Professional Documents
Culture Documents
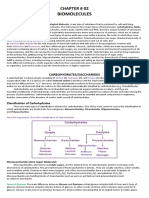
Carbohydrates and Monosacchirides
Uploaded by
aadityabhagchandani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesCarbohydrates and Monosacchirides
Uploaded by
aadityabhagchandaniCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
What are
Carbohydrates?
• Carbohydrates are organic compounds
composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
They are the most abundant organic
compounds on Earth and are vital for life.
Found in all plants and animals. Essential for
energy production, cell structure, and cell
signaling.
Monosaccharides
• Monosaccharides are the simplest type of
carbohydrate, consisting of a single sugar
molecule.
• Soluble in water and have a sweet taste.
Structure of
Monosaccharides
• Monosaccharides typically consist of 3-7
carbon atoms. Carbon atoms can be
arranged in a linear or cyclic chain.
Monosaccharides are classified as
aldoses or ketoses based on the
placement of the carbonyl group (C=O)
in the molecule.
• Common monosaccharides:
Examples of 1. Glucose: The primary source of energy
for cells.
Monosaccharides 2. Fructose: Found in fruits and honey,
used as a sweetener.
3. Galactose: Present in milk, dairy
products, and cell membranes.
Functions of
Monosaccharides
• Monosaccharides have several vital functions:
1. Energy production: Broken down into glucose for
cellular energy.
2. Cell structure: Building blocks of glycoproteins
and glycolipids in cell membranes.
3. Cell signaling: Involved in intercellular
communication.
Conclusion
• Carbohydrates are essential for life
and serve various critical functions.
• Monosaccharides are the simplest
type, acting as building blocks for
other carbohydrates.
• They play crucial roles in energy
production, cell structure, and cell
signaling.
You might also like
- Biological+Macromolecules KalmaDocument40 pagesBiological+Macromolecules Kalmajudy andradeNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts: BiochemistryDocument24 pagesKey Concepts: BiochemistryJustyNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument81 pagesBiological MoleculesShane Marcande Calicdan100% (1)
- Biomolecules: Dr. Vishwajeet S. GhorpadeDocument49 pagesBiomolecules: Dr. Vishwajeet S. GhorpadeVishwajeet GhorpadeNo ratings yet
- PS Week 5 - BiomoleculesDocument40 pagesPS Week 5 - BiomoleculesPrincess AguiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Chapter 2 - Macromolecules NotesDocument41 pagesUnit 2 - Chapter 2 - Macromolecules Notesapi-375285021No ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument17 pagesCarbohydratesShane Patrick Panilag0% (1)
- The Chemistry of Life Organic CompoundsDocument67 pagesThe Chemistry of Life Organic CompoundsHahe HshdbNo ratings yet
- Mic 322 (1) - 2023Document33 pagesMic 322 (1) - 2023kilanko timilehinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Biomolecules CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesLesson 7 Biomolecules CarbohydratesPsyche GaminNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument40 pagesBiological MacromoleculesCristinaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4: The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesDocument8 pagesLESSON 4: The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesArabela LendioNo ratings yet
- BTE101 Lecture3.1 Macromolecules1 MHU BRACU SpringSemester2023 FinalDocument57 pagesBTE101 Lecture3.1 Macromolecules1 MHU BRACU SpringSemester2023 FinalM.H. RafidNo ratings yet
- 044BIO11-09 Biomolecules (Study Notes)Document17 pages044BIO11-09 Biomolecules (Study Notes)Zen FredyNo ratings yet
- Biology UNIT 2Document72 pagesBiology UNIT 2suba052k09No ratings yet
- Unit-4 (Chemistry OfCarbohydrates)Document25 pagesUnit-4 (Chemistry OfCarbohydrates)NoorNo ratings yet
- Humans in The World of Biology Humans in The World of BiologyDocument32 pagesHumans in The World of Biology Humans in The World of BiologyJEANNo ratings yet
- BiologicalmoleculesDocument58 pagesBiologicalmoleculesrhaineNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds of ImportanceDocument11 pagesOrganic Compounds of ImportanceHibo rashidNo ratings yet
- Biology ReportDocument64 pagesBiology ReportChelo IlagNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument54 pagesBiomoleculeslevi0417No ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument11 pagesBiomoleculesAdul basit mughalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Introduction To Biochemistry, Occurrence and ClassificationDocument25 pagesLecture 1-Introduction To Biochemistry, Occurrence and ClassificationMohana MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- PolysaccharidesDocument5 pagesPolysaccharideszuharizwan715No ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument8 pagesBiological MoleculesQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 Day 2Document30 pagesBio 1 Day 2Bea SoledadNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument32 pagesCarbohydrateHaya NemerNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument6 pagesBiological MacromoleculesglennNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules 1Document29 pagesBiomolecules 1jefrillevaldezNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument35 pagesCarbohydratesJasmine-Nezzar ImbigNo ratings yet
- MACROMOLECULESDocument17 pagesMACROMOLECULESPhoebe Kate YaunNo ratings yet
- Biochemistery Mid TermDocument159 pagesBiochemistery Mid TermPh. Omar yasirNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument45 pagesBiomoleculesDummy AccountNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - CarbohydrateDocument29 pagesBiomolecules - CarbohydrateCharlene Marri BajuyoNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Biological Molecule Ppt.Document37 pages1.4 Biological Molecule Ppt.yohoho 87No ratings yet
- Organic Compounds in Living Things: PropertiesDocument96 pagesOrganic Compounds in Living Things: PropertiesTUĞRUL ERGÜLNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates PDFDocument31 pagesCarbohydrates PDFDara Arabella AndalesNo ratings yet
- Sbt1102 - Biochemistry Unit 1 CarbohydratesDocument22 pagesSbt1102 - Biochemistry Unit 1 CarbohydratesJeremy CorrenNo ratings yet
- 2019 BB3 CarbohydratesDocument13 pages2019 BB3 CarbohydrateserikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - BiomacromoleculesDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - BiomacromoleculesWafaaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Intro 2017Document24 pagesBiochem Intro 2017Dianne Joy LeybaNo ratings yet
- 1 Macromolecule 2ndQDocument82 pages1 Macromolecule 2ndQAllysa ChanNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument8 pagesBIOMOLECULESjorel marcoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Biochemistry LectureDocument48 pagesCarbohydrates Biochemistry Lecturerabiullah.edu987No ratings yet
- Module 5 CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesModule 5 CarbohydratesSpongebob SquarepantsNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 4th Quarter Week 3Document12 pagesGrade 10 4th Quarter Week 3KarenNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Module 33Document8 pagesScience 10 - Module 33Karlyn Kaye SalungaNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesDocument62 pagesThe Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesOussema Ben KasdallahNo ratings yet
- 4 BiomoleculesDocument23 pages4 BiomoleculesjoshuaandreicsabellanoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lec MidtermsDocument14 pagesBiochemistry Lec MidtermsSandoval, Ma. Carla TayagNo ratings yet
- CM 4Document9 pagesCM 4Michaella “hideyoshi girl” DavisNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and ProteinsDocument55 pagesCarbohydrates and ProteinsuwuwuwNo ratings yet
- UNITI BiomoleculesDocument19 pagesUNITI BiomoleculesPriyanka YadavNo ratings yet
- UPRB Biol 3011 Cap 3 2022Document104 pagesUPRB Biol 3011 Cap 3 2022Alexander FigueroaNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument120 pagesCarbohydratesEmmaNo ratings yet
- Learning Module General Biology 1Document18 pagesLearning Module General Biology 1John Paull CuaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates BiochemDocument4 pagesCarbohydrates Biochemsaythename.smmaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules A LevelDocument90 pagesBiomolecules A LevelPaa Kwesi ColemanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate ChemistryDocument16 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistrymay498550No ratings yet