Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Access 2010 QRG
Uploaded by
Syafiq AbdullahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Access 2010 QRG
Uploaded by
Syafiq AbdullahCopyright:
Available Formats
http://www.mousetraining.co.
uk
Access 2010
Quick Reference Card
Working with Databases and Objects
Getting Started
Window
To Create a Database: Click a
template category in the list and click
the template you want to use. Click
Create. Or, click the Blank Database
button.
To Open an Existing Database:
Click a database in the Recent
Database list or click Open and
browse for it.
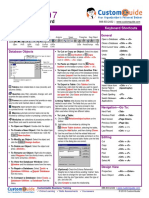
Access 2010 Screen
Database Objects
Tables store related data in rows (records) and columns (fields).
Queries view, filter, calculate, change, sort, and examine the data stored in tables.
Forms are custom screens that provide an easy way to enter and view data in a table.
Reports present data from a table or query in a printed format.
Macros automate common tasks and can be run by clicking a button or pressing a
shortcut key.
Modules are groups of procedures written in Visual Basic and used to automate tasks.
Page objects have been replaced by Windows Sharepoint Services. Pages in old
databases can still be viewedbut not editedin Internet Explorer.
To Open an Object: Double-click the object in the Navigation Pane.
To Create a New Object: Click the Create tab on the Ribbon and click a button for
the object or wizard you want to use on the Objects bar.
To Modify an Object: Open the object or click its tab in the window, click the Format
tab on the Ribbon, click the View button in the Views group and select Design View
or Layout View.
To Delete an Object: Select the object and press <Delete>. Click Yes.
To Rename an Object: Right-click the object, select Rename from the contextual
menu, enter the new name, and press <Enter>.
To Repair/Compress a Database:
Click the Office Button and select
Manage Compact and Repair
Database.
To Import Data: Click the External
Data tab on the Ribbon and click the
type of file you want to import from in
the Import group. Follow the onscreen
instructions.
To Export Data: Click the External
Data tab on the Ribbon and click the
type of file you want to export to in the
Export group. Follow the onscreen
instructions.
General
Open a Database <Ctrl> + <O>
Close a Database <Ctrl> + <W>
Print Current View <Ctrl> + <P>
Delete <Delete>
Undo <Ctrl> + <Z>
Help <F1>
Delete Record <Ctrl> + < - >
Cancel Changes <Esc>
Insert Date <Ctrl> + < ; >
Insert Time <Shift> + <Ctrl>
+ <:>
Insert Value from <Ctrl> + < >
Same Field in (Apostrophe)
Previous Record
Check Spelling <F7>
Switch Applications <Alt> + <Tab>
Navigation
Next Field <Tab>
Previous Field <Shift> + <Tab>
Next Screen <Page Down>
Previous Screen <Page Up>
First Record <Ctrl> + < f >
Last Record <Ctrl> + < J, >
Toggle Navigation Pane <F11>
Editing
Cut <Ctrl> + <X>
Copy <Ctrl> + <C>
Paste <Ctrl> + <V>
Find <Ctrl> + <F>
Replace <Ctrl> + <H>
Select All <Ctrl> + <A>
Design View
Properties <Alt> + <Enter>
Open object in <Ctrl> + <Enter>
Design View
Save Object <Ctrl> + <S>
Field Data Types
Creating Table Relationships
Linking Tables tells Access how two tables are related to each other.
The fields that you use to link two tables must contain the same concept
in two different tables. A primary key field from one table is often used
when linking two tables.
1. Click the Datasheet tab on the Ribbon and click the
Relationships button in the Relationships group.
2. If necessary, click the Show Table button in the Relationships
group on the Design tab. In the Show Table window, select a table
you want to link, click the Add button, and repeat for each table.
Click Close.
3. Drag a field from one table and drop it on the related field in the
second table. (Optional) Check the Enforce Referential
Integrity box. Click Create.
Working with Table Data
Database information can be directly added and modified from tables
and some queries and forms.
To Add a Field to a Table: Enter data in the cell below the Add
New Field column header. Or, click and drag a field from the Field
Templates pane to the table (to display the Field Templates pane,
click the Datasheet tab on the Ribbon and click the New Field
button in the Fields & Columns group).
To Add a New Record: Enter data in the bottom row of the
table.
To Select a Record: Click the Record selector to the left of
the record.
To Delete a Record: Select the record, click the Home tab on
the Ribbon and click the Delete button in the Records group. Click
Yes.
To Spell Check: Click the Home tab on the Ribbon and click the
Spelling button in the Records group.
To Find Information: Place the cursor in the field that contains
the value you want to search for, click the Home tab on the Ribbon
and click the Find button in the Find group or press <Ctrl> + <F>.
Type the value you want to search for in the Find What box and
click Find Next.
To Replace Information: Place the cursor in the field that
contains the value you want to replace, click the Home tab on the
Ribbon and click the Replace button in the Find group or press
<Ctrl> + <H>. Type the value you want to search for in the Find
What box and the new value in the Replace With box.
Click Find Next until youve found what youre looking for, then
click Replace or Replace All to replace every instance of the
value.
To Sort Information: Place the cursor in the field that you
want to sort by, click the Home tab and click either the
Ascending or Descending button in the Sort & Filter group.
To Filter Information: Place the cursor in the field that
contains the values you want to filter by, click the Home tab on
the Ribbon and click the Filter button in the Sort & Filter group.
Check the boxes for the values you want to filter for.
To Remove a Filter: Click the Toggle Filter button in the
Sort & Filter group.
To Change a Fields Data Type: Select the field you want
to change, click the Datasheet tab on the Ribbon, and click
the Data Type list arrow in the Data Type & Formatting group.
Select a data type.
Working with Queries
To Create a Select Query: Click the Create tab on the Ribbon
and click the Query Wizard button in the Other group. Click
Simple Query Wizard and click OK. Follow the onscreen
instructions to select the fields you want to use from the desired
tables and create the query. If you want to filter records, view the
query in Design view and enter the criteria in the Criteria row.
To Switch Views: Click the Home tab on the Ribbon and click
the View button in the Views group.
To Summarize Values: Open the Query in Datasheet View, click
the Home tab on the Ribbon and click the Totals button in the
Records group. Click the list arrow in a column in the Total row in the
query select a calculation type (Sum, Average, etc.).
Criteria Example Description
London Displays records where the field equals
London.
Between 1/1/00
and 12/31/00
Displays records where the date is between
1/1/00 and 12/31/00.
NOT "USA"
or <> ""
Displays records where the field does not
contain the text "USA" and is not blank.
Like S* Displays records where the field text starts with
an S.
IS NULL Displays records where the field is blank.
IS NOT NULL Displays records where the field is not blank.
>100 Displays records whose field value is greater
than 100.
Data Type Description
Text
(Default)
Stores text, numbers, or a combination of both, up
to 255 characters long.
Memo Stores long text entriesup to 64,000 characters
Number Stores numbers that can be used in calculations.
Date/Time Stores dates, times, or both.
Currency Stores numbers and symbols that represent money.
AutoNumber Automatically fills in a unique number for each
Yes/No Stores only one of two values, such as Yes or No.
OLE Object Stores objects created in other programs, such
as a graphic, Excel spreadsheet, or Word
Hyperlink Stores clickable links to Web pages on the Internet
or files on a network.
Lookup
Wizard
A wizard that helps you create a field whose
values are selected from another table, query, or
Attachment Allows you to attach files and images to your
d t b
You might also like
- Access 2007 Quick ReferenceDocument2 pagesAccess 2007 Quick ReferenceAdam ChinNo ratings yet
- Access 2007 Training: Access Quick Reference CardDocument2 pagesAccess 2007 Training: Access Quick Reference CardvishwassinghagraNo ratings yet
- Access Quick Reference 2007Document2 pagesAccess Quick Reference 2007MoMoNo ratings yet
- Access Quick Reference 2010 PDFDocument2 pagesAccess Quick Reference 2010 PDFPratama AbimanyuNo ratings yet
- Access 2003 Quick ReferenceDocument2 pagesAccess 2003 Quick Referencenadeem sadiqNo ratings yet
- Access 2003 QuikrefDocument2 pagesAccess 2003 Quikrefapi-3822138100% (1)
- Access 97: Quick Reference CardDocument2 pagesAccess 97: Quick Reference CardKhajahussain SyedNo ratings yet
- Internet Explorer Quick Reference 8Document3 pagesInternet Explorer Quick Reference 8Lamar GuthrieNo ratings yet
- Onenote Quick Reference 2007Document2 pagesOnenote Quick Reference 2007joNo ratings yet
- Word Quick Reference 2000Document2 pagesWord Quick Reference 2000doroodgarNo ratings yet
- ResumenPowerPoint PDFDocument2 pagesResumenPowerPoint PDFPedro FernándezNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint 2003 QuikrefDocument2 pagesPowerpoint 2003 Quikrefapi-3822138100% (1)
- PowerPoint 2013Document2 pagesPowerPoint 2013kevin.haklarNo ratings yet
- Publisher 2007 Quick ReferenceDocument2 pagesPublisher 2007 Quick ReferenceReina France Borja PinedaNo ratings yet
- Power Point 2003 QuickrefDocument2 pagesPower Point 2003 Quickrefakshayagarwal92No ratings yet
- Word 2013 - Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pagesWord 2013 - Quick Reference Guiderachelle marieNo ratings yet
- Word Quick Reference 2010Document2 pagesWord Quick Reference 2010faisal84inNo ratings yet
- Visio Quick Reference 2007Document3 pagesVisio Quick Reference 2007direNo ratings yet
- Word 2003 QuikrefDocument2 pagesWord 2003 Quikrefapi-3822138100% (1)
- Excel 2007-Fluor LogoDocument2 pagesExcel 2007-Fluor LogojargiaNo ratings yet
- Windows Quick Reference 7Document2 pagesWindows Quick Reference 7Parisa ArmanNo ratings yet
- Visio2007 PDFDocument2 pagesVisio2007 PDFMuhammadObaidullahNo ratings yet
- Macos Quick Reference 9Document3 pagesMacos Quick Reference 9Pablo CalderonNo ratings yet
- Mltbomlfkq: / - 0 Mboplk I Qo FkboDocument2 pagesMltbomlfkq: / - 0 Mboplk I Qo FkboWalid CasaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Office 2013Document13 pagesMicrosoft Office 2013kevin.haklarNo ratings yet
- Acrobat 8: Quick Reference CardDocument2 pagesAcrobat 8: Quick Reference Cardlyz leeNo ratings yet
- Visio 2010 QRGDocument2 pagesVisio 2010 QRGjohncaulfieldNo ratings yet
- Word 2013 Quick ReferenceDocument3 pagesWord 2013 Quick ReferenceAlex RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Publisher 2007 Quick ReferenceDocument2 pagesPublisher 2007 Quick ReferencekannappanrajendranNo ratings yet
- Word 2010: Quick Reference CardDocument2 pagesWord 2010: Quick Reference Cardarun7jNo ratings yet
- Excel 2003 QuikrefDocument2 pagesExcel 2003 Quikrefapi-3822138100% (1)
- Word 2007 Quick Reference CardDocument2 pagesWord 2007 Quick Reference Cardcabrera.adolfo1862No ratings yet
- Quick Office 2007Document9 pagesQuick Office 2007Sania KhanNo ratings yet
- Visio2002qr EncDocument3 pagesVisio2002qr EncEdi VoicuNo ratings yet
- Word 2013Document2 pagesWord 2013kevin.haklarNo ratings yet
- GS. Keyboard ShortcutsDocument3 pagesGS. Keyboard ShortcutsFrancis CayananNo ratings yet
- Win7 User GuideDocument2 pagesWin7 User GuidejargiaNo ratings yet
- GS. Keyboard ShortcutsDocument5 pagesGS. Keyboard ShortcutsGANDHILAL mNo ratings yet
- Power Point 2007 Quick ReferenceDocument2 pagesPower Point 2007 Quick ReferenceAdam Chin100% (1)
- Windows Keyboard ShortcutsDocument1 pageWindows Keyboard ShortcutsLambit TextsNo ratings yet
- Access 2007 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesAccess 2007 Cheat Sheetjuan antonio morales garciaNo ratings yet
- Hatch Quick ReferenceDocument5 pagesHatch Quick Referenceafzal47No ratings yet
- Excel 2002 QRDocument2 pagesExcel 2002 QRShubhambaderiyaNo ratings yet
- VS Code Cheat Sheet - Simple Cheat Sheet - Visual Studio CodeDocument10 pagesVS Code Cheat Sheet - Simple Cheat Sheet - Visual Studio CodePratik RamanNo ratings yet
- Visual Studio 2015 Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageVisual Studio 2015 Cheat Sheet PDFvali29No ratings yet
- C Computer Science by Christopher TopalianDocument59 pagesC Computer Science by Christopher TopalianCollegeOfScriptingNo ratings yet
- Computer Shortcut Keys List PDF Download (A To Z) - VidyaleafDocument20 pagesComputer Shortcut Keys List PDF Download (A To Z) - VidyaleafAryan PalNo ratings yet
- ShortCut Keys in JDeveloperDocument3 pagesShortCut Keys in JDeveloperShiva PriyaNo ratings yet
- Windows 98 - Quick-ReferenceDocument2 pagesWindows 98 - Quick-Referencejamespotter2No ratings yet
- Firefox ShortcutsDocument2 pagesFirefox ShortcutskayNo ratings yet
- Android Studio (Windows/Linux) Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesAndroid Studio (Windows/Linux) Cheat Sheet: by Viahanamachi09No ratings yet
- 50+ Windows Computer Keyboard ShortcutsDocument2 pages50+ Windows Computer Keyboard ShortcutsEthio Face Event Organizer & EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Comenzi AutocadDocument7 pagesComenzi AutocadAbubu30No ratings yet
- Microsoft Office Productivity Pack: Microsoft Excel, Microsoft Word, and Microsoft PowerPointFrom EverandMicrosoft Office Productivity Pack: Microsoft Excel, Microsoft Word, and Microsoft PowerPointNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Excel: Microsoft Excel User Interface, Excel Basics, Function, Database, Financial Analysis, Matrix, Statistical AnalysisFrom EverandMicrosoft Excel: Microsoft Excel User Interface, Excel Basics, Function, Database, Financial Analysis, Matrix, Statistical AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Lightroom Classic and Photoshop Keyboard Shortcuts: Pocket Guide: Keyboard Shortcuts for PhotographersFrom EverandLightroom Classic and Photoshop Keyboard Shortcuts: Pocket Guide: Keyboard Shortcuts for PhotographersNo ratings yet
- TVL-SMAW 12 - Week 4 - Lesson 1 - Concept of Welding Codes and StandardsDocument9 pagesTVL-SMAW 12 - Week 4 - Lesson 1 - Concept of Welding Codes and StandardsNelPalalonNo ratings yet
- A Review On PRT in IndiaDocument21 pagesA Review On PRT in IndiaChalavadi VasavadattaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Activty Rubrics Classroom Activty Rubrics: Total TotalDocument1 pageClassroom Activty Rubrics Classroom Activty Rubrics: Total TotalMay Almerez- WongNo ratings yet
- Viking 062293Document8 pagesViking 062293Lukman ZakariyahNo ratings yet
- LC 67002000 B Hr-Jumbo enDocument2 pagesLC 67002000 B Hr-Jumbo enJulio OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Warranty FormDocument13 pagesWarranty FormEmpyrean Builders Corp.No ratings yet
- MATLAB For Data VisualizationDocument63 pagesMATLAB For Data Visualizationfahmi fawjiNo ratings yet
- Ahu 1997 22 1 95Document15 pagesAhu 1997 22 1 95Pasajera En TranceNo ratings yet
- Inglês - Advérbios - Adverbs.Document18 pagesInglês - Advérbios - Adverbs.KhyashiNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Week 3-4Document2 pagesMath 10 Week 3-4Rustom Torio QuilloyNo ratings yet
- Th-Sunday Magazine 6 - 2Document8 pagesTh-Sunday Magazine 6 - 2NianotinoNo ratings yet
- A Database For Handwritten Text Recognition ResearchDocument5 pagesA Database For Handwritten Text Recognition Researchtweety492No ratings yet
- Symmetrir and Order. Reasons To Live According The LodgeDocument6 pagesSymmetrir and Order. Reasons To Live According The LodgeAnonymous zfNrN9NdNo ratings yet
- Thesis Preliminary PagesDocument8 pagesThesis Preliminary Pagesukyo0801No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Least Mastered Competencies Sy 2020-2021: Handicraft Making Dressmaking CarpentryDocument9 pagesGrade 8 Least Mastered Competencies Sy 2020-2021: Handicraft Making Dressmaking CarpentryHJ HJNo ratings yet
- 555 TimerDocument25 pages555 TimerDr-Muhammad Aqeel AslamNo ratings yet
- IJREAMV06I0969019Document5 pagesIJREAMV06I0969019UNITED CADDNo ratings yet
- Case StarbucksDocument3 pagesCase StarbucksAbilu Bin AkbarNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Gastrointestinal Organs: Muhammad ImranDocument21 pagesFunctions of The Gastrointestinal Organs: Muhammad ImranSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- BIR REliefDocument32 pagesBIR REliefJayRellvic Guy-ab67% (6)
- Synopsis SsDocument14 pagesSynopsis SsJYOTI KATIYAR SVUNo ratings yet
- TDS-11SH Top Drive D392004689-MKT-001 Rev. 01Document2 pagesTDS-11SH Top Drive D392004689-MKT-001 Rev. 01Israel Medina100% (2)
- VRealize Operations Manager Installation and Configuration Guide For Linux and WindowsDocument98 pagesVRealize Operations Manager Installation and Configuration Guide For Linux and Windowsamdusias67No ratings yet
- Project - Dreambox Remote Video StreamingDocument5 pagesProject - Dreambox Remote Video StreamingIonut CristianNo ratings yet
- Amazon VS WalmartDocument5 pagesAmazon VS WalmartBrandy M. Twilley100% (1)
- Dental Clinic - Floor Plan R3-2Document1 pageDental Clinic - Floor Plan R3-2kanagarajodisha100% (1)
- Fisker Karma - Battery 12V Jump StartDocument2 pagesFisker Karma - Battery 12V Jump StartRedacTHORNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Study Guide: VideoDocument7 pagesChapter 17 Study Guide: VideoMruffy DaysNo ratings yet
- Water Works RTADocument15 pagesWater Works RTAalfaza3No ratings yet
- Outbound Idocs Code Error Event Severity Sap MeaningDocument2 pagesOutbound Idocs Code Error Event Severity Sap MeaningSummit YerawarNo ratings yet