) or
Pentaksiran Sekolah starting from 2011. However, in 2016 the term
was changed into Pentaksiran Bilik Darjah (PBD) or CBA.
CBA is a part of the learning process, and it is also one of the
components of School-Based Assessment that focuses on the
development and progress of students holistically (Curriculum
Development Division, 2019).
The goal of the classroom-based assessment (CBA) is to decrease
the burden of the students who depend solely on the exam, albeit
each individual has their unique potential.
Classroom-based Assessment (CBA) was officially established and
introduced to focus on pupils' learning's holistic development and
eradicate exam-oriented learning.
The classroom based assessment (CBA) has been intensified and
given attention in recent years to improve classroom instructional
activities.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
Teachers play a vital and prominent role in implementing CBA by
determining learning objectives based on Learning Standards to
be assessed, planning and building assessment instruments,
performing assessments, recording assessment results, analyzing
assessment information, and reporting and follow-up steps.
Data obtained through CBA is regulated to assist the school and
parents in planning follow-up steps to uplift the students' mastery
and achievement in learning (Curriculum Development Division,
2021).
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
This classroom-based assessment benefits teachers in five aspects.
To identify students’ development as a whole.
To enable teachers in identifying the lesson’s strengths and
weaknesses.
To address the effectiveness of teaching.
To plan and adjust suitable teaching methods.
To take suitable immediate action.
References:
1. Curriculum Development Division. (2021). Classroom assessment
implementation study (PBD) primary school 2021. Malaysian Ministry of
Education.
2. Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia. (2019). Panduan pelaksanaan
pentaksiran bilik darjah. Bahagian Pembangunan Kurikulum.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
(2) Teacher assessing learners
Assessment of Learning - The purpose of this kind of
assessment is usually SUMMATIVE and is mostly done at
the end of a task, unit of work etc. (“It is designed to
provide evidence of achievement to parents, other
educators, the students themselves and sometimes to
outside groups)
Teachers’ Roles in Assessment of Learning
• Teachers have the responsibility of reporting student
learning accurately and fairly, based on evidence
obtained from a variety of contexts and applications.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
• A rationale for undertaking a particular assessment of
learning at a particular point in time.
• Clear descriptions of the intended learning - processes
that make it possible for students to demonstrate their
competence and skill.
• A range of alternative mechanisms for assessing the
same outcomes - public and defensible reference points
for making judgements.
• Transparent approaches to interpretation descriptions
of the assessment process.
• Strategies for recourse in the event of disagreement
about the decisions.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
Assessment for Learning - The emphasis shifts from
summative to FORMATIVE assessment in Assessment
for Learning.
Assessment for Learning happens during the
learning, often more than once, rather than at the end.
Students understand exactly what they are to learn,
what is expected of them and are given feedback and
advice on how to improve their work.
In Assessment for Learning, teachers use assessment
as an investigable tool to find out as much as they can
about what their students know and can do, and what
confusions, preconceptions, or gaps they might have.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
“Teachers also use assessment for learning to enhance
students’ motivation and commitment to learning.
When teachers commit to learning as the focus of
assessment, they change the classroom culture to one
of student success.”
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
Teachers’ Roles in Assessment for Learning:
• Assessment for learning occurs throughout the
learning process.
• It is interactive, with teachers: aligning instruction,
identifying particular learning needs of students or
groups.
• selecting and adapting materials and resources,
creating differentiated teaching strategies and
learning opportunities for helping individual
students move forward in their learning.
• providing immediate feedback and direction to
students.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
Assessment as Learning
Students reflect on their work on a regular basis, usually
through self and peer assessment and decide (often with
the help of the teacher, particularly in the early stages)
what their next learning will be.
• Assessment as learning helps students to take more
responsibility for their own learning and monitoring
future directions.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
Teachers’ Roles in Assessment as Learning
Guide students in developing internal feedback or self-
monitoring mechanisms to validate and question their
own thinking, and to become comfortable with ambiguity
and uncertainty that is inevitable in learning anything
new
Provide regular and challenging opportunities to practise,
so that students can become confident, competent self-
assessors
Monitor students’ megacognitive processes as well as
their learning, and provide descriptive feedback
Create an environment where it is safe for students to take
chances and where support is readily available.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
(3) Peer Assessment (PA)
Peer assessment defined as an arrangement in which individuals
consider the amount, level, value, worth, quality of success of the
products or outcomes of learning of peers of similar status.
Cheng and Warren (2005) believe that there are several approaches
to classroom assessment such as performance assessment, portfolio
assessment, self and peer assessment.
Teachers play a major role in traditional pen and paper and
performance assessment, whereas self and peer assessments are
more student-centered.
PA can be referred to as evaluating the work conducted by the
pupils within the framework of specific criteria by their classmates
(Tunagür, 2021)
Peer assessment is believed to enable learners to develop abilities
and skills denied to them in a learning environment in which the
teacher alone assesses their work.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
PA can enhance social skills, sense of ownership, self-
confidence responsibility, negotiations, and group work
among students. It can also convert passive learning into
active learning in a way that increases interest among
the students (Esfandiari & Tavassoli, 2019)
It provides learners with the opportunity to take
responsibility for analysing, monitoring and evaluating
aspects of both the learning process and product of their
peers.
Peer assessment can act as a socializing force and
enhances relevant skills and interpersonal relationships
between learner groups.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
Considerations for using peer assessment
Let students know the rationale for doing peer review. Explain the
expectations and benefits of engaging in a peer review process.
Consider having students evaluate anonymous assignments for more
objective feedback.
Be prepared to give feedback on students’ feedback to each other.
Display some examples of feedback of varying quality and discuss
which kind of feedback is useful and why.
Give clear directions and time limits for in-class peer review sessions
and set defined deadlines for out-of-class peer review assignments.
Listen to group feedback discussions and provide guidance and input
when necessary.
Student familiarity and ownership of criteria tend to enhance peer
assessment validity, so involve students in a discussion of the criteria
used. Consider involving students in developing an assessment rubric.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
(4) Feedback during oral work
Harmer (2003) states that in the learning process, the teacher
needs to manage the learners' mistakes and give appropriate and
relevant feedback in teaching and learning process.
Oral feedback is regarded as the essence of the interaction
between teachers and students. Oral feedback can be evaluative,
corrective, descriptive, or motivational.
Oral feedback is sometimes underestimated because it is less
formal, but it can be a very powerful and effective tool as it can be
provided easily in the 'teachable moment' and in a timely way.
A teacher's oral feedback facilitate classroom interaction (Irawan
& Salija, 2017; Sahyoni, 2018; Smith & Higgins, 2006) in the
classroom.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
Students realize that oral feedback gives positive effects to
improve their achievement in learning language.
Types of oral feedback are evaluative feedback, descriptive
feedback, corrective feedback, interactional feedback and
motivational feedback.
Oral feedback is effective because it is often given during, or
very quickly following, the learning or task. It offers more
opportunity for dialogue between you and your pupil, ensuring
that they understand the feedback, enabling them to respond to
it and to action the feedback straight away.
Oral feedback consists of positive comments such as “good”,
“ok”, “yes”, and “well done”, it validated a correct response
and also provides support to the learner and fortifies
motivation for learning sustainability (Ellis, 2009).
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
(5) Feedback during written work
Written feedback typically involves both marks or
grades and comments. It is typically given to pupils
after they have completed the task and is usually
intended for them to read on their own.
Written feedback involves feedback given to students’
written work. This type of feedback is usually not
immediate and the teacher has time to think about how
to give feedback and on what.
Assessment and Feedback for Primary
ESL Classroom
Written feedback is a record of guidance meant to help someone in
the workplace improve and develop professionally. Generally,
written feedback can include praise, a look at what can be
improved, and some next steps for the person to follow.
Giving too much of feedback in written form can be overwhelming
for students and difficult to understand. Some students have
difficulty understanding and processing written feedback.
Make comments specific rather than general. Teachers could say,
“use more examples from the text to support this argument,” for
example, rather than labeling a student essay as a “weak
argument.” Connect comments to the learning goals and criteria
associated with the assignment.
Teachers should be precise and thoughtful with their comments in
order to help students concentrate solely on the purposes of their
writing.
Thank you
Tutorial Tasks
Individual Task
1. Explain three characteristics of a good test.
2. What are the elements a teacher should
consider before administering a test to his/her
pupils?
3. List the strengths and weakness of peer
assessment.
4. Ready to share with others when you are
called.
E-LEARNING
Read the available articles from online journals
(MELTA- Malaysian Journal of ELT Research) / FOSTER – JELT /
Journal of Applied Linguistics and Language Research)
and prepare a minimum of 5 ppt slides on the
importance of giving constructive corrective
feedback to students’ work.
You might also like
- Assessment of LearningDocument8 pagesAssessment of LearningSuzette MiagaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Roles of Assessment 1 1Document9 pagesModule 2 Roles of Assessment 1 1Apple04No ratings yet
- Types of Assessment Applicable in CBA at The Early Years EducationDocument5 pagesTypes of Assessment Applicable in CBA at The Early Years EducationGILBERT KIMUTAINo ratings yet
- 03 Policy Guidelines K To 12 AssessmentDocument94 pages03 Policy Guidelines K To 12 AssessmentHenry Kahal Orio Jr.No ratings yet
- Competency 15 Ay 21-22Document11 pagesCompetency 15 Ay 21-22Combo Mary-AnnNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Types of Assessment MethodsDocument10 pagesModule 2 - Types of Assessment MethodsShervee PabalateNo ratings yet
- Task 4Document5 pagesTask 4api-293283735No ratings yet
- Measurement EvaluationDocument8 pagesMeasurement EvaluationSajan KsNo ratings yet
- Ele 127-Teaching and Assessment of Literature StudiesDocument8 pagesEle 127-Teaching and Assessment of Literature StudiesKathlyn Rose SerinoNo ratings yet
- ChapterDocument17 pagesChapterAnas AhmedNo ratings yet
- Education Assessment and Evaluation: Submitted By: Ayesha Khalid Assignment Number 1 B.ED 1.5 YearDocument14 pagesEducation Assessment and Evaluation: Submitted By: Ayesha Khalid Assignment Number 1 B.ED 1.5 YearAyesha KhalidNo ratings yet
- NỘI DUNG TẬP HUẤN HÈ 2018-2019 TIẾNG ANH THCSDocument17 pagesNỘI DUNG TẬP HUẤN HÈ 2018-2019 TIẾNG ANH THCSkiên ngôNo ratings yet
- Assessment Week 17Document4 pagesAssessment Week 17gileenNo ratings yet
- Aasti AssignmentDocument2 pagesAasti AssignmentSonal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 A Perspective On Educational AssessmentDocument8 pagesHandout 1 A Perspective On Educational AssessmentRizaldy GarciaNo ratings yet
- NATURE AND ROLE OF ASSESSMENT of LEARNINGDocument100 pagesNATURE AND ROLE OF ASSESSMENT of LEARNINGRose Dumayac100% (2)
- Action Research With ResultsDocument29 pagesAction Research With ResultsChrisNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Evaluation in Teacher EducatonDocument41 pagesAssessment and Evaluation in Teacher EducatonBOLD BEAUTIFULNo ratings yet
- Thebasic Concept of AssessmentDocument16 pagesThebasic Concept of AssessmentMary Ann Leona SelgaNo ratings yet
- 5440 Unit 4Document7 pages5440 Unit 4Katamelo Jane MofongaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1 (8602)Document25 pagesAssignment No 1 (8602)BILAL ASHRAFNo ratings yet
- Assessment and EvaluationDocument11 pagesAssessment and EvaluationreinaterNo ratings yet
- Educational Assessment: Context for Measurement and EvaluationDocument122 pagesEducational Assessment: Context for Measurement and EvaluationDennis Bautista88% (17)
- Module 2Document15 pagesModule 2Simply Show100% (3)
- Assessing Students in Multigrade ClassesDocument3 pagesAssessing Students in Multigrade ClassesJen LabaoNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document57 pagesModule 4Muminah DorayNo ratings yet
- Assessing Student Performance - EditedDocument8 pagesAssessing Student Performance - EditedDavis KobiaNo ratings yet
- Belano - BSEd3SocStud - Quiz No. 4Document3 pagesBelano - BSEd3SocStud - Quiz No. 4Lenard BelanoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Under The K To 12 For Private SchoolsDocument89 pagesAssessment Under The K To 12 For Private Schoolsrichard alicawayNo ratings yet
- What Is Educational AssessmentDocument24 pagesWhat Is Educational AssessmentKyla S. Gaboy- BTLED 1ANo ratings yet
- Critical Review On AssessmentDocument6 pagesCritical Review On Assessmentapi-402914832No ratings yet
- Assessment for Maximizing Student LearningDocument8 pagesAssessment for Maximizing Student LearningElla ElleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Assessment LearningDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Assessment Learningjudelyn ycotNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Assessment PhilosophyDocument3 pagesEvaluation Assessment Philosophyapi-239774394No ratings yet
- Group 10 Curriculum DevelopmentDocument7 pagesGroup 10 Curriculum DevelopmentWall SembilanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Assessment - Docx Noman ZafarDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Assessment - Docx Noman ZafarMujahid AliNo ratings yet
- Assessment Earl L (2003)Document8 pagesAssessment Earl L (2003)Pia Torres ParraguezNo ratings yet
- Example 2Document22 pagesExample 2Ishani ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Assessment TechniquesDocument4 pagesClassroom Assessment TechniquesFabricio FurtadoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PDFDocument90 pagesUnit 1 PDFJean MarceloNo ratings yet
- A Holistic Mid Semester Assessment - Ika Fathin - Full PaperDocument14 pagesA Holistic Mid Semester Assessment - Ika Fathin - Full PaperlysistratasmaraNo ratings yet
- Policy Guidelines On Classroom Assessment For The K-12 Basic Education ProgramDocument30 pagesPolicy Guidelines On Classroom Assessment For The K-12 Basic Education ProgramnhfdbhddhsdeyterhguyNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Special EducationDocument15 pagesAssessment in Special EducationpandaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Concepts For Web 14 Apr 2014Document6 pagesAssessment Concepts For Web 14 Apr 2014Bernard ChanNo ratings yet
- Name:: Muhammad Zaheer AbbasDocument38 pagesName:: Muhammad Zaheer AbbasZaheer AbbasNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment For Teachers and STDocument6 pagesFormative Assessment For Teachers and STJenny JosonNo ratings yet
- Classroom Assessment For Learning ChappuisDocument5 pagesClassroom Assessment For Learning ChappuisRothinam NirmalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Candidate: Vera Silva Workplace: Burbage Junior School Date Plan Agreed: Tutor: Completion Date: Unit AimDocument6 pagesUnit 7: Candidate: Vera Silva Workplace: Burbage Junior School Date Plan Agreed: Tutor: Completion Date: Unit AimLisa SilvaNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Evaluation 2024Document24 pagesAssessment and Evaluation 2024trevlynrobinsNo ratings yet
- Assessment For LearningDocument22 pagesAssessment For LearningMaria Ilia Yudi Rosita100% (1)
- Module 1 Basic Concepts and Principles in Assessing LearningDocument5 pagesModule 1 Basic Concepts and Principles in Assessing LearningLeth JoseNo ratings yet
- Purposes of Assessment Teaching and LearningDocument9 pagesPurposes of Assessment Teaching and LearningShashankNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment Is A Reflective Process That Intends To Promote Student AttainmentDocument7 pagesFormative Assessment Is A Reflective Process That Intends To Promote Student AttainmentHusni ArtNo ratings yet
- What Is Assessment?Document33 pagesWhat Is Assessment?Sheryl MahinayNo ratings yet
- Asessment of For As LearningDocument20 pagesAsessment of For As LearningGerald Ryan BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Ail2 AlarteDocument4 pagesAil2 AlarteArchie AlarteNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument11 pagesAssessmentAytac İsmayilovaNo ratings yet
- What is Assessment? Understanding its Types & Role in LearningDocument4 pagesWhat is Assessment? Understanding its Types & Role in LearningKai AbsinNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Part IDocument13 pagesTopic 3 Part Ig-ipgp21301227No ratings yet
- Topic 3 Part II TSLB3323Document20 pagesTopic 3 Part II TSLB3323g-ipgp21301227No ratings yet
- Topic 7Document20 pagesTopic 7g-ipgp21301227No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Model of Teaching - ADocument54 pagesTopic 2 - Model of Teaching - Ag-ipgp21301227No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Model of Teaching - BDocument51 pagesTopic 2 - Model of Teaching - Bg-ipgp21301227No ratings yet
- MUHAMMAD NADZMI HAKIM BIN MOHD NAWI - TESL 3 - EDUP3143i - TASK 2Document2 pagesMUHAMMAD NADZMI HAKIM BIN MOHD NAWI - TESL 3 - EDUP3143i - TASK 2g-ipgp21301227No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document13 pagesAssignment 1g-ipgp21301227No ratings yet
- Justification Task 2Document2 pagesJustification Task 2g-ipgp21301227No ratings yet
- The Snouters - Form and Life of - Harald StumpkeDocument126 pagesThe Snouters - Form and Life of - Harald StumpkeAlberto Humanes MuñozNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Fluid StaticsDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Fluid StaticsguhanNo ratings yet
- Strict Liability Offences ExplainedDocument7 pagesStrict Liability Offences ExplainedJoseph ClarkNo ratings yet
- The CatDocument2 pagesThe CatDodi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Nicholas Kaldor On Adam Smith and Allyn Young: Review of Political EconomyDocument20 pagesNicholas Kaldor On Adam Smith and Allyn Young: Review of Political EconomyAdolfo MedranoNo ratings yet
- Ripasso Inglese - ConditionalDocument7 pagesRipasso Inglese - ConditionalStefano Bocco100% (1)
- Selling & Negotiation SkillsDocument70 pagesSelling & Negotiation SkillsMojo JOjoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Relations and Trade Unions MainDocument32 pagesIndustrial Relations and Trade Unions MainKishore MuppaneniNo ratings yet
- Automatic Analysis of Annual Financial Reports: A Case StudyDocument11 pagesAutomatic Analysis of Annual Financial Reports: A Case StudyYuliana MargarettaNo ratings yet
- Status Signalling and Conspicuous Consumption: The Demand For Counterfeit Status GoodDocument5 pagesStatus Signalling and Conspicuous Consumption: The Demand For Counterfeit Status GoodMarliezel CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Historical CriticismDocument1 pageHistorical CriticismPatricia Ann Dulce Ambata67% (3)
- English Revision Notes XIIDocument41 pagesEnglish Revision Notes XIIRämíz MêmóñNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Introduction To Technical AnalysisDocument11 pagesTopic 1 - Introduction To Technical AnalysisZatch Series UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Lightning Attachment Models and Maximum Shielding Failure Current: Application To Transmission LinesDocument9 pagesLightning Attachment Models and Maximum Shielding Failure Current: Application To Transmission LinespedramNo ratings yet
- Guía BaccettiDocument11 pagesGuía BaccettiPercy Andree Bayona GuillermoNo ratings yet
- SAP FICO Resume - Exp - 3.5 YearsDocument3 pagesSAP FICO Resume - Exp - 3.5 Yearsranga67% (3)
- Boston University Student Research: Zipcar, IncDocument28 pagesBoston University Student Research: Zipcar, Incforeverjessx3No ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law and Vectors TutorialDocument9 pagesNewton's Third Law and Vectors TutorialpalparasNo ratings yet
- AOE 5104 Class Notes and ScheduleDocument26 pagesAOE 5104 Class Notes and ScheduleverbicarNo ratings yet
- Handout 2Document3 pagesHandout 2Cale CynthiaNo ratings yet
- Bretzing y Kulhavy (1981) Note-Taking Passage Style PDFDocument9 pagesBretzing y Kulhavy (1981) Note-Taking Passage Style PDFSergio Andrés Quintero MedinaNo ratings yet
- 5 All India Mobile Database SampleDocument15 pages5 All India Mobile Database Sampleali khan Saifi100% (1)
- Enhancing Health and Emotion: Mindfulness As A Missing Link Between Cognitive Therapy and Positive PsychologyDocument14 pagesEnhancing Health and Emotion: Mindfulness As A Missing Link Between Cognitive Therapy and Positive PsychologyTeresa ChuecaNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Carcinoma: Preceptor: Dr. Ratesh KhillanDocument37 pagesEsophageal Carcinoma: Preceptor: Dr. Ratesh KhillanVarun VarnNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Las in Science 5Document4 pages3rd Quarter Las in Science 5Michael Edward De VillaNo ratings yet
- Consortium of National Law Universities: Provisional 5th List - CLAT 2021 - PGDocument3 pagesConsortium of National Law Universities: Provisional 5th List - CLAT 2021 - PGLNo ratings yet
- Jnaanayogam Rushivaani Telugubhakthi ComDocument85 pagesJnaanayogam Rushivaani Telugubhakthi ComkomireddyNo ratings yet
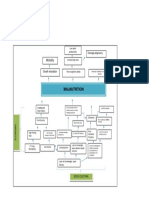
- Problem Tree Analysis MalnutritionDocument1 pageProblem Tree Analysis MalnutritionMho Dsb50% (6)
- Pengaruh Penerapan Model Pembelajaran Core Terhadap Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Matematis Berdasarkan Self-Confidence Siswa Smp/MtsDocument10 pagesPengaruh Penerapan Model Pembelajaran Core Terhadap Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Matematis Berdasarkan Self-Confidence Siswa Smp/MtsGresiya ayudiaNo ratings yet
- Emerald Emerging Markets Case Studies: Article InformationDocument25 pagesEmerald Emerging Markets Case Studies: Article InformationHannah CastroNo ratings yet