Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bandpass Demod
Uploaded by
seri126Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bandpass Demod
Uploaded by
seri126Copyright:
Available Formats
Digital Communications
1 _
_ 2
Today, we are going to talk about:
Some bandpass modulation schemes used
in DCS for transmitting information over
channel
M-PAM, M-PSK, M-FSK, M-QAM
How to detect the transmitted information
at the receiver
Coherent detection
Non-coherent detection
Why Modulation
Without Modulation:
To transmit 3000 Hz Baseband signals, the
antenna needed will be l/4 where
l=c/f=10
5
m and l/4=2.5x10
4
m
With Modulation:
Easy for transmission/ Spread spectrum
_ 3
_ 4
Block diagram of a DCS
Format
Source
encode
Format
Source
decode
Channel
encode
Pulse
modulate
Bandpass
modulate
Channel
decode
Demod.
Sample
Detect
C
h
a
n
n
e
l
Digital modulation
Digital demodulation
_ 5
Bandpass modulation
Bandpass modulation: The process of converting
a data signal to a sinusoidal waveform where its
amplitude, phase or frequency, or a combination of
them, are varied in accordance with the transmitting
data.
Bandpass signal:
where is the baseband pulse shape with energy .
We assume here (otherwise will be stated):
is a rectangular pulse shape with unit energy.
Gray coding is used for mapping bits to symbols.
denotes average symbol energy given by
( ) T t t t i t
T
E
t g t s
i c
i
T i
s s + A + = 0 ) ( ) 1 ( cos
2
) ( ) ( | e e
) (t g
T
) (t g
T g
E
s
E
=
=
M
i
i s
E
M
E
1
1
_ 6
Demodulation and detection
Demodulation: The receiver signal is converted to
baseband, filtered and sampled.
Detection: Sampled values are used for detection
using a decision rule such as the ML detection rule.
(
(
(
N
z
z
1
z =
}
T
0
) (
1
t
}
T
0
) (t
N
) (t r
1
z
N
z
z
Decision
circuits
(ML detector)
m
_ 7
Coherent detection
Coherent detection
requires carrier phase recovery at the
receiver and hence, circuits to perform
phase estimation.
Sources of carrier-phase mismatch at the
receiver:
Propagation delay causes carrier-phase offset in
the received signal.
The oscillators at the receiver which generate
the carrier signal, are not usually phased locked
to the transmitted carrier.
_ 8
Bandpass Modulation Schemes
One dimensional waveforms
Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK)
M-ary Pulse Amplitude Modulation (M-PAM)
Two dimensional waveforms
M-ary Phase Shift Keying (M-PSK)
M-ary Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
(M-QAM)
Multidimensional waveforms
M-ary Frequency Shift Keying (M-FSK)
_ 9
One dimensional modulation,
demodulation and detection
Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) modulation:
( ) | e+ = t
T
E
t s
c
i
i
cos
2
) (
( )
cos
2
) (
, , 1 ) ( ) (
1
1
i i
c
i i
E a
t
T
t
M i t a t s
=
+ =
= =
| e
) (
1
t
1
s
2
s
0
1
E
0 1
On-off keying (M=2):
_ 10
One dimensional mod.,
M-ary Pulse Amplitude modulation (M-PAM)
( ) t
T
a t s
c i i
e cos
2
) ( =
( )
( )
g s
g i i
g i
c
i i
E
M
E
M i E E
E M i a
t
T
t
M i t a t s
3
) 1 (
1 2
) 1 2 (
cos
2
) (
, , 1 ) ( ) (
2
2
2
1
1
=
= =
=
=
= =
s
e
4-PAM:
) (
1
t
2
s
1
s
0 g
E 3
00 01
4
s
3
s
11 10
g
E
g
E
g
E 3
_ 11
Example of bandpass modulation:
Binary PAM
_ 12
Coherent detection of M-PAM
}
T
0
) (
1
t
ML detector
(Compare with M-1 thresholds)
) (t r
1
z
m
One dimensional mod.,...contd
_ 13
Two dimensional modulation,
demodulation and detection (M-PSK)
M-ary Phase Shift Keying (M-PSK)
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
M
i
t
T
E
t s
c
s
i
t
e
2
cos
2
) (
( ) ( )
2
2 1
2 1
2 2 1 1
2
sin
2
cos
sin
2
) ( cos
2
) (
, , 1 ) ( ) ( ) (
i i s
s i s i
c c
i i i
E E
M
i
E a
M
i
E a
t
T
t t
T
t
M i t a t a t s
s = =
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
= =
= + =
t t
e e
_ 14
Two dimensional mod., (MPSK)
) (
1
t
2
s
1
s
b
E
0 1
b
E
) (
2
t
3
s
7
s
110
) (
1
t
4
s
2
s
s
E
000
) (
2
t
6
s
8
s
1
s
5
s
001
011
010
101
111
100
) (
1
t
2
s
1
s
s
E
00
11
) (
2
t
3
s
4
s
10
01
QPSK (M=4)
BPSK (M=2)
8PSK (M=8)
_ 15
Two dimensional mod.,(MPSK)
Coherent detection of MPSK
Compute
Choose
smallest
1
2
arctan
z
z
|
| | |
i
}
T
0
) (
1
t
}
T
0
) (
2
t
) (t r
1
z
2
z
m
_ 16
Two dimensional mod., (M-QAM)
M-ary Quadrature Amplitude Mod. (M-QAM)
( )
i c
i
i
t
T
E
t s e+ = cos
2
) (
( ) ( )
3
) 1 ( 2
and symbols PAM are and where
sin
2
) ( cos
2
) (
, , 1 ) ( ) ( ) (
2 1
2 1
2 2 1 1
=
= =
= + =
M
E a a
t
T
t t
T
t
M i t a t a t s
s i i
c c
i i i
e e
( )
(
(
(
(
(
+ + + + +
+ +
+ +
=
) 1 , 1 ( ) 1 , 3 ( ) 1 , 1 (
) 3 , 1 ( ) 3 , 3 ( ) 3 , 1 (
) 1 , 1 ( ) 1 , 3 ( ) 1 , 1 (
,
2 1
M M M M M M
M M M M M M
M M M M M M
a a
i i
QAM
Combination of MPSK and MASK.
p(t) = p(t)(a
i
cos
c
t + b
i
sin
c
t)
= p(t)[r
i
cos(
c
t +
i
)]
Where r
i
= (a
i
2
+ b
i
2
)
1/2
and
i
= tan
-1
b
i
/a
i
MASK MPSK
i
= 0 for all i r
i
is constant.
Only r
i
is different. Only
i
is different.
APK: both
and
r vary.
_ 17
_ 18
Two dimensional mod., (M-QAM)
) (
1
t
) (
2
t
2
s
1
s
3
s
4
s
0000 0001 0011 0010
6
s
5
s
7
s
8
s
10
s
9
s
11
s
12
s
14
s
13
s
15
s
16
s
1 3 -1 -3
1000 1001 1011 1010
1100 1101 1111 1110
0100 0101 0111 0110
1
3
-1
-3
16-QAM
_ 19
Two dimensional mod., (M-QAM)
Coherent detection of M-QAM
}
T
0
) (
1
t
ML detector
1
z
}
T
0
) (
2
t
ML detector
) (t r
2
z
m
Parallel-to-serial
converter
s) threshold 1 with (Compare M
s) threshold 1 with (Compare M
_ 20
Multi-dimensional modulation, demodulation &
detection
M-ary Frequency Shift keying (M-FSK)
() ( )
T
f
t i t
T
E
t
T
E
t s
c
s
i
s
i
2
1
2
) 1 ( cos
2
cos
2
) (
=
A
= A
A + = =
t
e
e e e
( )
2
1
0
cos
2
) (
, , 1 ) ( ) (
i i s
s
ij i i
M
j
j ij i
E E
j i
j i E
a t
T
t
M i t a t s
s = =
=
=
= =
= =
=
e
) (
1
t
2
s
1
s
3
s
) (
3
t
) (
2
t
s
E
s
E
s
E
_ 21
Multi-dimensional mod.,(M-FSK)
(
(
(
M
z
z
1
z =
}
T
0
) (
1
t
}
T
0
) (t
M
) (t r
1
z
M
z
z
ML detector:
Choose
the largest element
in the observed vector
m
_ 22
Non-coherent detection
Non-coherent detection:
No need for a reference in phase with the
received carrier
Less complexity compared to coherent
detection at the price of higher error rate.
_ 23
Non-coherent detection
Differential coherent detection
Differential encoding of the message
The symbol phase changes if the current bit is
different from the previous bit.
( ) ,...,M i T t t t
T
E
t s
i i
1 , 0 , ) ( cos
2
) (
0
= s s + = u e
) ( ) ) 1 (( ) ( nT T n nT
i k k
| u u + =
) (
1
t
i
|
1
s
2
s 0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1 1 0 1 0 1 1
1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1
t t t t t t
0 0
Symbol index:
Data bits:
Diff. encoded bits
Symbol phase:
k
u
k
m
k
_ 24
Non-coherent detection
Coherent detection for diff encoded mod.
assumes slow variation in carrier-phase mismatch during
two symbol intervals.
correlates the received signal with basis functions
uses the phase difference between the current received
vector and previously estimated symbol
( ) T t t n t t
T
E
t r
i
s s + + + = 0 ), ( ) ( cos
2
) (
0
o u e
) (
1
t
) (
2
t
) , (
1 1
b a
) , (
2 2
b a
i
|
( )( ) ) ( ) ) 1 (( ) ( ) ) 1 (( ) ( nT T n nT T n nT
i j i j i
| u u o u o u = = + +
_ 25
Non-coherent detection
Optimum differentially coherent detector
Sub-optimum differentially coherent detector
Performance degradation about 3 dB by using sub-
optimal detector
}
T
0
) (
1
t
) (t r
m
Decision
Delay
T
}
T
0
) (t r
m
Decision
Delay
T
_ 26
Non-coherent detection
Energy detection
Non-coherent detection for orthogonal signals
(e.g. M-FSK)
Carrier-phase offset causes partial correlation between
I and Q branches for each candidate signal.
The received energy corresponding to each candidate
signal is used for detection.
_ 27
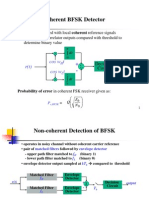
Non-coherent detection
Non-coherent detection of BFSK
}
T
0
) cos( / 2
1
t T e
}
T
0
) (t r
11
z
12
z
}
T
0
}
T
0
21
z
22
z
Decision stage:
) cos( / 2
2
t T e
) sin( / 2
2
t T e
) sin( / 2
1
t T e
( )
2
( )
2
( )
2
( )
2
+
-
) (T z
0 , 0 ) ( if
1 , 0 ) ( if
= <
= >
m T z
m T z
m
2
12
2
11
z z +
2
22
2
21
z z +
You might also like
- Major Scales WorksheetDocument1 pageMajor Scales Worksheetapi-386151936No ratings yet
- Have Faith in God - New (Bullock, Choir-Guitar, Em-GDocument2 pagesHave Faith in God - New (Bullock, Choir-Guitar, Em-GrobertchrystalNo ratings yet
- Suite Ben HurDocument40 pagesSuite Ben HureloysentanaNo ratings yet
- Lee Morgan TunesDocument14 pagesLee Morgan TunesDup Vlerd88% (8)
- Balanced Homodyne DetectorDocument31 pagesBalanced Homodyne DetectorKonstantinos Ladovrechis100% (1)
- C4 Isi 2013 PDFDocument32 pagesC4 Isi 2013 PDFAnh Bien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chuyên Đề Bài Tập Phát Hiện Lỗi Sai Tiếng Anh-Nguyễn Tiến Dũng PDFDocument20 pagesChuyên Đề Bài Tập Phát Hiện Lỗi Sai Tiếng Anh-Nguyễn Tiến Dũng PDFcauchutnt100% (1)
- Beyond Desolation Banjo TabDocument3 pagesBeyond Desolation Banjo TabNERONo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Radar System Jun2020Document87 pagesTopic 4 Radar System Jun2020Nabilah DaudNo ratings yet
- The 1 E & A Counting SystemDocument2 pagesThe 1 E & A Counting SystemMarco CocchiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 - Signal Space Approach and Gram Schmidt ProcedureDocument20 pagesLecture 04 - Signal Space Approach and Gram Schmidt ProcedureKhoa PhamNo ratings yet
- Saxophone Sheet Music AnalysisDocument3 pagesSaxophone Sheet Music AnalysismelfromsatinNo ratings yet
- Exam Drill Math 2Document3 pagesExam Drill Math 2Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM0% (1)
- 5 - Optimum Receivers For The AWGN Channel - Test - MODIFIED PDFDocument45 pages5 - Optimum Receivers For The AWGN Channel - Test - MODIFIED PDFajayroy12No ratings yet
- Ligeti-S-String-Quartet-No-1-Stylistic-Incongruence - Content File PDFDocument18 pagesLigeti-S-String-Quartet-No-1-Stylistic-Incongruence - Content File PDFtrish100% (1)
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsDocument17 pagesWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsashutoshsinghjssNo ratings yet
- How to Optimize Your Website for Search EnginesDocument17 pagesHow to Optimize Your Website for Search EnginesNano GomeshNo ratings yet
- Kpi ReferenceDocument49 pagesKpi ReferencemmlipuNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications I: Modulation and Coding Course: Term 3 - 2008 Catharina LogothetisDocument27 pagesDigital Communications I: Modulation and Coding Course: Term 3 - 2008 Catharina LogothetisUsman InayatNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications I: Modulation and Coding Course: Spring - 2013 Jeffrey N. DenenbergDocument25 pagesDigital Communications I: Modulation and Coding Course: Spring - 2013 Jeffrey N. DenenbergWaqar AsmatNo ratings yet
- DigComm Fall09-Chapter4Document81 pagesDigComm Fall09-Chapter4rachrajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - Qam Pam PSKDocument17 pagesLecture 10 - Qam Pam PSKdanilodspNo ratings yet
- Optimum Reception in Additive White GaussianNoise (AWGN)Document74 pagesOptimum Reception in Additive White GaussianNoise (AWGN)gau_loncon1511No ratings yet
- Digital Communications I: Modulation and Coding Course: Term 3 - 2008 Catharina LogothetisDocument23 pagesDigital Communications I: Modulation and Coding Course: Term 3 - 2008 Catharina LogothetisSyed Raheel AdeelNo ratings yet
- Elec3505 Formula SheetDocument10 pagesElec3505 Formula SheetDorothy FigueroaNo ratings yet
- TE312: Introduction To Digital Telecommunications: Lecture #4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Document25 pagesTE312: Introduction To Digital Telecommunications: Lecture #4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Ibra NazlaNo ratings yet
- Signal Space Analysis: Representing Signals in an N-Dimensional Orthogonal SpaceDocument17 pagesSignal Space Analysis: Representing Signals in an N-Dimensional Orthogonal SpaceRizky WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Bahl, Cocke, Jelinek and Raviv (BCJR) Algorithm: Markov Source Discrete Memoryles S Channel ReceiverDocument12 pagesBahl, Cocke, Jelinek and Raviv (BCJR) Algorithm: Markov Source Discrete Memoryles S Channel ReceivercaduzinhoxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document11 pagesChapter 6mvistroNo ratings yet
- Input SignalsDocument31 pagesInput SignalssmouhabNo ratings yet
- Lab 9: Timing Error and Frequency Error: 1 Review: Multi-Rate SimulationDocument15 pagesLab 9: Timing Error and Frequency Error: 1 Review: Multi-Rate Simulationhaiduong2010No ratings yet
- Emcs - 607P 11-07-2014Document68 pagesEmcs - 607P 11-07-2014abdulbari.abNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Digital Communication SystemDocument19 pagesElements of A Digital Communication SystemmonikNo ratings yet
- Frequency Offset Reduction Methods in OFDM: Behrouz Maham Dr. Said Nader-EsfahaniDocument59 pagesFrequency Offset Reduction Methods in OFDM: Behrouz Maham Dr. Said Nader-EsfahaniomjikumarpandeyNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document48 pagesCH 11Bulli KoteswararaoNo ratings yet
- ENSC327 Digital Bandpass ModulationDocument28 pagesENSC327 Digital Bandpass ModulationSaurabh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Optimal Receiver DesignDocument21 pagesOptimal Receiver DesignKhoa PhamNo ratings yet
- Bandpass Modulation Schemes Bandpass Modulation Schemes For Wireless SystemsDocument15 pagesBandpass Modulation Schemes Bandpass Modulation Schemes For Wireless SystemsTina BurgessNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet 1: Analog To Digital Conversion (ADC) and Digital To Analog Conversion (DAC) FundamentalsDocument13 pagesLab Sheet 1: Analog To Digital Conversion (ADC) and Digital To Analog Conversion (DAC) FundamentalsMasud SarkerNo ratings yet
- Wave Form GeometryDocument24 pagesWave Form GeometryMK KhnNo ratings yet
- Lab 9: M - Ary Amplitude and Frequency Shift Keying, Signal SpaceDocument19 pagesLab 9: M - Ary Amplitude and Frequency Shift Keying, Signal SpaceAyman YounisNo ratings yet
- B4 Detetcion KadambeDocument106 pagesB4 Detetcion Kadambekenjo138No ratings yet
- ECEN 4652 Lab 9: ASK, PSK, and FSKDocument37 pagesECEN 4652 Lab 9: ASK, PSK, and FSKAldawi SatNo ratings yet
- ML DetectorDocument37 pagesML DetectorMuhammad Wasif KhanNo ratings yet
- Golay CodesDocument50 pagesGolay CodesdshgjklopNo ratings yet
- תרגילים היילרןDocument83 pagesתרגילים היילרןMatanAbutbulNo ratings yet
- M-ary PSK and QAM Modulations over Bandlimited AWGN ChannelsDocument14 pagesM-ary PSK and QAM Modulations over Bandlimited AWGN ChannelsIulian NeagaNo ratings yet
- DegitalDocument7 pagesDegitalRICKNo ratings yet
- BPSK Probability of ErrorDocument85 pagesBPSK Probability of Errorمهند عدنان الجعفريNo ratings yet
- DSP LECTURE 1 - CLASSIFICATION OF SIGNALSDocument65 pagesDSP LECTURE 1 - CLASSIFICATION OF SIGNALSVinoth MuruganNo ratings yet
- Gsop PDFDocument19 pagesGsop PDFAyush PurohitNo ratings yet
- DSBSCDocument23 pagesDSBSCrajaniharshaNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Systems IDocument64 pagesAnalog Communication Systems Itadepeace23No ratings yet
- MSK PhaseDocument15 pagesMSK PhaseSaran KhalidNo ratings yet
- Digital 6Document20 pagesDigital 6Anikk DasNo ratings yet
- Receiver Filter: Baseband Output Is A Superposition of Filtered Pulses Plus Filtered NoiseDocument4 pagesReceiver Filter: Baseband Output Is A Superposition of Filtered Pulses Plus Filtered NoiseBiswajit SinghNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems Using Matlab Chapter 7 - Fourier Analysis in Communications and FilteringDocument21 pagesSignals and Systems Using Matlab Chapter 7 - Fourier Analysis in Communications and FilteringDiluNo ratings yet
- Binary PSK Receiver Block DiagramDocument9 pagesBinary PSK Receiver Block DiagramefedsfewNo ratings yet
- EECE 522 Notes - 08 CH - 3 CRLB Examples in BookDocument19 pagesEECE 522 Notes - 08 CH - 3 CRLB Examples in Bookkarim2005No ratings yet
- Analog Signal Transmission and ReceptionDocument109 pagesAnalog Signal Transmission and ReceptionMicheal MathanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of OfdmDocument28 pagesFundamentals of OfdmA_B_C_D_ZNo ratings yet
- z6 Amplitude ModulationDocument10 pagesz6 Amplitude ModulationtsegayNo ratings yet
- Equalization Ed Us atDocument50 pagesEqualization Ed Us atIgnatious MohanNo ratings yet
- Digital Control System-1Document47 pagesDigital Control System-1Makesh MäKzNo ratings yet
- 1 Coherent and Incoherent Modulation in OFDM: 1.1 Review of Differential ModulationDocument15 pages1 Coherent and Incoherent Modulation in OFDM: 1.1 Review of Differential ModulationRajib MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Generate and Demodulate ASK, PSK and FSK Signals in MATLABDocument44 pagesGenerate and Demodulate ASK, PSK and FSK Signals in MATLABVadlani Dinesh100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Tvlist 2Document12 pagesTvlist 2NarcizioAragãoNo ratings yet
- JADWAL Tim Pemuji & Penyembah IR SCEP November'2022Document1 pageJADWAL Tim Pemuji & Penyembah IR SCEP November'2022Bena MichaelNo ratings yet
- TV Repeater'S Repeater: A Transverter For 10Ghz DVB-TDocument13 pagesTV Repeater'S Repeater: A Transverter For 10Ghz DVB-TBenjamin DoverNo ratings yet
- Sanders' Union Fourth Reader by Sanders, Charles W.Document276 pagesSanders' Union Fourth Reader by Sanders, Charles W.Gutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- James Brown Research PaperDocument7 pagesJames Brown Research Paperaflbskroi100% (1)
- EC VI SemDocument11 pagesEC VI SemSanket SapateNo ratings yet
- Dance Education Definition and ClassificationsDocument5 pagesDance Education Definition and ClassificationsRose Anne CalmaNo ratings yet
- Avian Guitars EuropeDocument5 pagesAvian Guitars EuropeRosario BlancaNo ratings yet
- Music of Palawan LPDocument6 pagesMusic of Palawan LPNhey CawiganNo ratings yet
- Norman Mclaren y Su Proceso CreativoDocument4 pagesNorman Mclaren y Su Proceso Creativottap79No ratings yet
- PM700 ManualDocument192 pagesPM700 ManualsiggoNo ratings yet
- TRue Point 5000Document6 pagesTRue Point 5000Luni RodgerdsNo ratings yet
- Equus - Normality EssayDocument3 pagesEquus - Normality EssayJackMaxwellNo ratings yet
- Evan J. Horowitz: ObjectiveDocument1 pageEvan J. Horowitz: Objectiveok00l14No ratings yet
- Vii Form Society AdditionDocument25 pagesVii Form Society AdditionMr.Gopikrishnan.K.V placementNo ratings yet
- 4 PDFsam WB DHFW Bulletin 04th AUGUST REPORT FINALDocument1 page4 PDFsam WB DHFW Bulletin 04th AUGUST REPORT FINALJoyRoyNo ratings yet
- Morgan Lanahan ResumeDocument3 pagesMorgan Lanahan Resumeapi-254208388No ratings yet
- Purc-Iwill-SSATB I Will Sing Unto The LordDocument7 pagesPurc-Iwill-SSATB I Will Sing Unto The LordDavidMackorNo ratings yet