Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiration Vs Ventilation
Uploaded by
Boris Faktorovich0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageRespiration and ventilation are different processes. Respiration is the physiologic exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and blood, and within cells. Ventilation is the mechanical process of breathing, moving air in and out of the lungs. Specifically, respiration refers to the exchange of gases within the alveoli of the lungs (external respiration) and within cells (internal respiration), while ventilation describes the physical inhalation and exhalation of air.
Original Description:
ola!
Original Title
respiration-vs-ventilation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRespiration and ventilation are different processes. Respiration is the physiologic exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and blood, and within cells. Ventilation is the mechanical process of breathing, moving air in and out of the lungs. Specifically, respiration refers to the exchange of gases within the alveoli of the lungs (external respiration) and within cells (internal respiration), while ventilation describes the physical inhalation and exhalation of air.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageRespiration Vs Ventilation
Uploaded by
Boris FaktorovichRespiration and ventilation are different processes. Respiration is the physiologic exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and blood, and within cells. Ventilation is the mechanical process of breathing, moving air in and out of the lungs. Specifically, respiration refers to the exchange of gases within the alveoli of the lungs (external respiration) and within cells (internal respiration), while ventilation describes the physical inhalation and exhalation of air.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
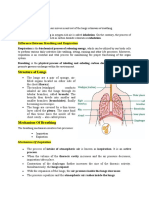
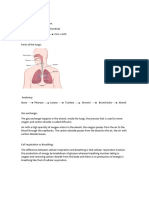
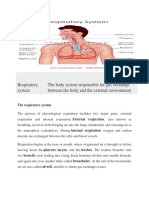
Respiration vs Ventilation
Respiration and ventilation are two different things.
Ventilation is mechanical and involves the movement of air, Respiration
is physiologic and involves the exchange of gases in the alveoli (external
respiration) and in the cells (internal respiration).
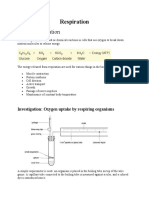
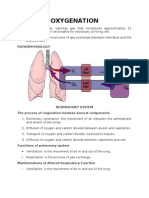
• RESPIRATION: The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
• VENTILATION: the mechanical drawing in and expelling out air via
breathing.
• OXYGENATION: oxygen dissolved in blood and body fluids; specifically,
this is the process of loading oxygen molecules onto hemoglobin
molecules in the bloodstream.
In medicine the process of moving air is called ventilation, respiration is
specifically the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide inside the alveoli of the
lungs.
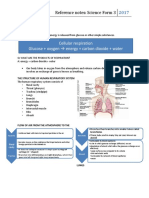
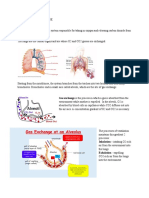
EXTERNAL RESPIRATION: Within the alveoli, oxygen from the
air diffuses across the thin cell membrane and attaches to the red blood cells
which have a low concentration of oxygen. At the same time, the carbon dioxide-
rich deoxygenated red blood cells release carbon dioxide which diffuses across
the cell membrane to the area of a lower carbon dioxide concentration (the
inspired air in the lungs), for expiration.
INTERNAL RESPIRATION: The cells exchange gases with the red blood cells
in the capillaries in the same manner as the alveoli exchange gases. When this
occurs in the cells it is known as "internal respiration," as there is no exchange of
gases with the environment outside the body.
You might also like
- Lung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Ext RespDocument17 pagesExt RespMuuubbbbbbbbNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy & PhysiologyJohn Erlan LipataNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Science Chapter 1Document25 pagesForm 3 Science Chapter 1Mukilan MurugasanNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of RespirationDocument18 pagesMechanism of RespirationHoney BoneyNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Inspiration (Inhalation)Document2 pagesRespiration: Inspiration (Inhalation)Zunaira NoreenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 1 NotesLim Zhi EnNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Biology Notes on Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument6 pages7th Grade Biology Notes on Respiration and Gas ExchangeSahithi PNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Document36 pagesTopic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Breathing Study SheetDocument8 pagesBreathing Study Sheetshimaa youssifNo ratings yet
- File 1667629685 GUSBAS202232069 UpdatedRespiration-module2Document4 pagesFile 1667629685 GUSBAS202232069 UpdatedRespiration-module2pranjal dubeyNo ratings yet
- Internal RespirationDocument9 pagesInternal RespirationRhose ReyesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesRespiratory SystemWanti LenteraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Chapter 3Document49 pagesUnit 2 - Chapter 3Zin Min KhantNo ratings yet
- Respiration & Breathing ExplainedDocument18 pagesRespiration & Breathing ExplainedKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System of Frog: External RespirationDocument3 pagesRespiratory System of Frog: External RespirationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Respiration: The Exchange of GasesDocument42 pagesRespiration: The Exchange of GasesNaureen Khaliq100% (1)
- Human Respiratory System: Gas Exchange ProcessDocument15 pagesHuman Respiratory System: Gas Exchange Processpraneeth satishNo ratings yet
- Week 7 (A) Human and Social BiologyDocument4 pagesWeek 7 (A) Human and Social BiologyBeyonce SkekelNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemNicole PinedaNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument7 pagesRespirationMemona KhalidNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document5 pagesDocument 5kauthar hassanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesPhysiology of Respiratory SystemAngelica Joan SorianoNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Humans PDFDocument6 pagesGaseous Exchange in Humans PDFKevin JacksonNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument4 pagesRespiration NotesJana AldourNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: The Organs That Help To Get Oxygen From The Air Into Your Blood, and To Get Rid of Carbon DioxideDocument22 pagesRespiratory System: The Organs That Help To Get Oxygen From The Air Into Your Blood, and To Get Rid of Carbon DioxideTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesRespiratory Systemsouha kahilNo ratings yet
- Breathing and RespirationDocument30 pagesBreathing and Respirationhamzahazard527No ratings yet
- Biology Notes - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesBiology Notes - Respiratory SystemnoorbdeirNo ratings yet
- The Human Breathing SystemDocument5 pagesThe Human Breathing SystemHarry Cianne Luther Sayon100% (1)
- IGCSE Biology: Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument29 pagesIGCSE Biology: Respiration and Gas Exchangemiriam odonkorNo ratings yet
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument37 pagesGaseous ExchangeSolángé MirembeNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageNotes On The Respiratory SystemNessa GNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and the LungsDocument21 pagesHuman Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and the LungsEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation BaseDocument2 pagesOxygenation BaseRehan ThomasNo ratings yet
- Chapter II - Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesChapter II - Respiratory SystemIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument5 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gaseslpc4944No ratings yet
- Respiratory System Physiology PDFDocument121 pagesRespiratory System Physiology PDFVizhiNo ratings yet
- Science Senior 2Document4 pagesScience Senior 2ajichristianbaniadamNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Gas ExchangeDocument30 pagesRespiratory System: Gas ExchangeDawn Regile MorilloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs: How They WorkDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Lungs: How They WorkMayownski TejeroNo ratings yet
- Pt3 Revision ScienceDocument62 pagesPt3 Revision ScienceDeepa Darshini100% (2)
- Lesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument60 pagesLesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsBeng QuinnNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Gas Exchange: Presented By: Mrdaniel Angelitog Hernandez, LPTDocument17 pagesMechanism of Gas Exchange: Presented By: Mrdaniel Angelitog Hernandez, LPTjayson reyesNo ratings yet
- Physiology of RespirationDocument2 pagesPhysiology of RespirationIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument27 pagesRespirationBighnaraj SwainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 BioDocument18 pagesChapter 11 BioRylee LNo ratings yet
- S2 - Bio - RevisionNotes 1.1 To 1.4 - PreMidDocument7 pagesS2 - Bio - RevisionNotes 1.1 To 1.4 - PreMidKaung ThihaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Scs f3Document15 pagesChapter 1 Scs f3putridequenoNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange & Lung FunctionDocument23 pagesGas Exchange & Lung FunctionIna NordsethNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Respiratory FunctionDocument36 pagesAssessment of Respiratory FunctionErica Clerigo LandichoNo ratings yet
- HBVHB B HBGVGHBDocument9 pagesHBVHB B HBGVGHBbaneNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMzDocument12 pagesANATOMY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMzalthea jade villadongaNo ratings yet
- Kim LesterDocument6 pagesKim LesterKim Lester ValeraNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Respiratory System SEM 2 SESI 2019/2020 Group: A: Name: Mohamad Aiman Iqbal Bin Nordin MATRIC NO: D20192091516Document8 pagesModule 2: Respiratory System SEM 2 SESI 2019/2020 Group: A: Name: Mohamad Aiman Iqbal Bin Nordin MATRIC NO: D20192091516muhd ariffNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemRaluca MoldovanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes on Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument4 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes on Breathing and Exchange of GasesParimala deviNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsDocument11 pagesRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System The Body System Responsible For Gas Exchange Between The Body and The External EnvironmentDocument3 pagesRespiratory System The Body System Responsible For Gas Exchange Between The Body and The External EnvironmentJona ThanNo ratings yet
- 2.1 - Breathing and Gaseous ExchangeDocument16 pages2.1 - Breathing and Gaseous ExchangeZawata Afnan ShararaNo ratings yet
- 1755 EarthquakeDocument1 page1755 EarthquakeBoris FaktorovichNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Respiratory TractDocument3 pagesRespiratory System Respiratory TractBoris FaktorovichNo ratings yet
- Evaluate Nutrition and Digestion With Interactive QuestionsDocument6 pagesEvaluate Nutrition and Digestion With Interactive QuestionsBoris FaktorovichNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument4 pagesExcretory SystemBoris FaktorovichNo ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)