0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views32 pagesPumps
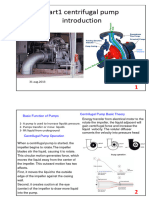
The document discusses different types of pumps used in sewerage systems. It describes centrifugal pumps, including radial flow and mixed flow centrifugal pumps. Centrifugal pumps work by using an impeller to impart kinetic energy to liquid, increasing its pressure. They are commonly used when high flow rates and moderate head increases are required. Radial flow pumps discharge fluid radially and have low specific speeds up to 4200. Mixed flow pumps have specific speeds ranging from 4200 to 9000 and are used for medium heads from 8 to 15 meters.
Uploaded by
Ro CkyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views32 pagesPumps
The document discusses different types of pumps used in sewerage systems. It describes centrifugal pumps, including radial flow and mixed flow centrifugal pumps. Centrifugal pumps work by using an impeller to impart kinetic energy to liquid, increasing its pressure. They are commonly used when high flow rates and moderate head increases are required. Radial flow pumps discharge fluid radially and have low specific speeds up to 4200. Mixed flow pumps have specific speeds ranging from 4200 to 9000 and are used for medium heads from 8 to 15 meters.
Uploaded by
Ro CkyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd