Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1: Elastic Solid: Even The Mountains Flowed Before The Lord
Uploaded by
Hossein Eslami0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
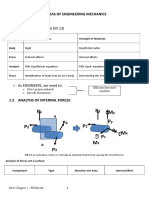
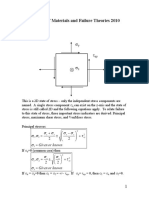
18 views6 pagesElastic solid from the song of Deborah afte her victory over the Philistines, Judges 5:5 force versus extension f DL stress and strain by Rita Greer, from written descriptions, 2009. The stress tensor (notation) determine the values of s: eigenvalue problem also eigenvectors (principal stress directions)
Original Description:
Original Title
Rheol_Chap01
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentElastic solid from the song of Deborah afte her victory over the Philistines, Judges 5:5 force versus extension f DL stress and strain by Rita Greer, from written descriptions, 2009. The stress tensor (notation) determine the values of s: eigenvalue problem also eigenvectors (principal stress directions)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views6 pages1: Elastic Solid: Even The Mountains Flowed Before The Lord
Uploaded by
Hossein EslamiElastic solid from the song of Deborah afte her victory over the Philistines, Judges 5:5 force versus extension f DL stress and strain by Rita Greer, from written descriptions, 2009. The stress tensor (notation) determine the values of s: eigenvalue problem also eigenvectors (principal stress directions)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
even the mountains flowed before the lord
1: elastic solid
from the song of Deborah afte her victory over the Philistines, Judges 5:5 (translated by M. Reiner, Physics today, Jan. 1964
Coast of Bretagne, France
force versus extension f ~L
stress & strain
By Rita Greer, from written descriptions, 2009
Hooke, 1678 (??)
the stress tensor
the stress tensor
the stress tensor (notation)
the stress tensor (notation)
the stress tensor (symmetry)
the stress tensor (pressure)
the stress tensor (normal stress differences)
eliminate pressure
Uniaxial extension by compression
fluid at rest
fluid in motion; extra stress
special case: simple shear
N1: first normal stress difference N2: second normal stress difference
the stress tensor (principal stresses & invariants)
principal plane, principal stress
the stress tensor (principal stresses & invariants)
determine the values of : eigenvalue problem
also eigenvectors (principal stress directions)
first, ,second & third invariant
finite deformation tensors
(examples of deformations)
finite deformation tensors (components of F)
finite deformation tensors (examples of deformations)
finite deformation tensors (examples of deformations)
uniaxial extension (incompressible)
uniaxial extension
simple shear simple shear
solid body rotation solid body rotation
finite deformation tensors
Finger deformation tensor B simple shear
finite deformation tensors
Cauchy-Green tensor C
finite deformation tensors
strain tensor E = B - I inverse deformation tensors B-1, C-1 principal strains (eigenvalue problem) Hooke: 1678,
neo-Hookean solid
Cauchy: 1820 (small deformations. Metals ceramics)
G: elastic shear modulus Incompressible: IIIB = detF = 0 the other two invariants IB IIB bind the possible deformations T = 0 in rest state: p = G p = 0 in rest state:
general elastic solid
strain energy function
for an elastic solid the stress is a function of the internal energy U only
- gi functions of the invariants of B - incompressible: IIIB = 0
with W = 0 U and for an incompressible, isotropic material:
- Cayley Hamilton theorem: any tensor satisfies its own characteristic equation
Examples Neo-Hookean: Mooney-Rivlin:
You might also like
- Design of Machine Elements NotesDocument483 pagesDesign of Machine Elements NotesHarsha VardhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 LectureDocument48 pagesChapter3 LectureAlaaNo ratings yet
- ES13 - CHAPTER 1 (Stress) StudentDocument8 pagesES13 - CHAPTER 1 (Stress) StudentBianca Asis100% (1)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Chapter 7 Mechanical PropertiesDocument29 pagesChapter 7 Mechanical Propertiesapi-269630671No ratings yet
- 10 - Fundamentals of Metal Forming (Chapter 14)Document37 pages10 - Fundamentals of Metal Forming (Chapter 14)Taher al suhamiNo ratings yet
- 9-10 - Mechanical Properties of Solids and Fluids - Merge File-R&R-FinalDocument36 pages9-10 - Mechanical Properties of Solids and Fluids - Merge File-R&R-FinalUrvashi RaoNo ratings yet
- Slide 5 Metal Forming IntroDocument72 pagesSlide 5 Metal Forming IntrogunjanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1c - Mech ProperDocument63 pagesChapter 1c - Mech PropermaiNo ratings yet
- 09 - Constitutive Models 21Document36 pages09 - Constitutive Models 21Veli YılmazNo ratings yet
- TM-2122 Mekanika Kekuatan Material: Distribusi TeganganDocument37 pagesTM-2122 Mekanika Kekuatan Material: Distribusi TeganganwahyuNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Stresses & Strains PDFDocument48 pages1.introduction To Stresses & Strains PDFErNo ratings yet
- Elasticity PDFDocument7 pagesElasticity PDFSajal SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- הרצאה 7Document44 pagesהרצאה 7api-26922789No ratings yet
- Stress and Deformation AnalysisDocument64 pagesStress and Deformation AnalysisSara Ben AmaraNo ratings yet
- 7 Properties of Bulk MatterDocument19 pages7 Properties of Bulk Matterranipal90688No ratings yet
- Soil Constitutive Model 2Document37 pagesSoil Constitutive Model 2adnan-651358No ratings yet
- C1 Simple Stress and StrainDocument45 pagesC1 Simple Stress and Strainاحمد رباطNo ratings yet
- REF1Document82 pagesREF1Vijay WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium and Elasticity: Conditions Under Which A Rigid Object Is in Equilibrium Problem-Solving Strategy ElasticityDocument19 pagesEquilibrium and Elasticity: Conditions Under Which A Rigid Object Is in Equilibrium Problem-Solving Strategy ElasticitymeerhamzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Deformation of Solids: Tensile CompressiveDocument11 pagesChapter 11: Deformation of Solids: Tensile CompressiveAzmira AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Theoritical BackgroundDocument7 pagesLecture 2 Theoritical BackgroundBerli Octaviana ManurungNo ratings yet
- State of StressDocument19 pagesState of StressHarun HodžićNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Failure TheoriesDocument45 pagesStrength of Materials and Failure Theoriesstallone21No ratings yet
- Self Weight Deflection of Circular PlatesDocument8 pagesSelf Weight Deflection of Circular PlatesJay KumarNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of StrucureSubjective NotesDocument22 pagesMechanics of StrucureSubjective NotesShyam Sundar YadavNo ratings yet
- The Mechanical Properties of PolymersDocument27 pagesThe Mechanical Properties of PolymersFranco GentiliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Stress and Strain - Axial LoadingDocument43 pagesChapter 2 Stress and Strain - Axial Loadingtaymar18No ratings yet
- 1994 - Second-Order Generalised Beam TheoryDocument21 pages1994 - Second-Order Generalised Beam TheoryJosue LewandowskiNo ratings yet
- Emf AssignmentDocument27 pagesEmf AssignmentBhaskar KumarNo ratings yet
- Review of Stress-Strain Due To Flexure: CE 437/537, Spring 2014 1 / 5Document5 pagesReview of Stress-Strain Due To Flexure: CE 437/537, Spring 2014 1 / 5Hussein MouzannarNo ratings yet
- L4 Mechanical PropertiesDocument41 pagesL4 Mechanical PropertiesHeamenth KumarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PropertiesDocument37 pagesMechanical PropertiesahamathNo ratings yet
- 07 - Mechanical Properties of MetalsDocument31 pages07 - Mechanical Properties of MetalsLizvel Keith TorresNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction & ReviewDocument38 pagesLecture 1 Introduction & Reviewهاني احمدNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties: Stress Strain Elastic PlasticDocument32 pagesMechanical Properties: Stress Strain Elastic Plasticmadee024No ratings yet
- Me A Chapter 1Document92 pagesMe A Chapter 1arandersNo ratings yet
- GY403 DynamicAnalysisDocument37 pagesGY403 DynamicAnalysissaira tahirNo ratings yet
- Hook's Law: Modulus of Elasticity or Coefficient of Elasticity: (E)Document30 pagesHook's Law: Modulus of Elasticity or Coefficient of Elasticity: (E)sanjog kshetriNo ratings yet
- Materials Properties 2009Document62 pagesMaterials Properties 2009sam skNo ratings yet
- EEAQ 2118 - 5 Mechanical PropertiesDocument34 pagesEEAQ 2118 - 5 Mechanical PropertiesOdhiambo AustinNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials EquationsDocument9 pagesStrength of Materials EquationsSiti Zahiratul HaniyahNo ratings yet
- MOS Study Material - Strut&TieDocument200 pagesMOS Study Material - Strut&TieSuhail SuhiNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain RelationshipDocument92 pagesStress Strain RelationshipUpulHettiarachchiNo ratings yet
- Me16A: Introduction To Strength of Materials: CourseDocument92 pagesMe16A: Introduction To Strength of Materials: CourseRimti BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Constitutive ModelsDocument36 pagesConstitutive ModelsWalter Moises Alvarez AjataNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Basic Rock MechanicsDocument44 pagesModule 1 Basic Rock MechanicsMaría Marquina100% (1)
- Review of Stress Strain Due To FlexureDocument5 pagesReview of Stress Strain Due To FlexureIhab SorourNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Class NotesDocument26 pagesFluid Mechanics: Class Notesengineer63No ratings yet
- Metal Forming - Chap.3Document20 pagesMetal Forming - Chap.3하은No ratings yet
- Fatigue Mechanism: - Crack Grows IncrementallyDocument27 pagesFatigue Mechanism: - Crack Grows IncrementallyprakashNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter 1semDocument27 pagesProperties of Matter 1semkjhkhuihuNo ratings yet
- Issues To Address... : Stress Strain Elastic PlasticDocument36 pagesIssues To Address... : Stress Strain Elastic PlasticdennisNo ratings yet
- Topic 06 Mechanical Properties - Compatibility ModeDocument34 pagesTopic 06 Mechanical Properties - Compatibility ModeSelviya AvaurumNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Metals: ความเครียด การเสียรูป (deformation)Document46 pagesMechanical Properties of Metals: ความเครียด การเสียรูป (deformation)ภาคภูมิ เหมยากรNo ratings yet
- Euler Bernoulli EquationDocument16 pagesEuler Bernoulli EquationBoon FuiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Mechanical Properties of Metals: (Part I - Basic Concepts)Document85 pagesStructure and Mechanical Properties of Metals: (Part I - Basic Concepts)VITHYAA RUHBINI GUNARAJANNo ratings yet
- LN12 PDFDocument31 pagesLN12 PDFelty TanNo ratings yet