Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Measuring Distance Corrections
Uploaded by
JaireOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Measuring Distance Corrections
Uploaded by
JaireCopyright:
Available Formats
Surveying Set 1
Corrections in Measuring Distances
Pace Factor
Correction for Measuring Distances
General Formula
CD = RD + C
where:
CD = Correct Distance
RD = Recorded Distance
C = all applicable Corrections
Tape Correction
=
+ too long
-too short
=
+ too long
-too short
Correction Due to Temperature (Ct)
Ct = k( Tm Ts ) L
Where:
k coefficient of linear expansion
0.0000116/
0
C
0.00000645/
0
F
Tm Temperature during measurement
Ts Standard Temperature
Problem 1:
When the temperature was 48
0
C, the measured
distance from B to C was 318m. The steel tape used has a
standard length at 20
0
C, with a coefficient of thermal
expansion of 0.0000116/
0
C. Find the correct distance BC
in m.
Soln:
Ct = k( Tm Ts ) L
Ct = 0.0000116/
0
C(48
0
C- 20
0
C)(318m)
Ct = +0.103m too long
CD = CD Ct
CD = 318 + 0.103
CD = 318.103m
Problem 2:
When the temperature was 5
0
C, the measured
distance from D to E was 674.25m. The steel tape used
has a standard length at 20
0
C, with a coefficient of
thermal expansion of 0.0000116/
0
C. What is the correct
distance from D to E in m?
Soln:
Ct = k( Tm Ts ) L
Ct = 0.0000116/
0
C(5
0
C- 20
0
C)(674.25m)
Ct = -0.117m too short
CD = CD Ct
CD = 674.25 0.117
CD = 674.133m
Correction due to Pull (Cp)
Where:
Pm = Pull during measurement
Ps = Standard Pull
A = Cross Sectional Area of Tape
E = Modulus of Elasticity of Tape
Cp=
PmPs L
AE
Problem 3:
A line was determined to be 2395.25m when
measured with a 30m steel tape supported throughout its
length under a pull of 4 kg. Tape used is of standard
length at a pull of 5kg. Cross sectional area of tape is 0.03
sq.cm. Modulus of elasticity of tape is 2x10
6
kg/cm
2
.
Soln:
AE
L Ps Pm
Cp
) (
) 10 2 )( 03 . 0 (
) 25 . 2395 )( 5 4 (
6
x
Cp
m Cp 0399 . 0
Correction due to Sag (Csag)
Where:
w weight of tape per linear meter
W
tape
/ L
tape
Pm Pull during measurement
Csag=
w
2
Lsag
3
24Pm
2
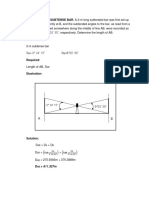
Problem 4:
A 100m tape weighs 0.0508 kg/m. During field
measurements, the tape was subjected to a tension of
45N and was supported at the end points, midpoints and
quarter points. Find the correction per tape length due to
sag.
Soln:
2
3 2
24Pm
Lsag w
Csag
2
3 2
) 45 ( 24
) 25 ( ) 81 . 9 0508 . 0 ( x
Csag
m Csag 0798 . 0
cm or m x Csag
Total
32 32 . 0 4 0798 . 0
Pace Factor
=
.
= .
A line 100m long was paced by a surveyor for four
times with the following data. 142, 145, 145.5, and 146.
Then another line eas paced for four times again with the
following results, 893, 893.5, 891 and 895.5.
1. Determine the pace factor.
2. Determine number of paces for the new line.
3. Determine the distance of the new line.
Problem 5: CE Board Nov. 1998
Solution:
1. Pace factor:
No. of paces = (142+145+145.5+146)/5
No. of paces = 144.625
Pace factor = 100/144.625 = 0.691
2. Number of paces for the new line:
No. of paces = (893+893.5+891+895.5)/5
No. of paces = 893.25
3. Distance of the new line:
Distance of new line = 893.25(0.691)
Distance of new line = 617.236m.
Chaining
Prob1: A line was measured to have 5 tallies, 6 marking pins and 63.5 links. How long is the line in
feet?
Prob 2:Determine the length of the line, in m, it there were 3 tallies, 8pins and the last pin was
9m from the end of the line. The tape used was 50m.
Conversion:
(For a 100ft Tape) (For a 50m tape)
1 link = 1 ft 1 link = 0.5m
1 chain = 100 ft 1 chain = 50m
1 pin = 1 chain 1 pin = 1 chain
1 pin = 100 ft 1 pin = 50m
1 tally = 10 pins 1 tally = 10 pins
Soln:
(1) Dist = 5 tallies(10pins/tally)(100ft/1pin)+(6pins)(100ft/1pin)+(63.5links)(1ft/1link)
Dist = 5663.5ft
(2) Dist = 3 tallies(10pins/tally)(50m/1pin)+(8pins)(50m/1pin)+9m
Dist = 1909m
Probable Value and Error
Probable Error (PE)
Where:
E = Probable error
2
= sum of the squares of the residuals
n = number of observation
= 0.6745
2
( 1)
Standard Error (SE)
=
2
( 1)
Where:
SE = Standard error
2
= sum of the squares of the residuals
n = number of observation
Standard Deviation
=
2
( 1)
Where:
SD = Standard Deviation
2
= sum of the squares of the residuals
n = number of observation
Precision of Measurement
Precision of Measurement = PE/PV
Weight
Probable Value
W = k x M (no. of measurement)
W = k x 1/D (distance)
W = k x 1/PE (probable error)
Correct Value
W = k x M (no. of measurement)
W = k x 1/D (distance)
W = k x 1/PE (probable error)
The following interior angles of a triangle traverse
were measured with the same precision.
1. Determine the most probable value of angle A.
2. Determine the most probable value of angle B.
3. Determine the most probable value of angle C.
Angle Value (Degrees) No. of Measurements
A 41 5
B 77 6
C 63 2
Problem 5: CE Board May 2003
1. Probable value of angle A.
A + B + C = 41 + 77 + 63 = 181
0
Error = 181-180 = 1
0
Error = 60 mins.
LCD of 5, 6, and 2 is 30
Sta. Weight Correction
A
B
C
Solution:
30 = 6
5
6 (60) = 13.84
26
30 = 5
6
5 (60) = 11.54
26
30 = 15
2 26
15 (60) = 34.62
26 60
Corrected value of A = 41
0
13.84 = 40
0
46.16
3. Probable value of angle B:
Corrected value of B = 77
0
11.54 = 76
0
48.46
4. Probable value of angle C:
Corrected value of C = 63
0
34.62 = 62
0
25.38
Leveling
You might also like
- Tape Corrections by Broddett AbatayoDocument14 pagesTape Corrections by Broddett AbatayoBroddett Bello Abatayo100% (2)
- Measuring Distances Using Tape: Types of Errors in TapingDocument6 pagesMeasuring Distances Using Tape: Types of Errors in TapingRogieNo ratings yet
- Compre Prob Set 4Document42 pagesCompre Prob Set 4Aira Isahmay Galope Carpio0% (1)
- Higher SurveyingDocument103 pagesHigher SurveyingChristian GudinoNo ratings yet
- Simple Curve PDF FreeDocument21 pagesSimple Curve PDF FreeHedrene TolentinoNo ratings yet
- CE 21 CorrectionDocument4 pagesCE 21 CorrectionGintokiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 21 Reciprocal Leveling and Trigonometric Leveling: Fundamental of Surveying Engr. Richard VillamoraDocument18 pagesLesson 21 Reciprocal Leveling and Trigonometric Leveling: Fundamental of Surveying Engr. Richard VillamoraHernan BeñabonNo ratings yet
- Lec 12 - Missing DataDocument9 pagesLec 12 - Missing DataMarc Dared Cagaoan0% (2)
- Funsur FInalDocument27 pagesFunsur FInalSuzette FloranzaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 Final Final FinalDocument4 pagesLab Report 1 Final Final FinalChristopher Joshua MartinezNo ratings yet
- STADIA SURVEYINGDocument10 pagesSTADIA SURVEYINGJGon100% (1)
- Engineering SurveyingDocument5 pagesEngineering SurveyingEldwin Jay L MonteroNo ratings yet
- T4 - Corrections in Taping PDFDocument34 pagesT4 - Corrections in Taping PDFAngelica TalandronNo ratings yet
- Problem Set in CEngr 320 (Simple Curves)Document20 pagesProblem Set in CEngr 320 (Simple Curves)Evaline Faith Tacadena Blanco44% (9)
- Module 4 - FOSDocument21 pagesModule 4 - FOSHades Vesarius RiegoNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3erica surtida0% (1)
- Fieldwork Experiment No. 10Document5 pagesFieldwork Experiment No. 10Justine BotillaNo ratings yet
- SurveyingDocument3 pagesSurveyinglakr lama67% (3)
- Module 2Document34 pagesModule 2acurvz2005No ratings yet
- PDF Ce Board Problems in SurveyingDocument15 pagesPDF Ce Board Problems in SurveyingJoshua T ConluNo ratings yet
- T11 - Tacheometry PDFDocument28 pagesT11 - Tacheometry PDFAngelica TalandronNo ratings yet
- Problems Surveying QDSGDocument4 pagesProblems Surveying QDSGCalvin Ador DionisioNo ratings yet
- Ce TopicDocument8 pagesCe TopicKyle MarfsNo ratings yet
- Compound and Reversed Curve ProblemsDocument2 pagesCompound and Reversed Curve ProblemsAngela BautistaNo ratings yet
- Closing The HorizonDocument4 pagesClosing The HorizonLucero Don50% (4)
- Worksheet No. 56 - 63Document10 pagesWorksheet No. 56 - 63Dante M Suarez Jr.No ratings yet
- Design of Summit Parabolic CurveDocument4 pagesDesign of Summit Parabolic CurveDaryl Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Reversed CurveDocument7 pagesReversed CurveBenjo SantosNo ratings yet
- Problems in SurveyingDocument13 pagesProblems in SurveyingMiko Supremo100% (1)
- Fundamentals of SurveyingDocument9 pagesFundamentals of SurveyingRoxanne BorjaNo ratings yet
- Palma Bsce-2a Assignment2 Pce2Document4 pagesPalma Bsce-2a Assignment2 Pce2CHRISTIAN NATHANIEL PALMANo ratings yet
- BESA Mathematics Preboard Solutions 18 Feb. 2022Document50 pagesBESA Mathematics Preboard Solutions 18 Feb. 2022Chaythina CortezaNo ratings yet
- Construction Surveying and LayoutDocument55 pagesConstruction Surveying and LayoutElla TalinoNo ratings yet
- 5 PDFDocument1 page5 PDFshemal100% (1)
- Surveying 2019bDocument30 pagesSurveying 2019bhazel100% (1)
- Exercise 4 - Distance Measurment by Stadia MethodDocument5 pagesExercise 4 - Distance Measurment by Stadia MethodMark100% (1)
- StaticsDocument5 pagesStaticslakr lama100% (1)
- Besavilla Surveying TraverseDocument25 pagesBesavilla Surveying TraverseZaineNo ratings yet
- Theodolite Surveying FundamentalsDocument33 pagesTheodolite Surveying FundamentalsDelina Tedros67% (3)
- Plates PDFDocument13 pagesPlates PDFCRIISSY100% (1)
- Earth's Curvature and Atmospheric RefractionDocument11 pagesEarth's Curvature and Atmospheric RefractionCharles Carpo67% (3)
- Evaluation Exam in Surveying and Transportation EngineeringDocument45 pagesEvaluation Exam in Surveying and Transportation EngineeringJoseph LantoNo ratings yet
- SURVEYING Module 1 To 4Document17 pagesSURVEYING Module 1 To 4Hades Vesarius Riego100% (1)
- PSU-U Campus Module on Vertical Parabolic CurvesDocument5 pagesPSU-U Campus Module on Vertical Parabolic CurvesGerovic ParinasNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Unsymmetrical Parabolic CurveDocument23 pagesLecture - Unsymmetrical Parabolic CurveKemuel Tabamo67% (3)
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - FOSDocument9 pagesModule 3 - FOSHades Vesarius Riego67% (3)
- Engineering Surveys: Reversed CurvesDocument2 pagesEngineering Surveys: Reversed CurvesJazel Esteban-Sano50% (2)
- Lab Exercise No 7Document3 pagesLab Exercise No 7Clarise AlmeriaNo ratings yet
- Curvature and Refraction lighthouse height tower intervisibilityDocument9 pagesCurvature and Refraction lighthouse height tower intervisibilityAnony MousNo ratings yet
- SURVEYING I and IIDocument10 pagesSURVEYING I and IIBer Ryl0% (1)
- Mistakes and Errors in Surveying MeasurementsDocument19 pagesMistakes and Errors in Surveying MeasurementsAlfred TinoyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Surveying Correction On Taping Sample ProblemsDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Surveying Correction On Taping Sample Problemsneal saladagaNo ratings yet
- BSCE student's assessment scores and solutionsDocument4 pagesBSCE student's assessment scores and solutionsKRISTIANA KYSIA DUYOGANNo ratings yet
- Elementary Surveying Lecture Part 1Document7 pagesElementary Surveying Lecture Part 1soontobengineer100% (1)
- Module 1 Lesson 4Document18 pagesModule 1 Lesson 4Rainiel Montalba100% (1)
- Technical Report 2 CE215Document5 pagesTechnical Report 2 CE215Liezl Joy MainarNo ratings yet
- Correction Taping DistancesDocument10 pagesCorrection Taping DistancesMaria Olivia GabionzaNo ratings yet
- GEE 1 Chapter 3Document11 pagesGEE 1 Chapter 3Rheymarkbutron RamadaNo ratings yet
- GEE 1 Chapter 3Document11 pagesGEE 1 Chapter 3Rheymarkbutron RamadaNo ratings yet
- Types of Polygons ChartDocument2 pagesTypes of Polygons ChartJaireNo ratings yet
- Improving Wastewater Treatment and Membrane Filtration ProcessesDocument5 pagesImproving Wastewater Treatment and Membrane Filtration ProcessesJaireNo ratings yet
- Carolling Lyrics Tagalog EnglishDocument1 pageCarolling Lyrics Tagalog EnglishJaireNo ratings yet
- Terzaghi Bearing CapacityDocument42 pagesTerzaghi Bearing CapacityJaireNo ratings yet
- Sewer Design Process and Hydraulic CalculationsDocument79 pagesSewer Design Process and Hydraulic CalculationsJaire100% (2)
- How Satan Stops Our PrayersDocument17 pagesHow Satan Stops Our PrayersJaire100% (4)
- Sewer Appurtenances Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 pagesSewer Appurtenances Multiple Choice QuestionsJaire100% (1)
- RC Stirrups DesignDocument11 pagesRC Stirrups DesignJaireNo ratings yet
- CE500Document56 pagesCE500JaireNo ratings yet
- Promotional New FormatDocument22 pagesPromotional New FormatJaireNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire Water ResourceDocument1 pageQuestionnaire Water ResourceJaireNo ratings yet
- Bridge Designers AND Their ProjectsDocument25 pagesBridge Designers AND Their ProjectsJaireNo ratings yet
- Tell Me Very GentlyDocument5 pagesTell Me Very GentlyJaireNo ratings yet
- Highway Bridge StructuresDocument52 pagesHighway Bridge StructuresJaireNo ratings yet
- Precipitation Probability: Which Is Often Expressed As The "Chance of Rain" or "Chance of Precipitation"Document5 pagesPrecipitation Probability: Which Is Often Expressed As The "Chance of Rain" or "Chance of Precipitation"JaireNo ratings yet
- Regional Flood FrequencyDocument13 pagesRegional Flood FrequencyJaireNo ratings yet
- DroughtDocument20 pagesDroughtJaire100% (1)
- Report HydrologyDocument13 pagesReport HydrologyJaireNo ratings yet
- Role of Hydrology in Water Resources Planning andDocument10 pagesRole of Hydrology in Water Resources Planning andJaire59% (17)
- Reported By: Ybonne Mae O. Juverillo: Introduction To WatershedDocument25 pagesReported By: Ybonne Mae O. Juverillo: Introduction To WatershedJaireNo ratings yet
- Regional Flood FrequencyDocument13 pagesRegional Flood FrequencyJaireNo ratings yet
- Mine (Ondoy Typhoon)Document16 pagesMine (Ondoy Typhoon)JaireNo ratings yet
- DroughtDocument20 pagesDroughtJaire100% (1)
- Hyd OlogyDocument10 pagesHyd OlogyJaire100% (1)
- Precipitation Probability: Which Is Often Expressed As The "Chance of Rain" or "Chance of Precipitation"Document5 pagesPrecipitation Probability: Which Is Often Expressed As The "Chance of Rain" or "Chance of Precipitation"JaireNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument26 pagesReportJaireNo ratings yet
- Report HydrologyDocument13 pagesReport HydrologyJaireNo ratings yet
- Well DrawdownDocument16 pagesWell DrawdownJaireNo ratings yet
- Aquifers Movement of Soil MoistureDocument10 pagesAquifers Movement of Soil MoistureJaireNo ratings yet
- ManuscriptDocument2 pagesManuscriptVanya QuistoNo ratings yet
- Fictional Narrative: The Case of Alan and His FamilyDocument4 pagesFictional Narrative: The Case of Alan and His Familydominique babisNo ratings yet
- Elements of Ayurveda Daily Routine GuideDocument1 pageElements of Ayurveda Daily Routine GuideShivani GargNo ratings yet
- Assignment of A Glass Transition Temperature Using Thermomechanical Analysis: Tension MethodDocument4 pagesAssignment of A Glass Transition Temperature Using Thermomechanical Analysis: Tension MethodEric GozzerNo ratings yet
- Cat TSDDocument55 pagesCat TSDvarsha sharmaNo ratings yet
- Digitrip 520Document40 pagesDigitrip 520HACNo ratings yet
- 2.7.3 Lab Use Steganography To Hide Data Answer KeyDocument3 pages2.7.3 Lab Use Steganography To Hide Data Answer KeyVivek GaonkarNo ratings yet
- HUMAN RIGHTS, RATIONALITY, AND SENTIMENTALITYDocument13 pagesHUMAN RIGHTS, RATIONALITY, AND SENTIMENTALITYJohn HunterNo ratings yet
- The German eID-Card by Jens BenderDocument42 pagesThe German eID-Card by Jens BenderPoomjit SirawongprasertNo ratings yet
- Variolink Esthetic Brochure 673400Document6 pagesVariolink Esthetic Brochure 673400wuhan lalalaNo ratings yet
- My Son The Fanatic, Short StoryDocument4 pagesMy Son The Fanatic, Short StoryScribdAddict100% (2)
- L P 10Document13 pagesL P 10Bình Minh HoàngNo ratings yet
- Nataraja Stotram - A Hymn Without 'CharaNa' and 'ShRi~NgaDocument8 pagesNataraja Stotram - A Hymn Without 'CharaNa' and 'ShRi~NgaSiva Krishna100% (1)
- EMarketer Time Spent With Media SnapshotDocument13 pagesEMarketer Time Spent With Media SnapshotWei ShingNo ratings yet
- Health Optimizing Physical Education: Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) Quarter 4Document7 pagesHealth Optimizing Physical Education: Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) Quarter 4John Wilfred PegranNo ratings yet
- Elective Course (2) - Composite Materials MET 443Document16 pagesElective Course (2) - Composite Materials MET 443يوسف عادل حسانينNo ratings yet
- Chams 1Document78 pagesChams 1Das RavindraNo ratings yet
- History shapes Philippine societyDocument4 pagesHistory shapes Philippine societyMarvin GwapoNo ratings yet
- Prodelin 1385Document33 pagesProdelin 1385bebebrenda100% (1)
- CA-Endevor Quick EditDocument31 pagesCA-Endevor Quick Editmariela mmascelloniNo ratings yet
- S 212 Pre Course WorkDocument5 pagesS 212 Pre Course Workafiwierot100% (2)
- 7 Tools for Continuous ImprovementDocument202 pages7 Tools for Continuous Improvementvivekanand bhartiNo ratings yet
- Youre The Inspiration CRDDocument3 pagesYoure The Inspiration CRDjonjammyNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Doña Asuncion Lee Integrated School: Division of Mabalacat CityDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education Doña Asuncion Lee Integrated School: Division of Mabalacat CityRica Tano50% (2)
- How 50 Million People Are Changing the WorldDocument5 pagesHow 50 Million People Are Changing the WorldCTRCTR0% (1)
- APM200 Outdoor Power Supply System User Manual-20060628-B-1.0Document52 pagesAPM200 Outdoor Power Supply System User Manual-20060628-B-1.0Andrés MarroquínNo ratings yet
- Litz Wire Termination GuideDocument5 pagesLitz Wire Termination GuideBenjamin DoverNo ratings yet
- 50 Ways To Balance MagicDocument11 pages50 Ways To Balance MagicRodolfo AlencarNo ratings yet
- New ALS MADRASAH COMBINEDDocument6 pagesNew ALS MADRASAH COMBINEDJane BaysaNo ratings yet
- Reading in Philippine History (Chapter 3)Document14 pagesReading in Philippine History (Chapter 3)AKIO HIROKINo ratings yet