Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Data Communication
Uploaded by
pmbrahvee115Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Data Communication
Uploaded by
pmbrahvee115Copyright:
Available Formats
Human beings are the only creatures on the earth who are able to communicate
with each other through the medium of language. But humans take this gift
to another extent. Distance, time, and physical existence of the person don’t
matter in communication these days because they build a communication
system through which they can communicate or share data like images, videos,
text, files, etc with their loved ones anytime anywhere. Communication is
defined as a process in which more than one computer transfers
information, instructions to each other and for sharing resources. Or in
other words, communication is a process or act in which we can send or
receive data. A network of computers is defined as an interconnected collection
of autonomous computers. Autonomous means no computer can start, stop or
control another computer.
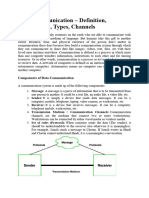
Components of Data Communication
A communication system is made up of the following components:
•Message: A message is a piece of information that is to be transmitted from one
person to another. It could be a text file, an audio file, a video file, etc.
•Sender: It is simply a device that sends data messages. It can be a
computer, mobile, telephone, laptop, video camera, or workstation, etc.
•Receiver: It is a device that receives messages. It can be a computer,
telephone mobile, workstation, etc.
•Transmission Medium / Communication
Channels: Communication
channels are the medium that connect two or more workstations.
Workstations can be connected by either wired media or wireless media.
•Set of rules (Protocol): When someone sends the data (The sender), it
should be understandable to the receiver also otherwise it is meaningless.
For example, Sonali sends a message to Chetan. If Sonali writes in Hindi
and Chetan cannot understand Hindi, it is a meaningless conversation.
Therefore, there are some set of rules (protocols) that is followed by every
computer connected to the internet and they are:
TCP(Transmission Control Protocol): It is responsible for dividing
messages into packets on the source computer and reassembling the
received packet at the destination or recipient computer. It also makes sure that
the packets have the information about the source of the message data, the
destination of the message data, the sequence in which the message data
should be re-assembled, and checks if the message has been sent correctly
to the specific destination.
IP(Internet Protocol): Do You ever wonder how does computer determine
which packet belongs to which device. What happens if the message you
sent to your friend is received by your father? Scary Right. Well! IP is
responsible for handling the address of the destination computer so that
each packet is sent to its proper destination.
Type of data communication
As we know that data communication is communication in which we can
send or receive data from one device to another. The data communication is
divided into three types:
•Simplex Communication: It is one-way communication or we can say that
unidirectional communication in which one device only receives and another
device only sends data and devices uses their entire capacity in
transmission. For example, IoT, entering data using a keyboard, listing music
using a speaker, etc.
•Half Duplex communication: It is a two-way communication or we can say that
it is a bidirectional communication in which both the devices can send
and receive data but not at the same time. When one device is sending data then
another device is only receiving and vice-versa. For example, walkie-
talkie.
•Full-duplex communication: It is a two-way communication or we can say that
it is a bidirectional communication in which both the devices can send and
receive data at the same time. For example, mobile phones, landlines, etc.
Communication Channels
Communication channels are the medium that connects two or more
workstations. Workstations can be connected by either wired media or wireless
media. It is also known as a transmission medium. The transmission medium or
channel is a link that carries messages between two or more devices. We can
group the communication media into two categories:
Guided media transmission
Unguided media transmission
1. Guided Media: In this transmission medium, the physical link is created
using wires or cables between two or more computers or devices, and then the
data is transmitted using these cables in terms of signals. Guided media
transmission of the following types:
1. Twisted pair cable: It is the most common form of wire used in
communication. In a twisted-pair cable, two identical wires are wrapped
together in a double helix. The twisting of the wire reduces the crosstalk. It
is known as the leaking of a signal from one wire to another due to which
signal can corrupt and can cause network errors. The twisting protects the
wire from internal crosstalk as well as external forms of signal interference.
Types of Twisted Pair Cable :
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): It is used in computers and telephones
widely. As the name suggests, there is no external shielding so it does not
protects from external interference. It is cheaper than STP.
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP): It offers greater protection from crosstalk due
to shield. Due to shielding, it protects from external interference. It is heavier and
costlier as compare to UTP.
•Coaxial Cable: It consists of a solid wire core that is surrounded by one or
more foil or wire shields. The inner core of the coaxial cable carries the
signal and the outer shield provides the ground. It is widely used for television
signals and also used by large corporations in building security systems.
Data transmission of this cable is better but expensive as compared to twisted
pair.
•Optical fibers: Optical fiber is an important technology. It transmits large
amounts of data at very high speeds due to which it is widely used in
internet cables. It carries data as a light that travels inside a thin glass fiber.
The fiber optic cable is made up of three pieces:
•Core: Core is the piece through which light travels. It is generally created
using glass or plastic.
•Cladding: It is the covering of the core and reflects the light back to the
core.
•Sheath: It is the protective covering that protects fiber cable from the
environment.
2. Unguided Media: The unguided transmission media is a transmission mode
in which the signals are propagated from one device to another
device wirelessly. Signals can wave through the air, water, or vacuum. It is
generally used
various parts : to transmit signals in all directions. Unguided Media is further
divided into
1.Microwave: Microwave offers communication without the use of cables.
Microwave signals are just like radio and television signals. It is used in
long- distance communication. Microwave transmission consists of a
transmitter, receiver, and atmosphere. In microwave communication, there are
parabolic antennas that are mounted on the towers to send a beam to
another antenna. The higher the tower, the greater the range.
2.Radio wave: When communication is carried out by radio frequencies, then
it is termed radio waves transmission. It offers mobility. It is consists of the
transmitter and the receiver. Both use antennas to radiate and capture the radio
signal.
1.Infrared: It is short-distance communication and can pass through any
object. It is generally used in TV remotes, wireless mouse, etc.
You might also like
- Data Communication TypesDocument3 pagesData Communication TypesRana Sarfraz NawazNo ratings yet
- Transmission ModesDocument18 pagesTransmission ModesMedhanshu KaushikNo ratings yet
- DC 1Document19 pagesDC 1olivianatasha40No ratings yet
- Computer Communications and NetworksDocument19 pagesComputer Communications and NetworksArslan Baloch AshuNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Unit - 1Document28 pagesData Communication Unit - 1shersuraj09No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ICTDocument19 pagesChapter 4 ICTJOHN CONo ratings yet
- Computer Communications and Networks: (Week 1) by Hafiz Aamir HafeezDocument26 pagesComputer Communications and Networks: (Week 1) by Hafiz Aamir HafeezAbdullah AnwaarNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Unit 1Document74 pagesComputer Networks Unit 1appuzzz2000zzzzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Networking: IncludesDocument19 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Networking: IncludesDawod YimerNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document12 pagesUnit 5Ashish JoshiNo ratings yet
- Data Communication CircuitsDocument19 pagesData Communication Circuitsshikha singhNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Unit 1Document71 pagesComputer Networks Unit 1sadiq AadilNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument11 pagesInformation Technologysana taseerNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Data Communication NetworkDocument39 pagesUnit 7 Data Communication NetworksimantNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Introduction To Computer Networks: M.Sc. (Computer Application) Sem-IIDocument537 pagesComputer Networks Introduction To Computer Networks: M.Sc. (Computer Application) Sem-IITanya JindalNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument8 pagesData Communicationlorry lamNo ratings yet
- Ict NotesDocument18 pagesIct NotesUmar MaazNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER THREE Intro To CompDocument16 pagesCHAPTER THREE Intro To CompSintudNo ratings yet
- Internet: Short Cut To Remember Wet Figce WWW E-Mail Telnet FTP Intranet Gopher Chat Group ExtranetDocument15 pagesInternet: Short Cut To Remember Wet Figce WWW E-Mail Telnet FTP Intranet Gopher Chat Group ExtranetMaruf AhmedNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationsDocument13 pagesData CommunicationsEmmanuel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- As Old GrowDocument25 pagesAs Old GrowTemesgenNo ratings yet
- Data Communication-Converted-1Document27 pagesData Communication-Converted-1Zain SahbNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemDocument5 pagesComputer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemShepherd AndoliniNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Introduction To Network Architectures, Protocol Layers, and Service ModelsDocument42 pagesUnit 1-Introduction To Network Architectures, Protocol Layers, and Service ModelsKartik PandeyNo ratings yet
- BSC VI Sem CN Unit IDocument33 pagesBSC VI Sem CN Unit IG51Mamatha PatlollaNo ratings yet
- CSE 321 Principles of Telecommunication - Lecture - NoteDocument10 pagesCSE 321 Principles of Telecommunication - Lecture - Notejohnnnabugwu515No ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document8 pagesChapter 03Muqadas HakimNo ratings yet
- Data Communication NotesDocument8 pagesData Communication NotesandreeNo ratings yet
- LSN 1Document5 pagesLSN 1Prashant sapkotaNo ratings yet
- Data Communications: Unit - 1Document22 pagesData Communications: Unit - 1Dhanashri DevalapurkarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Data Communication and Computer NetworkDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 5 Data Communication and Computer NetworkKinfe BeregaNo ratings yet
- Presentatio N ON Data CommunicationsDocument27 pagesPresentatio N ON Data CommunicationsGeetansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- CN Course MaterialsDocument19 pagesCN Course MaterialsRajiNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemDocument10 pagesComputer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemShepherd AndoliniNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument13 pagesComputer NetworkAyushman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document7 pagesChapter 6haileNo ratings yet
- Ca CH-3 Note 1Document17 pagesCa CH-3 Note 1Satya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 DCNDocument17 pagesMod 1 DCNSUREDDY TANUJA MSCS2018No ratings yet
- Cs3591 CN Unit 1 Notes EduenggDocument67 pagesCs3591 CN Unit 1 Notes Eduenggraheshj21No ratings yet
- Data Communication - Lesson 4Document29 pagesData Communication - Lesson 4moizarain.mzNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument13 pagesComputer NetworkParidhi GaurNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument103 pagesComputer NetworksNitinNo ratings yet
- Computer ApplicationDocument11 pagesComputer ApplicationVineet PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter No: 1 Introduction To Data CommunicationDocument21 pagesChapter No: 1 Introduction To Data CommunicationRavindra MahajanNo ratings yet
- DATA CommunicationsUNIT 3Document69 pagesDATA CommunicationsUNIT 3Anonymous l0bNv6G0% (1)
- Uses of Computer NetworksDocument19 pagesUses of Computer NetworksSushant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Data Communication ConceptsDocument22 pagesData Communication ConceptsDibyendu BiswasNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemDocument6 pagesComputer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemShepherd AndoliniNo ratings yet
- DICO DCC 22414 Chap. 1 To 5 NotesDocument116 pagesDICO DCC 22414 Chap. 1 To 5 NotesAll most HereNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument136 pagesComputer NetworksEr Navdeep Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Internet & Web Design Reviewer PDFDocument14 pagesInternet & Web Design Reviewer PDFPatricia May CayagoNo ratings yet
- Chapter No: 1 Introduction To Data CommunicationDocument21 pagesChapter No: 1 Introduction To Data CommunicationPrernaNo ratings yet
- Course Material 1Document63 pagesCourse Material 1Ehtisham SaeedNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NetworkingDocument29 pagesUnit 1 NetworkingVanshika SharmaNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 1Document52 pagesCN Unit 1megha.bhoityNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks NotesDocument204 pagesComputer Networks Notessatishchinni1245No ratings yet
- Network Components EnamDocument5 pagesNetwork Components EnamturiagabaNo ratings yet
- Cs1302 Computer Networks Full NotesDocument135 pagesCs1302 Computer Networks Full NotesRengabilla100% (6)
- ITK User InterfaceDocument40 pagesITK User InterfaceSergio Ernesto Villegas Milano100% (1)
- Ring and Johnson CounterDocument5 pagesRing and Johnson CounterkrsekarNo ratings yet
- Riello 40 FsDocument7 pagesRiello 40 FsNebojsaNo ratings yet
- Ubidots MQTT Broker - Ubidots Help CenterDocument7 pagesUbidots MQTT Broker - Ubidots Help CenterMiguel Garcia OchoaNo ratings yet
- Ds 1621Document16 pagesDs 1621AnassFouadNo ratings yet
- BGD 500-S Automatic Digital Pull-Off Adhesion TesterDocument2 pagesBGD 500-S Automatic Digital Pull-Off Adhesion TesterNguyễn Xuân NamNo ratings yet
- Assessment Guideline July 2021Document10 pagesAssessment Guideline July 2021Seminar Group09No ratings yet
- CNC Turning Programming Exellent ExplainationDocument29 pagesCNC Turning Programming Exellent ExplainationschrienerNo ratings yet
- Back-UPS®RS BR400G-JP & 550G-JPDocument8 pagesBack-UPS®RS BR400G-JP & 550G-JPcezarignatNo ratings yet
- Epson FX 890 DatasheetDocument2 pagesEpson FX 890 DatasheetMarcos ZamorioNo ratings yet
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument40 pagesRepublic of The Philippinesrussell apura galvezNo ratings yet
- Man Inst Mru 5 r9Document148 pagesMan Inst Mru 5 r9Miguel Martinez100% (1)
- 3.1 Faster - R-CNN - Towards - Real-Time - Object - Detection - With - Region - Proposal - NetworksDocument13 pages3.1 Faster - R-CNN - Towards - Real-Time - Object - Detection - With - Region - Proposal - NetworksAmrutasagar KavarthapuNo ratings yet
- A Primer On A Good Instrument Grounding SystemDocument26 pagesA Primer On A Good Instrument Grounding SystemwlmostiaNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Communication Engineering: Projectbased Lab Report OnDocument21 pagesElectronics and Communication Engineering: Projectbased Lab Report OnGowtham RoxtaNo ratings yet
- Networking AssignmentDocument125 pagesNetworking AssignmentAthl S100% (5)
- TWIDO-TWD LCAE 40DRF DocumentDocument8 pagesTWIDO-TWD LCAE 40DRF DocumentA MNo ratings yet
- KePol Prospekt E Doppelseiten Self Service LockersDocument9 pagesKePol Prospekt E Doppelseiten Self Service LockersAJNo ratings yet
- Sales InvoiceDocument11 pagesSales InvoiceEdril HermayendraNo ratings yet
- Jet Airways Web Booking ETicket (YFHOWT) - Puthiya VeetilDocument3 pagesJet Airways Web Booking ETicket (YFHOWT) - Puthiya VeetilpetrishiaNo ratings yet
- Eaton VFDDocument94 pagesEaton VFDsalimskaini1990No ratings yet
- LT5012 PCB BroInside Final PDFDocument39 pagesLT5012 PCB BroInside Final PDFDavid LopezNo ratings yet
- Google Apps For Education Tips For Teachers by TeachersDocument19 pagesGoogle Apps For Education Tips For Teachers by TeachersmnorkunNo ratings yet
- Logistics & SCM SyllabusDocument1 pageLogistics & SCM SyllabusVignesh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Ranap Release CauseDocument397 pagesRanap Release CauseKamana Khare0% (1)
- Financial Accounting Assignment: Home Assignment by MehakDocument3 pagesFinancial Accounting Assignment: Home Assignment by MehakAnam TahirNo ratings yet
- TR400 Tachometer ES400 Rev F 111813Document2 pagesTR400 Tachometer ES400 Rev F 111813Juan GalvesNo ratings yet
- Testing of TranformerDocument7 pagesTesting of Tranformerkanchan206100% (1)
- 14JE000423-Rajat Kumar Jain - B.Tech (Computer Science and Engineering)Document2 pages14JE000423-Rajat Kumar Jain - B.Tech (Computer Science and Engineering)AshNo ratings yet
- Article by NSHIMIYIMANA GASTON & GERMAINDocument12 pagesArticle by NSHIMIYIMANA GASTON & GERMAINngaston2020No ratings yet
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.From EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNFrom EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksFrom EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsFrom EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNo ratings yet
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionFrom EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- PHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZFrom EverandPHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsFrom EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo ratings yet
- Designing and Building Security Operations CenterFrom EverandDesigning and Building Security Operations CenterRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityFrom EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Mastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionFrom EverandMastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionNo ratings yet
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachFrom EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNo ratings yet
- FTTx Networks: Technology Implementation and OperationFrom EverandFTTx Networks: Technology Implementation and OperationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)From EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)No ratings yet
- ITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideFrom EverandITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)