Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Form 3 Chapter 6
Uploaded by
Yatt YatiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Form 3 Chapter 6
Uploaded by
Yatt YatiCopyright:
Available Formats
Form 3 Science Chapter 6
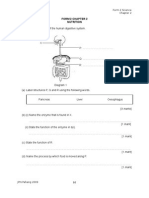
FORM 3 CHAPTER 6 LAND AND ITS RESOURCES 1. Diagram 1 shows how some petroleum is heated to different temperatures. .
Thermometer
Delivery tube Petroleum Porcelain chips
Heat
Water
Petroleum fraction
Diagram 1 (a) Name the process used in Diagram 1 to obtain the petroleum fractions [1 mark] (b) Table 5.2 shows the four fractions of petroleum collected in four separate test tubes according to different temperature. Distilled oil P Q R S Range of boiling point 30-800C 80-1200C 120-1600C 160-2000C Table 5.2 Colour Colourless Yellow Orange Red
169
Form 3 Science Chapter 6
(i) What is the relationship between P and S in terms of their boiling points and the colour of the distillate? . [1 mark] (ii) Using the words given below, name fractions P, Q, R and S. Kerosene . Diesel Petrol Lubricating oil
P: Q: R: S:
.. .. . .. [2 marks]
(c)
(i) State one use of P. [1 mark] (ii) Explain why we have to use P wisely. [1 mark]
170
Form 3 Science Chapter 6
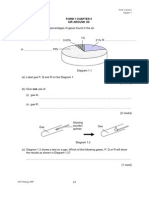
2.
Diagram 2 shows an activity to study the reaction between metal and oxygen.
Diagram 2 (a) What is the function of the potassium permanganate crystals? .. [1 mark] (b) Between zinc and copper, which metal is more reactive towards oxygen? [1 mark] (c) Name the product formed when zinc reacts with oxygen. .. [1 mark] (d) Write the word equation for the reaction between copper and oxygen. + [2 marks] (e) Give one reason why metals such as gold and silver do not react with oxygen. [1 mark]
171
Form 3 Science Chapter 6
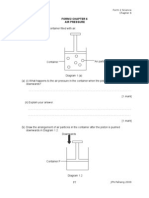
3. Diagram 3 shows some limestone powder being heated in a boiling tube. Liquid W turns cloudy after five minutes.
Limestone powder
W Diagram 3
(a) (i)
What is liquid W?
. (ii) Why does it turn cloudy? .. [2 marks] (b) Liquid W can be produced from limestone by the processes shown below. P Limestone Name (i) process P : (ii) substance Q : . (iii) process R : .. [3 marks] (c) List two uses of slaked lime (i) .. Q R Slaked lime dissolve in water Liquid W
(ii) .. 172
Form 3 Science Chapter 6
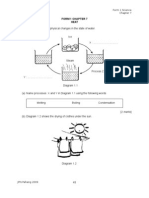
[2 marks] 4. Diagram 4 shows an activity carried out to study the effect of heat on copper sulphide. Copper sulphide
Solution M Diagram 3
(a) What is solution M?
[1 mark] (b)(i) What happen to solution M when the copper sulphide is heated strongly? . [1 mark] (ii) Name the gas released that causes the change in solution M b (i). . [1 mark] (c) Name the product left in the test tube after the copper sulphide was heated strongly. . [1 mark] (d) Complete the word equation for the above reaction. Copper sulphide
Heat
+ [2 marks] 173
Form 3 Science Chapter 6
5. Diagram 5 shows an activity carried out to study the property of calcium carbonate.
Dilute sulphuric acid Calcium carbonate Diagram 5 (a)(i) What happens to the limewater? [1 mark] (ii) Name the gas that is produced. .. [1 mark] (b) Complete the equation to show the reaction in Diagram 5. Calcium carbonate limewater
Sulphuric acid
+ +
[2 marks]
(c) Calcium carbonate is a compound. Name the elements found in calcium carbonate. [2 marks]
174
Form 3 Science Chapter 6
(d) Which of the following can be used to replace calcium carbonate in this activity? Tick ( ) the correct answers.
[2 marks]
175
You might also like
- V250MDC Project Guide GEK-115179b PDFDocument174 pagesV250MDC Project Guide GEK-115179b PDFElias Abu FakherNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 3Document7 pagesForm 3 Chapter 3naza977582% (11)
- Biodiversity Form 2 Science Chapter 3Document18 pagesBiodiversity Form 2 Science Chapter 3Angie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42taimurmalik5562100% (1)
- Form 3 Chapter 3Document7 pagesForm 3 Chapter 3naza977582% (11)
- Form 2 Chapter 2Document7 pagesForm 2 Chapter 2naza977579% (19)
- Introduction of The Mercedes 0M651 EngineDocument58 pagesIntroduction of The Mercedes 0M651 Enginejacksayshi100% (14)
- Gas Enginee Vs Gas TurbineDocument13 pagesGas Enginee Vs Gas TurbineTrung Quan VoNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 1Document6 pagesForm 3 Chapter 1naza977590% (29)
- Form 2 Chapter 5Document10 pagesForm 2 Chapter 5naza977587% (15)
- Exercise Chemistry Form 5 Carbon CompoundsDocument6 pagesExercise Chemistry Form 5 Carbon CompoundsWan ShuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 7Document15 pagesForm 3 Chapter 7naza9775100% (5)
- Form 3 Chapter 4Document7 pagesForm 3 Chapter 4naza9775100% (7)
- Form 3 Chapter 9Document3 pagesForm 3 Chapter 9naza9775100% (5)
- Form 3 Chapter 8Document8 pagesForm 3 Chapter 8naza9775100% (6)
- Pt3 Science Seminar ModuleDocument28 pagesPt3 Science Seminar ModuleSuntharan Muniandy100% (5)
- Form 3 Chapter 10Document4 pagesForm 3 Chapter 10naza977575% (4)
- Soalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4 PDFDocument22 pagesSoalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4 PDFIsmaliza Ishak0% (1)
- Form 3 Chapter 2Document9 pagesForm 3 Chapter 2Mariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Biology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2Document13 pagesBiology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2SanjeefKumrIINo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 5Document4 pagesForm 3 Chapter 5naza9775100% (3)
- Science Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 8 RadioactivityDocument19 pagesScience Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 8 Radioactivitysakinah100% (1)
- Chapter 3 QuestionDocument9 pagesChapter 3 QuestionShila KaurNo ratings yet
- Latihan Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 4Document11 pagesLatihan Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 4李友志67% (3)
- Chapter 7 Linear InequalitiesDocument8 pagesChapter 7 Linear InequalitiesROSMAWATI BINTI MOHAMED -No ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Blood Circulation and TransportDocument8 pagesScience Form 3 Blood Circulation and Transportkc_hani0% (1)
- Form 3 Chapter 2Document9 pagesForm 3 Chapter 2naza9775100% (17)
- Topical Test Biology Form 4Document14 pagesTopical Test Biology Form 4Siti Wahida SuleimanNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 6Document9 pagesForm 2 Chapter 6naza9775100% (7)
- Revision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Document21 pagesRevision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Shureen Baskaran100% (1)
- Science Module Form 3 Chapter 4Document23 pagesScience Module Form 3 Chapter 4Hazira HaidzirNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions.: Sains Pt3 Tingkatan 3 Set 1Document9 pagesAnswer All Questions.: Sains Pt3 Tingkatan 3 Set 1Wan NazrinaNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 7Document8 pagesForm 2 Chapter 7naza977589% (9)
- F2 Chap 3 MCQDocument5 pagesF2 Chap 3 MCQSuriya GunalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MatterDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Matternaza9775100% (2)
- Modul 1 - Form 1 STFDocument31 pagesModul 1 - Form 1 STFmadrosli100% (3)
- Quiz f3Document10 pagesQuiz f3Hafizah PakahNo ratings yet
- Softcopy Science Form 2 (Book A)Document144 pagesSoftcopy Science Form 2 (Book A)VANAJA A/P NALLAPPAN Moe100% (1)
- Form 2 Chapter 8Document6 pagesForm 2 Chapter 8naza9775100% (4)
- Chemistry Form 4 - Paper 1Document13 pagesChemistry Form 4 - Paper 1adikmuk0% (1)
- Sci F1 T1 (E)Document7 pagesSci F1 T1 (E)Sylvia ChinNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Module Chapter 4 Reativity of MetalsDocument11 pagesForm 3 Module Chapter 4 Reativity of Metalsgrace_lo_1100% (1)
- SCIENCE FORM 3 Chapter 4 ExerciseDocument7 pagesSCIENCE FORM 3 Chapter 4 ExerciseWan Shuhaimi Wan Ali100% (1)
- Exercise On Chapter 8 Science Form 3Document3 pagesExercise On Chapter 8 Science Form 3Sasi RekaNo ratings yet
- Module Science Pt3Document11 pagesModule Science Pt3lccjane8504No ratings yet
- Modul F2 Science Chapter 1Document21 pagesModul F2 Science Chapter 1NorelyanaAli95% (21)
- Form 3 Chapter 1 QuestionsDocument11 pagesForm 3 Chapter 1 QuestionsCheah Foo Kit50% (2)
- PMR 2012 Science 108 MantraDocument16 pagesPMR 2012 Science 108 MantraJun MingNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 1Document6 pagesForm 2 Chapter 1naza977562% (13)
- Exercise Chapter Land and Its ResourcesDocument6 pagesExercise Chapter Land and Its ResourcesWan ShuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Section A (40 Marks) Answer All QuestionsDocument23 pagesSection A (40 Marks) Answer All QuestionsDalilaNo ratings yet
- Kimia - Revision Final ExamDocument37 pagesKimia - Revision Final ExamYu LyzaNo ratings yet
- Chem Trial 2012Document14 pagesChem Trial 2012Han LingNo ratings yet
- SMK Seri Perak, Parit Buntar Mid-Year Examination Form 5 2010Document16 pagesSMK Seri Perak, Parit Buntar Mid-Year Examination Form 5 2010Mohd Faizal Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Chemistry Paper - 42Document12 pages1st Term Chemistry Paper - 42Krish PatelNo ratings yet
- SOALANnnDocument13 pagesSOALANnnKeertanaNo ratings yet
- SPM Form 4 Chemistry Chap 7 & 8 ExercisesDocument20 pagesSPM Form 4 Chemistry Chap 7 & 8 ExercisesJames Wong100% (1)
- Malam Doc Chemistry Form 5: Chapter 2: Name: . ClassDocument7 pagesMalam Doc Chemistry Form 5: Chapter 2: Name: . ClassAzie Nurul AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Chem F2Document8 pagesChem F2Festus NanokNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 3 2024 - Question PaperDocument8 pagesChemistry Form 3 2024 - Question Paperwinfredmwende44No ratings yet
- Example PTE Structured QuestionsDocument5 pagesExample PTE Structured Questions301 Dhia JaharahNo ratings yet
- Irp Set 2Document22 pagesIrp Set 2rajaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008: Chapter 1: Rate of ReactionDocument21 pagesAnalysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008: Chapter 1: Rate of ReactionKarti ViveygenNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Paper 2 2010 f4Document14 pagesFinal Exam Paper 2 2010 f4Norzilah MazaharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Linear InequalitiesDocument11 pagesChapter 5 Linear Inequalitiesnaza9775No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Algebraaic ExpressionsDocument33 pagesChapter 7 Algebraaic Expressionsnaza9775100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Directed NumbersDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Directed Numbersnaza9775100% (3)
- Chapter 4 Algebraic FormulaeDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Algebraic Formulaenaza9775100% (1)
- Chapter 6 IndicesDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Indicesnaza9775No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Square Square Roots Cubes & Cubes RootsDocument23 pagesChapter 2 Square Square Roots Cubes & Cubes Rootsnaza9775100% (2)
- Form 3 Chapter 8Document8 pagesForm 3 Chapter 8naza9775100% (6)
- Form 2 Chapter 10Document10 pagesForm 2 Chapter 10naza9775100% (7)
- Exercise Form 1 Chapter 5 Air Around UsDocument9 pagesExercise Form 1 Chapter 5 Air Around UsN Dingz UpsNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 9Document3 pagesForm 3 Chapter 9naza9775100% (5)
- Form 3 Chapter 10Document4 pagesForm 3 Chapter 10naza977575% (4)
- Form 2 Chapter 7Document8 pagesForm 2 Chapter 7naza977589% (9)
- Form 3 Chapter 2Document9 pagesForm 3 Chapter 2naza9775100% (17)
- Form 3 Chapter 5Document4 pagesForm 3 Chapter 5naza9775100% (3)
- Form 2 Chapter 9Document10 pagesForm 2 Chapter 9naza9775100% (3)
- Form 2 Chapter 6Document9 pagesForm 2 Chapter 6naza9775100% (7)
- Form 2 Chapter 8Document6 pagesForm 2 Chapter 8naza9775100% (4)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Sciencenaza977583% (18)
- Chapter 7 HeatDocument12 pagesChapter 7 Heatnaza977583% (6)
- Form 1 Science: Form 1 Chapter 6 Sources of EnergyDocument9 pagesForm 1 Science: Form 1 Chapter 6 Sources of Energynaza9775100% (2)
- Exercise Form 1 Chapter 4 Variety of Resources On EarthDocument5 pagesExercise Form 1 Chapter 4 Variety of Resources On EarthSyahrul100% (1)
- Form 2 Chapter 3Document7 pagesForm 2 Chapter 3naza977588% (8)
- Chapter 2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Cell As A Unit of Lifenaza9775100% (5)
- Chapter 3 MatterDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Matternaza9775100% (2)
- Form 2 Chapter 1Document6 pagesForm 2 Chapter 1naza977562% (13)
- Fusibles Jetta 2001 2.0LDocument21 pagesFusibles Jetta 2001 2.0LLuis Angel BarajasNo ratings yet
- HT BotellasDocument2 pagesHT BotellasrafaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Class: Propulsion Aircraft Generates Mechanical Power Gas TurbinesDocument3 pagesIntroduction Class: Propulsion Aircraft Generates Mechanical Power Gas Turbinesjoseph prasanna kumarNo ratings yet
- Yanmar ViO57U BrochureDocument12 pagesYanmar ViO57U BrochureLuka BornaNo ratings yet
- Method 8015dDocument37 pagesMethod 8015dplayerboy111No ratings yet
- FME OP BrochureDocument2 pagesFME OP BrochureMartin KratkyNo ratings yet
- Model AC660 Generator Set: AOSIF Cummins SeriesDocument7 pagesModel AC660 Generator Set: AOSIF Cummins SeriesLilan Sameera - TISARA ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- F004-P006-Gfpi Guia de ApreDocument165 pagesF004-P006-Gfpi Guia de Aprejuan perezNo ratings yet
- Station 3 Ngs Support, I&m Engines TPM Uk 2017.01Document65 pagesStation 3 Ngs Support, I&m Engines TPM Uk 2017.01jose breno vieira silva100% (2)
- FAW-18W Foaming Additive - Overview - HiresDocument1 pageFAW-18W Foaming Additive - Overview - Hirespedro taquichiriNo ratings yet
- Snox Pet Coke BoilersDocument14 pagesSnox Pet Coke BoilersФранческо ЛеньямеNo ratings yet
- Mikuni Motorcycle Carburetor Theory 101Document8 pagesMikuni Motorcycle Carburetor Theory 101Riski HartonoNo ratings yet
- Eurol Super Lite 5W40 Full SyntheticDocument1 pageEurol Super Lite 5W40 Full SyntheticDanilo DamianNo ratings yet
- LPK 909ex Bs-Iii: (Parts List)Document216 pagesLPK 909ex Bs-Iii: (Parts List)shivamNo ratings yet
- Data Sheets Nta855 g7Document4 pagesData Sheets Nta855 g7Macra MatthewNo ratings yet
- 3 - Ra 8749 - The Clean Air ActDocument108 pages3 - Ra 8749 - The Clean Air ActVitaliano Francia, Jr. IINo ratings yet
- Zytel 70 G13 HS1 LBK031Document3 pagesZytel 70 G13 HS1 LBK031vikram goralNo ratings yet
- Engineering Inspiration - Brake System Design CalculationsDocument17 pagesEngineering Inspiration - Brake System Design CalculationsManjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Corona-Guia de Aplicacion Ejes Motriz Spicer Axag-0200Document106 pagesCorona-Guia de Aplicacion Ejes Motriz Spicer Axag-0200Antony Moreno0% (1)
- Hino 500 Ranger FG 235 JJ Fire Truck 5500 Water Foam, Double Cabin, SNI Standart PROTEKTA FIREFORT VATORDocument8 pagesHino 500 Ranger FG 235 JJ Fire Truck 5500 Water Foam, Double Cabin, SNI Standart PROTEKTA FIREFORT VATORKasidinNo ratings yet
- 1KD Engine Coolan Drain PlugDocument2 pages1KD Engine Coolan Drain Plugkampee100% (1)
- Framo Presentation With AnimationDocument26 pagesFramo Presentation With AnimationManmadhaNo ratings yet
- P0773Document5 pagesP0773Noel Alejandro Cordova RangelNo ratings yet
- 4006-23 TAG2A - 3A - TPD1512 Al Cooling Pack June '14Document12 pages4006-23 TAG2A - 3A - TPD1512 Al Cooling Pack June '14DEEPAKNo ratings yet
- Raphite: by Rustu S. KalyoncuDocument11 pagesRaphite: by Rustu S. KalyoncudimasNo ratings yet