Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 - Ecology
Uploaded by
ysa.antonio120 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views13 pagesCell is the fundamental living unit that exhibits the basic characteristics of life. There are two main types of cells - eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles and have a nucleus containing DNA, while prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and complex organelles. Prokaryotic cells are also about 10 times smaller than eukaryotic cells.
Original Description:
Original Title
2.-Ecology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCell is the fundamental living unit that exhibits the basic characteristics of life. There are two main types of cells - eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles and have a nucleus containing DNA, while prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and complex organelles. Prokaryotic cells are also about 10 times smaller than eukaryotic cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views13 pages2 - Ecology
Uploaded by
ysa.antonio12Cell is the fundamental living unit that exhibits the basic characteristics of life. There are two main types of cells - eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles and have a nucleus containing DNA, while prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and complex organelles. Prokaryotic cells are also about 10 times smaller than eukaryotic cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Cell
Fundamental living unit of any
organism that exhibit the basic
characteristic of life.
Two types of cell
• Eukaryotic cell
• Prokaryotic cell
Eukaryotic Cell
• Contain membrane bound organelles
• With true nucleus containing DNA.
• With cell wall that provide rigidity, shape and
protection
• Cell wall contain cellulose, pectin, chitin and
mineral salts.
• Energy is produced with in the mitochondria.
Prokaryotic Cell
• Exhibits all the characteristic of life
• No true nucleus or a complex system of
membranes and membrane bound organelles.
• Bacterial cell wall are more complex, containing
peptidoglycan or sometimes
lipopolysaccharides.
• 10x smaller than eukaryotic cells
• Reproduction is by binary fission
• Energy came from cell wall.
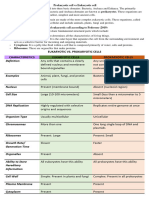
Difference between Eukaryotic and
Prokaryotic cell
Features Prokaryotic Organism Eukaryotic Organism
Nucleus Absent Present
Membrane bound ed Absent Present
organelles
Chromosomes Single chromosomes Chromosomes appear in
pairs
Cell division Divides by fission Divides by mitosis
Flagella Simple flagella Complex flagella
Ribosomes Small ribosomes Larger ribosomes
Cytoskeleton Absent Present
Cellulose Absent Present in cell wall
cytoplasm Not separated from the Separated from nucleus
nucleus
Microbial Ecology
• is the study of the numerous
interrelationships between microorganisms
and the world around them.
• how microbes interact with organisms other
than microbes, and how microbes interact
with the non living world around them.
Symbiosis
• Defined as the living together or close
association of two dissimilar organism.
(usually two dissimilar species)
SYMBIONTS- the organism that live in a
symbiotic relationship.
Symbiotic relationship
• Mutualism-Is a symbiotic relationship that is
beneficial to both symbionts
• Commensalism- A symbiotic relationship that
is beneficial to one symbionts and is of no
consequence to the other.
HOST- is define as a living organism that
harbors another living organism.
• Parasitism- is a symbiotic relationship that is
beneficial to one symbiont (the parasite) and
detrimental to the other symbiont (the host).
• Synergism- two or more microorganism may
team up to produce a disease neither could
cause by itself.
Indigenous microflora of Humans
• Refers on the past as normal microflora
• It includes all the mirobes such as bacteria,
fungi, protozoa, and viruses that reside on or
with in the person
Areas of the body where most indigenous
microflora reside
• Skin
• Mouth
• Eyes
• Upper respiratory tract
• Gastrointestinal tract
• Genitourinary tract
Beneficial and harmful roles of indigenous
microflora
• Microbes provides constant source of irritants
and antigens to stimulate the immune system.
• Enhance body’s protection against microbes.
Microbial antagonism
• Microbes against microbes.
• Adverse effect that some microbes have on
other microbes
• Production of antibodies and bacteriocins.
You might also like
- Class9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesDocument7 pagesClass9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesabhishekNo ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument76 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To MicrobiologyFjNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Notes Cell Basic Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCH 1 Notes Cell Basic Unit of LifetsudheraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 (Sep 9) - Microscopy and ProkaryotesDocument46 pagesLecture 2 (Sep 9) - Microscopy and ProkaryotesRhomoneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 2Document52 pagesLecture 1 2مروه عماد عيسىNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 - MicrobiologyDocument127 pagesUnit 9 - Microbiologynumberr515No ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- An Overview of Microbiology: Dr. Thaigar Parumasivam Email: Thaigarp@usm - MyDocument26 pagesAn Overview of Microbiology: Dr. Thaigar Parumasivam Email: Thaigarp@usm - MyHuii Jiing WongNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument5 pages1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesJosh Miguel BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document4 pagesCell (Biology)Marella SatorreNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Structure 1Document30 pagesBacterial Structure 1محمد ناصرNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Bacterial CellDocument41 pagesParts of A Bacterial CellAbegail AguirreNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Study of Life: Dr. Sajeela AhmedDocument32 pagesWelcome To The Study of Life: Dr. Sajeela AhmedMohammad NaqashNo ratings yet
- Lesson II: The Living Cells: Jonald P. Regio, RN, RMTDocument30 pagesLesson II: The Living Cells: Jonald P. Regio, RN, RMTDana TabingNo ratings yet
- Farmasi 1Document50 pagesFarmasi 1Suci Umniyah RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Cells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic CellDocument3 pagesCells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic Cellgafir1230No ratings yet
- Module 3-P. E. CellsDocument4 pagesModule 3-P. E. CellsRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- Biol 1017-Cell Biology: Prokaryotes & MicrosDocument50 pagesBiol 1017-Cell Biology: Prokaryotes & MicrosJoshua HarveyNo ratings yet
- Cellular Diversity (Lec, 4)Document21 pagesCellular Diversity (Lec, 4)Maryum JavedNo ratings yet
- EUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Document2 pagesEUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Alea AicoNo ratings yet
- Botany Full PDF EMDocument72 pagesBotany Full PDF EMAbinaya PalaniNo ratings yet
- CellDocument6 pagesCellHONEYLYN CASINGNo ratings yet
- Training Manual For Medical RepresentativesDocument74 pagesTraining Manual For Medical RepresentativesAman Ghayas50% (4)
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDocument14 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDaniella Pasilbas SabacNo ratings yet
- MicroorganismsDocument51 pagesMicroorganismsAchira DeemanthaNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- BNC MicroorganismsDocument11 pagesBNC Microorganismsashenafihailemariam43No ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument21 pagesProkaryotes and EukaryotesJeff Hambre100% (2)
- Robert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byDocument11 pagesRobert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byKamlesh RatnamNo ratings yet
- Medical Microbiology Anesthesia Lecture 2Document39 pagesMedical Microbiology Anesthesia Lecture 2Ubaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Medical Microbiology Anesthesia Lecture 2Document39 pagesMedical Microbiology Anesthesia Lecture 2Ubaid KhanNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument45 pagesCELLKimberly Clarisse VegaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document14 pagesUnit 1Pratik PawarNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Basic Cell BiologyDocument116 pagesUnit-I Basic Cell Biologyvishav sharmaNo ratings yet
- Micro Chapter 2Document34 pagesMicro Chapter 2Farrah GwynethNo ratings yet
- Zoology 100 Notes 2Document27 pagesZoology 100 Notes 2Bethany Jane Ravelo IsidroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and 2-LecDocument10 pagesChapter 1 and 2-LecPam ArienzaNo ratings yet
- The Building Blocks of LifeDocument105 pagesThe Building Blocks of LifePradhees BtechNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument25 pagesCell StructuresAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document67 pagesChapter 1Serra ÖzışıkNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Notes Final-2Document58 pagesMicrobiology Notes Final-2arvindk962706No ratings yet
- Lab 3Document6 pagesLab 3عبد اللطيف عبد الستار اسماعيل ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument33 pagesCell Structure and FunctionFahim Abid100% (1)
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellDocument49 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellArthe RajarajanNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 3Document22 pagesLecturer 3Rao ChandNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Cell OrganisationDocument3 pagesGeneral Principles of Cell Organisation22194No ratings yet
- CeluarDocument7 pagesCeluarJef PerezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Sep 10) - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument56 pagesLecture 3 (Sep 10) - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesRhomoneNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 3Document32 pagesUnit 1 - 3Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- SBT 2173: Introduction To Microbiology: Dr. Elizabeth Mitaki Lesson 1Document30 pagesSBT 2173: Introduction To Microbiology: Dr. Elizabeth Mitaki Lesson 1Derrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- HSCI100 Lecture02 F2023Document56 pagesHSCI100 Lecture02 F2023niko.carson.9No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsDocument62 pagesChapter 2: Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsIsabelle Hazel BenemileNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes & EukaryotesDocument10 pagesProkaryotes & EukaryotesJogie De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Post Lab - Activity 1 Cell BioDocument32 pagesPost Lab - Activity 1 Cell Bioraphael100% (1)
- Introduction To CellsDocument39 pagesIntroduction To CellsShardul DalviNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Sensitivity Test and DrugDocument3 pagesAntibiotic Sensitivity Test and DrugRajeshNo ratings yet
- Mastitis Prevention and TreatmentDocument52 pagesMastitis Prevention and TreatmentIbrahim Elkamash0% (1)
- Structure of BacteriaDocument95 pagesStructure of BacteriaMaulyda Awwaliyah PawallungiNo ratings yet
- Annan 2023Document8 pagesAnnan 2023Ana Beatriz Vasquez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 2 - Tugas Pengendalian Vektor - Pertemuan 2Document13 pagesKelompok 2 - Tugas Pengendalian Vektor - Pertemuan 2Irene Pramesti DiningrumNo ratings yet
- Establishment and Validation of A Pseudovirus Neutralization AssayDocument7 pagesEstablishment and Validation of A Pseudovirus Neutralization AssayNandagopal PaneerselvamNo ratings yet
- Monuril Vs CiproDocument7 pagesMonuril Vs Ciproalaa morsyNo ratings yet
- Preparing A Bacterial SmearDocument5 pagesPreparing A Bacterial SmearReg Lagarteja100% (1)
- Amebia PDFDocument6 pagesAmebia PDF04lubna_869632400No ratings yet
- Jurnal TC KohDocument4 pagesJurnal TC KohariefNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Report - Exercise 4 - Isolation and Cultivation of MicroorganismsDocument18 pagesPost Lab Report - Exercise 4 - Isolation and Cultivation of MicroorganismsDara KwonNo ratings yet
- EVS033 Environmental Microbiology - Toxilogy PDFDocument285 pagesEVS033 Environmental Microbiology - Toxilogy PDFRahulNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology: TalaroDocument50 pagesFoundations in Microbiology: Talaromertx013No ratings yet
- B.sc. Medical Laboratory Sciences Medical Bacteriology (MLS 2413) (PDFDrive)Document101 pagesB.sc. Medical Laboratory Sciences Medical Bacteriology (MLS 2413) (PDFDrive)Isah MohammedNo ratings yet
- BD Diagnostic Systems CatalogueDocument197 pagesBD Diagnostic Systems CatalogueadvokatdaliborNo ratings yet
- Namita JaggiDocument4 pagesNamita JaggiIJAMNo ratings yet
- Vaginal MicrobiomeDocument9 pagesVaginal MicrobiomeRika Yulizah GobelNo ratings yet
- Bone and Joint Infection: Matthew Dryden RHCH WinchesterDocument29 pagesBone and Joint Infection: Matthew Dryden RHCH Winchesterdryden123No ratings yet
- Report Text COVID-19Document1 pageReport Text COVID-19Baba NanaNo ratings yet
- Exp6 Mic220 Discussion and ConclusionDocument3 pagesExp6 Mic220 Discussion and ConclusionameliaNo ratings yet
- LatrinesDocument13 pagesLatrinesSaurav ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Report: Patient Name: Hemant Kumar HEMAM339748730 0127VA002698Document2 pagesDiagnostic Report: Patient Name: Hemant Kumar HEMAM339748730 0127VA002698Hemant ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Celulitis PDFDocument9 pagesCelulitis PDFGazade GarciaNo ratings yet
- Program Outcomes (PO's), Program Specific Outcomes (PSO's) and Course Outcomes (CO's)Document35 pagesProgram Outcomes (PO's), Program Specific Outcomes (PSO's) and Course Outcomes (CO's)Mukesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Penta VaccineDocument4 pagesPenta VaccineArlyn Barte AlboloteNo ratings yet
- Black FliesDocument54 pagesBlack FliesTadesse MenjettaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial ConjunctivitisDocument32 pagesBacterial ConjunctivitisYouhengNo ratings yet
- South Africa CMV Viral Load Testing May2015Document4 pagesSouth Africa CMV Viral Load Testing May2015EnergadeNo ratings yet
- Infection With Toxoplasma Gondii Can Promote Chronic Liver Diseases in HIV-infected IndividualsDocument7 pagesInfection With Toxoplasma Gondii Can Promote Chronic Liver Diseases in HIV-infected IndividualsVerena AlvesNo ratings yet
- Pertussis Whooping Cough Letter To ParentsDocument1 pagePertussis Whooping Cough Letter To ParentsPiper Garner RiddleNo ratings yet