0% found this document useful (0 votes)
700 views76 pagesUnintentional Injury Prevention, Safety and First Aid
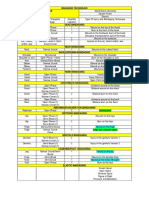
The document outlines the basics of first aid, emphasizing its role in providing immediate care for unintentional injuries, particularly in a school setting. It covers essential techniques for dressing and bandaging wounds, as well as first aid procedures for common injuries such as fractures, dislocations, sprains, and heat exhaustion. Additionally, it discusses the importance of proper transportation methods for injured individuals and the characteristics of a good first aider.
Uploaded by
shielokiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
700 views76 pagesUnintentional Injury Prevention, Safety and First Aid
The document outlines the basics of first aid, emphasizing its role in providing immediate care for unintentional injuries, particularly in a school setting. It covers essential techniques for dressing and bandaging wounds, as well as first aid procedures for common injuries such as fractures, dislocations, sprains, and heat exhaustion. Additionally, it discusses the importance of proper transportation methods for injured individuals and the characteristics of a good first aider.
Uploaded by
shielokiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd