Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transport of Oxygen in The Human Body
Uploaded by
Nik Nazihah NmnOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transport of Oxygen in The Human Body
Uploaded by
Nik Nazihah NmnCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
TRANSPORT OF OXYGEN IN THE HUMAN BODY
By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the diffusion of oxygen from the alveoli into the blood capillaries Describe the transport of oxygen by blood Describe the diffusion of oxygen from the blood capillaries into the cells
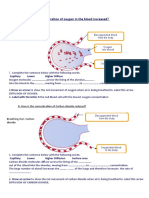
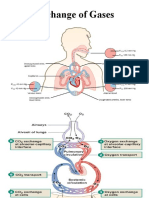
INTRODUCTION: - Feature of alveoli and capillaries walls is one cell thick which easy to oxygen to move in or out. - The movement of oxygen from the alveolus to blood capillaries involves diffusion.
The movements of molecules from a region of higher concentration of molecules to a region lower of concentration of molecules.
HOW THE DIFFUSION OF OXYGEN FROM THE ALVEOLI INTO THE BLOOD CAPILLARIES OCCUR IN OUR BODY? - More oxygen present in the inhaled air than in the blood.(why?) - So, oxygen diffuses from alveolus through to the blood.(how diffusion occur) HOW THE TRANSPORT OF OXYGEN BY BLOOD? - Red blood cell contain dark red compound called haemoglobin. - The blood capillaries have a higher concentration of oxygen. - Therefore, haemoglobin combines with oxygen form oxyhaemoglobin. HAEMOGLOBIN + OXYGEN OXYHAEMOGLOBIN
- Oxyhaemoglobin is transported from the lungs to over the body.
HOW THE DIFFUSION OF OXYGEN FROM THE BLOOD CAPILLARIES INTO THE CELLS OCCUR? - Oxyhaemoglobin is unstable and bright red compound. - Oxyhaemoglobin will break down and release the oxygen at lower oxygen place.
OXYHAEMOGLOBIN
HAEMOGLOBIN + OXYGEN
Example: Cell surrounding blood capillaries usually have lower concentration of oxygen. So, oxyhaemoglobin breaks into haemoglobin and oxygen. Then oxygen diffuse through blood capillaries into cells. SUMMARY Oxygen transport from: Inhaled air alveoli blood cell (a) cells of the body b)
a) OXYHAEMOGLOBIN HAEMOGLOBIN + OXYGEN
b) HAEMOGLOBIN + OXYGEN OXYHAEMOGLOBIN
You might also like
- Biology Presentation F4 8.3Document11 pagesBiology Presentation F4 8.3Michael AbishekapriyanNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-2.2 Gases Exchange-NtmDocument14 pagesChapter 2-2.2 Gases Exchange-NtmNITIASSWARENo ratings yet
- Factors Regulating BreathingDocument15 pagesFactors Regulating BreathingShubha DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument11 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemTania Ferdous RipaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Transport of OxygenDocument6 pages1.2 Transport of OxygenDanielle HughesNo ratings yet
- (Notes) Science Form 3 - Chapter 2 (Respiration)Document12 pages(Notes) Science Form 3 - Chapter 2 (Respiration)Aizzat BahiahNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Presentation MERGEDDocument20 pagesPulmonary Presentation MERGEDShubha DiwakarNo ratings yet
- How Is The Concentration of Oxygen in The Blood Increased?Document1 pageHow Is The Concentration of Oxygen in The Blood Increased?Rohma Umair100% (1)
- SPM Notes On Chapter RespirationDocument18 pagesSPM Notes On Chapter RespirationSyamila YusofNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Blood: PlasmaDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Blood: Plasmaعبدالحكيم النهديNo ratings yet
- Concept of Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesConcept of Respiratory SystemNur Oktavia RhosaniNo ratings yet
- Form 3 ScienceDocument10 pagesForm 3 ScienceCK100% (1)
- Unit 3 Respiratory PhysiologyDocument4 pagesUnit 3 Respiratory PhysiologyMandeep DebnathNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument5 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessonu kumarNo ratings yet
- Pt3 Revision ScienceDocument62 pagesPt3 Revision ScienceDeepa Darshini100% (2)
- Gas Exchange and Alveoli 2Document18 pagesGas Exchange and Alveoli 213obasuyioNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 - Chapter 2 (Respiration)Document12 pagesScience Form 3 - Chapter 2 (Respiration)Aizzat Bahiah60% (5)
- Class11th BREATHINGEXCHANGEOFGASES PDFDocument31 pagesClass11th BREATHINGEXCHANGEOFGASES PDFJaved Ahmed ChandioNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Physiology PDFDocument121 pagesRespiratory System Physiology PDFVizhiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory Systemapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Asgmt Anscie2.2Document1 pageAsgmt Anscie2.2Karl Sean UbinaNo ratings yet
- Breathing & Exchange of GasesDocument5 pagesBreathing & Exchange of GasesMamta TiwariNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange at The MuscleDocument6 pagesGas Exchange at The Muscleraian claudeNo ratings yet
- Biology Semester 2Document49 pagesBiology Semester 2MoonNo ratings yet
- 11.17 Breathing and Exchanges of GasesDocument7 pages11.17 Breathing and Exchanges of GasesMoonesh MKNo ratings yet
- 7) Exchange of Respiratory Gases by Shaltalo KhanDocument14 pages7) Exchange of Respiratory Gases by Shaltalo KhanHasin's QueenNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Human Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiration: Human Respiratory SystemSheehan MathurNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Function Is To Provide Oxygen To Tissues and Remove Carbon DioxideDocument10 pagesRespiration: Function Is To Provide Oxygen To Tissues and Remove Carbon DioxideAl Glen Diagan EgarleNo ratings yet
- Answer Discussion Share: (A) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)Document8 pagesAnswer Discussion Share: (A) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)gopeabhijit85No ratings yet
- Lecture 7 (Gasses & Pressure)Document9 pagesLecture 7 (Gasses & Pressure)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange & O2 TransportDocument11 pagesGas Exchange & O2 Transportmina mounirNo ratings yet
- Internal RespirationDocument9 pagesInternal RespirationRhose ReyesNo ratings yet
- G7 - Respiration - NotesDocument6 pagesG7 - Respiration - NotesSahithi PNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Transport of OxygenDocument8 pages1.2 Transport of OxygenMNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument4 pagesRespiration NotesJana AldourNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Gaseous Exchange in HumansDocument27 pages8.3 Gaseous Exchange in Humanswickedbiology101No ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 7Document18 pagesBiology Chapter 7edain84No ratings yet
- Tugas Bio JejeDocument1 pageTugas Bio JejenoorlailyNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Disediakan Oleh: Kamaruzaman Bin Abd SamadDocument11 pagesRespiration: Disediakan Oleh: Kamaruzaman Bin Abd SamadAmanz SamadNo ratings yet
- Estructuras Del PulmonDocument1 pageEstructuras Del PulmonAlex Vaca VacaNo ratings yet
- Exchange of GasesDocument14 pagesExchange of GasesSudhaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic RespirationDocument1 pageAerobic RespirationGrace JosephNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Dissociation CurvesDocument11 pagesOxygen Dissociation CurvesSajin Sali75% (4)
- Oxygen Delivery and ConsumptionDocument2 pagesOxygen Delivery and ConsumptionAde YonataNo ratings yet
- 224392278 BMAT Biology Revision Notesรรร PDFDocument9 pages224392278 BMAT Biology Revision Notesรรร PDFB. ChillNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Gas ExchangeDocument9 pages1.2 Gas ExchangesiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Scs f3Document15 pagesChapter 1 Scs f3putridequenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESDocument7 pagesChapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESprernatiwary508No ratings yet
- Gas ExchangeDocument8 pagesGas Exchangeapi-277602677No ratings yet
- Respiration Vs VentilationDocument1 pageRespiration Vs VentilationBoris FaktorovichNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Humans PDFDocument6 pagesGaseous Exchange in Humans PDFKevin JacksonNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in The LungsDocument30 pagesGas Exchange in The LungsYasasviNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Human Respiratory System - 1.2 Gas Exchange - 1.3 BreathingDocument26 pages1.1 The Human Respiratory System - 1.2 Gas Exchange - 1.3 BreathingAla' ShehadehNo ratings yet
- List Major Muscles Involved in Respiration (Inspiration and Expiration) at Rest and During ExerciseDocument5 pagesList Major Muscles Involved in Respiration (Inspiration and Expiration) at Rest and During ExerciseEmMa DHieyahNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange Presentation FinalDocument13 pagesGas Exchange Presentation FinalTharun BNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sunita Saxena - Breathing and Exchange of GassesDocument48 pagesDr. Sunita Saxena - Breathing and Exchange of GassesDivya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Transport - PPTX JONELTADocument32 pagesOxygen and Carbon Dioxide Transport - PPTX JONELTArithikaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration - Glucose + Oxygen Water + EnergyDocument3 pagesAerobic Respiration - Glucose + Oxygen Water + EnergyEsteban OrtegaNo ratings yet