Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design of Saddle Supports Stresses in Vessel On Two Saddles Using ZICK S Method by Abdel Halim Galala
Design of Saddle Supports Stresses in Vessel On Two Saddles Using ZICK S Method by Abdel Halim Galala
Uploaded by
terranzOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design of Saddle Supports Stresses in Vessel On Two Saddles Using ZICK S Method by Abdel Halim Galala
Design of Saddle Supports Stresses in Vessel On Two Saddles Using ZICK S Method by Abdel Halim Galala
Uploaded by
terranzCopyright:
Available Formats
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 90 of 126 Sheet : 1 of 7 Rev. : 1
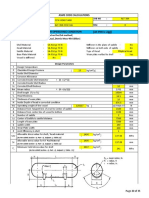
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 N. Design of Saddle Supports The design of saddle supports for horizontal cylindrical pressure vessel shall include the required plate thicknesses calculations for the following saddle components : I. Top flange (reinforcement/wear) thickness , tf. II. Web (saddle plate) thickness , tw. III. Stiffener (rip plates) thickness , ts. IV. Base plate thickness , tb. The Design Data is as Follows : Vessel type & position Design pressure , P Design temperature Radiography (only for pressure parts, BW) Vessel inside dia., D Vessel outside dia., Do Vessel outside radius, Ro Vessel wall thickness, t Corrosion allowance, C Material : shell heads saddles Min. tensile stress : shell heads saddles Min. yield stress, sy : shell & heads saddles Allowable tensile stress: shell heads saddles Vessel weight , empty , W liquid (water), Wc Vessel total weight , Wt Number of saddles used Load per saddle , Q Saddle angle of contact , B Saddle width, b Ring stiffeners adjacent to saddle
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
Cylindrical & Horizontal 257.898 PSI 18.156 o 149 F 65 85% 61.2598 INCH 1556 62.9921 INCH 1600 31.4961 INCH 800 0.86614 INCH 22 0.23622 INCH 6 ASME SA516 Grade 70 ASME SA516 Grade 70 ASME SA283 Grade C 60000 PSIG 4224 60000 PSIG 4224 55000 PSIG 3872 32000 PSIG 2252.8 30000 PSIG 2112 20000 PSIG 1408 20000 PSIG 1408 15700 PSIG 1105.28 16377.3 lb 7428 22383.1 lb 10152 38760.4 lb 17580 2 19380.2 lb 8790 120 DEG 11.811 INCH 300 N.A.
Kg/CM2G
o
MM MM MM MM MM
Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg Kg Kg Kg MM
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 91 of 126 Sheet : 2 of 7 Rev. : 1
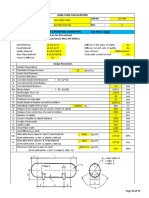
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 N. Design of Saddle Supports (cont.) Vessel Layout :
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
Figure (3)
Shell Inside Diameter, D Shell wall thickness, ts Head wall thickness (min.), th Distance from tangent line - to - saddle support , A Head depth - to - tangent line , Ho = ID / 4 + th Shell length from Tangent - to - tangent (T/T) , L Distance from tangent line - to - welding line (Skirt), l Shell length from Welding - to - welding (W/W) , L' Saddle - to - saddle distance (S/S) , L" = L - 2 A Total Ellipsoidal Head depth (external depth), H = Ho + l Total vessel overall length = L + 2 Ho Vessel weight , empty , W liquid (water), Wc Vessel total weight (water), Wt
61.2598 0.86614 0.7874 22.0472 16.1024 189.764 1.5748 186.614 145.669
INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH
1556 22 20 560 409 4820 40 4740 3700 449 5638 7428 10152 17580
MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM
Kg Kg Kg
17.6772 INCH 221.969 INCH 16377.3 lb 22383.1 lb 38760.4 lb
Figure (4)
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 92 of 126 Sheet : 3 of 7 Rev. : 1
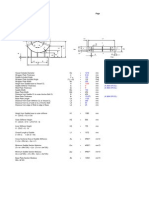
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 N. Design of Saddle Supports (cont.) (a) Determining the number of stiffeners (rip plates) and its thickness, ts *An approximate approach for determining the number of stiffeners, N is : N = m" / 24 + 1 (empirical formula) where m" = total length of base plate , in. 50.3937 INCH = 0.8 x vessel O.D. , in. N 3.09974 Use 4 stiffeners, n * Total length of base plate m , can also be calculated in accordance with saddle angle of contact, B : m' = 2 (Ro + tf) sin B Use m * The stiffener (rip plate) thickness (ts) is 3/8" (9.5 mm) min. for vessels up to 6 ft (1830 mm) in diameter , Therefore use 4 stiffeners with thickness , ts Baseplate-Stiffeners' fillet weld clearance, cl = Min. (ts , tb) The stiffeners are equaly spaced by, Ss = [m-2(0.5ts+cl)]/(n-1) Use equally spaced stiffeners, Ss
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
1280 4
MM
55.5075 INCH 62.9921 INCH
1409.889 MM 1600 MM
0.55118 INCH 0.59055 INCH 20.4199 INCH 20.4199 INCH
14 15
MM MM
518.6667 MM 518.6667 MM
Use b Use rip plate width, Rw = 1/2[b - (2*cl + tw)] Use distance, c
11.811 INCH 5.03937 INCH 37.8346 INCH
300 128 961
MM MM MM
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 93 of 126 Sheet : 4 of 7 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 N. Design of Saddle Supports (cont.) (b) Calculation of top flange (reinforcement) thickness, tf : Flange thickness , tf = SQRT(6*Mb / Sb) Where , Mb = Bending Moment, lb-in. Sb = Allowable design bending stress = 0.66 Sy ( per AISC Spesifications)
P b b II M b = ---- x ---- x ---- = P b 2 4 b ----8
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
19800
PSIG
1393.92
Kg/CM2G
II
Pll = Linear load per unit lengh , lb/in.
Q 1 + cos B P = ---- [ --------------------------] . II Ro II - B + cos B * sin B
Q = load per one saddle , lb Ro = Vessel outside radius , in. 0 = Angle of contact , deg.
B . . PI = 180 - 0 /2
19380.2 31.4961 120 120
lb 8790 INCH 800 Degree Degree
Kg MM
500.925 lb/in
8945.495 Kg/M
. . Bending moment , Mb Flange thickness , tf = SQRT(6*Mb / Sb) Use top flange plate thickness , tf
739.555 lb-in 0.4734 INCH 0.55118 INCH
8.520584 Kg-M 12.02436 MM 14 MM
Use top flange plate width, B = 2* Rip width + 2*(55) + tw
14.9606 INCH
380
MM
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 94 of 126 Sheet : 5 of 7 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 N. Design of Saddle Supports (cont.) (c) Calculation of web (saddle) plate thickness , tw : Use 0.5" thick plate min. ( i.e. assume tw = 0.5" ) Calculate the max. allowable height h of a 1" wide strip column 0.5" thick under PII . 2 Area , a = 1 x 0.5 IN. Min. radius of gyration , k = 0.289 tw 0.5 INCH
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
13
MM
From
----- ---------------------------] = a 2 1 h
18000 1+ -------- [ ---- ]
18000 k
We get h = tw * SQRT [(1500/PII)(18000 tw - PII )] = 2127 MM > distance c (961 MM) Where c Use web ( saddle ) with thickness , tw
79.7655 INCH 37.8346 INCH 0.55118 INCH
2026.044 MM 961 14 MM MM
(d) Calculation of base plate thickness , tb : tb = SQRT [(Q * b) / 26400 * m] Use base plate with thickness , tb 0.371 INCH 9.423482 MM 25 MM
0.98425 INCH
* Check for the bearing pressure : Bearing pressure = Q / (b*m)
26.0486 PSIG 1.833821 Kg/CM2G < 750 PSI allowable OK
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 95 of 126 Sheet : 6 of 7 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 N. Design of Saddle Supports (cont.) D. Stresses in Shell Due to Temperature Expansion : Expansion dl = a * l * dT Where dl = a = Thermal expansion coefficent l = Tangent - to - tangent distance (T/T) , in. dT = Difference in temp. = 167-70 (consider ampient temp. 70 oF ) Expansion , dl Therefore use slots for anchor bolts located in the sliding saddle with distance c/c 65 MM , and provide lubrite plates underneath the sliding saddle . Friction coefficient, fo Shear force at the saddle base, fo * Q Centroid of saddle arc, xo = ro * sin 60 / rad. 60 Use Saddle height under vessel Distance, c Elevation , Z =Ro + tf + c + tb Support Saddle Detail : 0.1 1938.02 26.047 3.28084 37.8346 70.8661
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
7.1E-06
o 79 F o 70 F 0.10644 INCH
26.11111 oC 21.11111 oC 2.703538 MM
lb
INCH ft. INCH INCH
879 661.5947 1000 961 1800
Kg MM MM MM MM
Figure (5)
m b B Width of outside stiffeners, Sw = 2 Rw + tw
62.9921 11.811 14.9606 10.6299
INCH INCH INCH INCH
1600 300 380 270
MM MM MM MM
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 96 of 126 Sheet : 7 of 7 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 N. Design of Saddle Supports (cont.) Bending moment = fo * Q ( Z - xo ) This bending moment is counteracted by the weight of the vessel , Q * b/2 . i.e fo * Q ( Z - xo ) = Q * b/2 Therefore , the min. value for b = 2 * BM /Q ( the value used for b = 300 MM > 227.68 MM ) 86860.3 lb-in.
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
1000.738 Kg-M
8.96382 INCH 227.6811 MM OK < 300 MM
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 114 of 126 Sheet : 1 of 8 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 T. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method Shell material Heads material Saddles material Heads type Design temperature Vessel internal pressure, P Allowable stress in shell, Sts Allowable stress in heads, Sth Allowable stress in web, Sw Shell compression yield point, Y Saddle & anchor bolt compression yield point, Re Outer shell diameter, Do Wall nominal thickness of shell, ts Wall nominal thickness of heads (min.), th Corrosion allowance for shell & heads, Cas Shell joint efficiency, Es Head joint efficiency, Eh Head internal depth, h Head depth -to- tangent line (external depth), Ho Insulation thickness, tis Wear (reinf./top flange) plate width, B Wear (reinf./top flange) plate thickness, tf Wall corroded thickness of shell Wall corroded thickness of heads Wall corroded thickness of shell + reinf. plate Outer shell radius, Ro = Do / 2 Shell length from Tangent - to - tangent (T/T), L Saddle - to - saddle distance (S/S), L" Transverse distance between anchor bolts, Y Distance from tangent line -to- center of saddle support, A Saddle contact angle, B Longitudinal width of saddle at shell, b Transverse width of saddle at shell (baseplate length), m Height of saddle to vessel center line, Z Web width of saddle, hs Web thickness of saddle, tw Equivalent diameter of vessel, Deq = 1.5 (Do + 2 * tis) Equivalent length of vessel, Leq = L + 2Ho + 2 tis
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
ASME SA516 Grade 70 ASME SA516 Grade 70 ASME SA283 Grade C Ellipsoidal 2:1 o 149 F 65 255.682 PSIG 18 20000 PSIG 1408 20000 PSIG 1408 15700 PSIG 1105.28 32000 PSIG 2252.8 30000 PSIG 2112 62.9918 INCH 1600 0.866 INCH 22 0.7874 INCH 20 0.236 INCH 6 0.85 0.85 15.315 16.102 0 14.961 0.551 0.236 0.551 0.787 31.496 189.764 145.669 39.3701 22.047 120 14.961 62.992 70.866 62.992 0.551 94.488 221.969 INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH Degree INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH INCH 389 409 0 380 14 6 14 20 800 4820 3700 1000 560 380 1600 1800 1600 14 2400 5638
Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G
MM MM MM MM
MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM MM
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 115 of 126 Sheet : 2 of 8 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 T. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.) 1. Seismic & wind forces on vessel a. Seismic force UBC-1997 Total design force or shear at the base, F = z . I . C . Wt / Rw 5329.18 lb Seismic Zone 2A : For zone 2A : z = Seismic zone factor [Table No. 23-I] 0.15 I = Importance factor [Table No. 23-L] 1 C = Numerical coefficient [Table No. 23-P] 2.75 Max. Rw = Numerical coefficient [TableS NoS. 23-O & 23-Q] 3
= 3 ( horizontal vessel on pier)
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
2417.25
Kg
Total vessel dead weight, Wt b. Wind force F = Cf . Gh . qz . Af qz = 0.00256 . kz . (I V)2 For exposure C : h = Height kz = Velocity pressure exposure coefficient Wind Velocity, V = Basic wind speed Gh = Gust response factor Cf = Force coefficient c. Forces in longitudinal direction
38757.7 lb ANSI A58.1 27.0848 PSF 0-15 0.8 115 1.32 0.8 Ft MPH
17580
Kg
13.49792 N/M2
51.399
M/Sec.
Figure ( 6 )
Seismic longitudinal force, Fls = z . I . C . Wt / Rw Wind longitudinal exposed area, Afl = (pi/8*Deq + Z) * Deq Wind longitudinal force, Flw = Cf . Gh . qz . Afl Fl = Greater value of Fls & Flw
5329.18 70.8472 2026.34 5329.18
lb Ft2 lb lb
2417.25 6.58192 919.1228 2417.25
Kg M2 Kg Kg
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 116 of 126 Sheet : 3 of 8 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 T. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.) d. Forces in transverse direction
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
Figure ( 7 )
Seismic transverse force, Fts = 0.5 Fls = 0.5 x z x I x C x Wt / Rw Wind transvere exposed area, Aft = Deq * Leq Wind transverse force, Ftw = 0.5 x Cf x Gh x x qz x Aft Ft = Greater value of Fts & Ftw 2. Reaction force per saddle support a. Reaction due to full vessel weight, Qo = Wt/2 b. Reaction in longitudinal direction due to earthquake & wind : By taking moments about saddle support : Fl . Z = Ql . L" Ql = Fl . Z / L" c. Reaction in transverse direction due to earthquake & wind : By taking moments about saddle support : Ft . Z = Qt . (m/2) Qt = 3 ( 2 . Ft . Z / m) d. Max. reaction due to earthquake & wind, Qmax. = Max. (Ql , Qt) e. Total reaction due to full vessel weight, earthquake and wind, Q Total longitudinal reaction, Qlt = Qo + Ql Total transverse reaction, Qtt = Qo + Qt Q = Greater value of Qlt & Qtt 3. Modified stresses at saddles : Ratio (Qo + Qmax.) / Qo
a. Modified circumferential stresses, SIG 5' = Ratio . SIG 5' = Ratio .
2664.59 145.649 2082.89 2664.59
lb Ft2 lb lb
1208.625 13.5312 944.7727 1208.625
Kg M2 Kg Kg
19378.8 lb
8790
Kg
2592.57 lb
1175.959 Kg
17986 17986
lb lb
8158.219 Kg 8158.219 Kg
21971.4 lb 37364.8 lb 37364.8 lb
9965.959 Kg 16948.22 Kg 16948.22 Kg
1.92813
< OK < OK
SIG 4' = Ratio .
<
OK
b. Modified tangential stresses,
SIG 2' = Ratio .
<
OK
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 117 of 126 Sheet : 4 of 8 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 T. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.) a. Stresses in longitudinal direction Longitudinal force, Fl 5329.18 lb Max. moment, Mmax. = Fl . Z 377658 lb-in.
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
2417.278 Kg 4351.091 Kg-M
Figure ( 8 )
Cross-sectional Area, A = Lw * tw + 2 Sw * ts+ 2(n-2) Rw * ts Moment of inertia, Ix-x = Lw*tw3/12+(n-2) ts*Sw3/12+2ts(Sw3-tw3)/12 Section modulus, Wx-x =Lw*tw2/6+2ts*Sw2/6+2ts(Sw3-tw3)/(6 Sw) Dimension X1 = Ix-x / Wx-x Bending stress, Sb = Mmax. / Wx-x Allowable bending stress, S' = 1.2 . S Shear stress, T = Fl / A Allowable shear stress, S' = 0.5 . S b. Stresses in transverse direction Transverse force, Ft Max. moment, Mmax. = Ft . Z
56.2899 221.512 44.5915 4.96758 8469.26 18840 94.6738 7850 OK
INCH2 INCH4 INCH3 INCH PSIG PSIG PSIG PSIG
36316 92200201 730724.6 126.1764 596.2362 1326.336 6.665034 552.64
MM2 MM4 MM3 MM
Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G
2664.59 lb 188829 lb-in.
1208.639 Kg 2175.546 Kg-M
Figure ( 9 )
Cross-sectional Area, A 56.2899 Moment of inertia, Iy-y = tw*Lw3/12+Sw[(Lw+2ts)3-Lw3]/12+2Rw((Ss(n-1-2)+ts)3 22429.5 Section modulus, Wy-y =tw*Lw2/6+Sw*[(Lw+2ts)3-Lw3]/6(Lw+2ts)]+2Rw[(Ss+ts 804.78 Dimension Y1 = Iy-y / Wy-y 27.8703 Bending stress, Sb = Mmax. / Wy-y 234.634 Allowable bending stress, S' = 1.2 . S 18840 OK Shear stress, T = Ft / A 47.3369 Allowable shear stress, S' = 0.5 . S 7850 OK
INCH2 INCH4 INCH3 INCH PSI PSI PSI PSI
36316 9.34E+09 13187989 707.9063 16.51823 1326.336
MM2 MM4 MM3 MM
Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G
3.332517 Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G 552.64
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 118 of 126 Sheet : 5 of 8 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
T. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.) 1. Bending moment & bending stress at saddles Bending moment at saddle in tension & compression, M1
A R 2 H 1 + L 2A L = Q A 1 4H 1+ 3L
2
823586
lb-in
9488.744 Kg-M
2 201.4689 Kg/CM G 2 -111.9271 Kg/CM G
Longitudinal bending stress in tension, S1 = M1 / K1 R2 ts Longitudinal bending stress in compression, S1 = - M1 / K8 R ts 2. Bending moment & bending stress at midspan Bending moment at midspan, M2
R 2 H2 1+ 2 4 A L2 M = QL 4H L 1+ 3L
' 1
2861.77 PSIG
2
-1589.87 PSIG
3333925 lb-in
38411.02 Kg-M
Longitudinal bending stress at midspan, S1' = - M1 / 3.14 R ts 3. Stress in the shell due to internal pressure, S = P R / (2 Es ts) 4. Sum of tensile stress Value of S1 + S Value of S1' + S Greater value of (S1 + S) & (S1 + S) Shell allowable tensile stress Stress ratio = Greater stress/Allowable stress 5.Tangential shear stress, S2 5.a. Tangential shear stress on shell, S2 In case of A > R/2 and ring not used or rings are adjacent to the saddle.
S2 = K2 Q L 2 A 4 H R ts L + 3
'
'
-1235.31 PSIG
-86.9661
Kg/CM G
5470.01 PSIG
385.089
Kg/CM2
8331.79 PSIG -2825.19 PSIG 8331.79 PSIG 20000 PSIG 0.41659 < 1
2 586.5578 Kg/CM G 2 -198.8932 Kg/CM G 2 586.5578 Kg/CM G
1408
Passed
Kg/CM2G
1106.25 PSIG
77.88014 Kg/CM2G
Shell allowable tangential stress = 0.8 S Stress ratio = S2 / 0.8 S
16000 PSIG 0.06914 < 1
1126.4
Passed
Kg/CM2G
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 119 of 126 Sheet : 6 of 8 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
T. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.) 5.b. Tangential shear stress on shell, S2 In case of A > R/2 and ring used in plane of saddle.
S2 K 3Q L 2A = R ts L + 4H 3
301.362 PSIG
21.21585 Kg/CM2G
Shell allowable tangential stress = 0.8 S Stress ratio = S2 / 0.8 S 5.c. Tangential shear stress on head, S2h In case of A > R/2 and ring not used or rings are adjacent to th saddle.
S
2h
16000 PSIG 0.01884 < 1
1126.4
Passed
Kg/CM2G
K 2 Q L2A = 4H R t h L+ 3
1216.68 PSIG
85.65414 Kg/CM2G
Head allowable tangential stress = 0.8 S Stress ratio = S2 / 0.8 S 5.d. Tangential shear stress on shell In case of A <= R/2 S2 = K4 Q / R ts Shell allowable tangential stress = 0.8 S Stress ratio = S2 / 0.8 S 5.e. Tangential shear stress on head In case of A <= R/2
16000 PSIG 0.07604 < 1
1126.4
Passed
Kg/CM2G
1205.51 PSIG 16000 PSIG 0.07534 < 1
84.86817 Kg/CM2G 1126.4 Kg/CM2G
Passed
S2 = K4 Q / R th
1325.85 PSIG 16000 PSIG 0.08287 < 1
2 93.33971 Kg/CM G
Shell allowable tangential stress = 0.8 S Stress ratio = S2 / 0.8 S 5.f. Additional tangential shear stress in head In case of A <= R/2 S3 = K5 Q / R th S3 + stress due to int. pres. (PR/(2Es ts) Head allowable tensile stress = 1.25 S Stress ratio = S3 / 1.25 S
1126.4
Passed
Kg/CM2G
604.165 PSI 5470.01 PSI 25000 0.2188 PSI <1
2 42.53321 Kg/CM G
385.089 1760
Passed
Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 120 of 126 Sheet : 7 of 8 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 T. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.) 6. Circumferential stress 6.a. Circumferential stress at saddle horn In case of L >= 8 R (unstiffened)
S = 4 Q 4 ts ( +1 56 Rts ) b . 3K Q 6
2 2ts
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
-1806.46 PSIG
-127.1747 Kg/CM2G
Shell allowable circumferential stress = 1.5 S Stress ratio = S4 / 1.5 S 6.b. Circumferential stress at saddle horn In case of L < 8 R (unstiffened)
30000 PSIG 0.06022 < 1
2112
Passed
Kg/CM2G
S = 4
Q 4 ts (b +1 56 R ts ) .
12K QR 6
2 Lts
-2828.5
PSIG
-199.1262 Kg/CM2G
Shell allowable circumferential stress = 1.5 S Stress ratio = S4 / 1.5 S 6.c. Circumferential stress at bottom of shell (stiffened or unstiffened)
30000 PSIG 0.09428 < 1
2112
Passed
Kg/CM2G
K
5
Q R ts )
-1419.03 PSIG
-99.89967 Kg/CM2G
t s ( b + 1 . 56
0.5 compression yield point of shell material Stress ratio = S5 / 0.5 S 7. Check tension in web saddle Horizontal force in web, Fw = K8 Q Effective web area, Aw = hs tw Stress in web, Sw = Fw / Aw Allowable stress in web, Saw = 0.6 Y Stress ratio = Sw / 0.6 Y Vertical force in web, Fv = Q Stress in web, Sv = Fv / Aw Allowable stress in web (compressiuon), Saw = 0.33 Y Stress ratio = Sv / 0.33 Y
16000 PSIG 0.08869 < 1
1126.4
Passed
Kg/CM2G
22531
lb 2 34.7086 INCH 649.147 PSIG 18000 PSIG 0.03606 < 1 37364.8 1076.53 9900 0.10874 lb lb PSIG <1
10219.78 Kg 2 22392.6 MM 45.69996 Kg/CM2G 1267.2 Kg/CM2G
Passed
16948.22 Kg 488.3004 Kg 696.96 Kg/CM2G
Passed
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 121 of 126 Sheet : 8 of 8 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 T. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.) 8. Check of the saddle at the lowest section (web plate thickness) : The saddle at the lowest section must resist the horizontal force (F). The effective cross section of the saddle to resist this load is R/3.
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
Figure (10)
F = K11 . Q To resist this force, the effective area of web plate, A = (R/3) . tw The calculated stress, Scal. = F / A The allowable stress, Sall. = (2/3) Sw Stress ratio = Scal. / Sall. So, the thickness of the web plate is satisfactory for horizontal force (F).
7622.42 5.78668 1317.24 10466.7 0.12585
lb INCH2 PSIG PSIG <1
3457.437 3733.333 92.73342 736.8534
Passed
Kg MM2 Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G
Values of Constant K For contact angle B = 120o : K1 (K1 = 3.14 if the shell is stiffened by ring or head, A > R/2) K2 K3 (K3 is constant for any contact angle) K4 K5 K6 (K6 depends on the ratio A/R, see chart in vessel handbook) K6 for A/R > 1.00 K6 for A/R < 0.5 A R A/R K6 for A/R = 0.69 K7 K8
120o 0.335 1.171 0.319 0.88 0.401 0.053 0.013 22.047 INCH 560 31.496 INCH 800 0.69999 0.0238 [From table] 0.76 0.603 MM MM
K11
0.204
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF PRESSURE VESSEL
According to ASME Code, Section VIII, Division 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (assist.)
Page : 122 of 126 Sheet : 1 of 1 Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Procurement of ASME Pressure Vessel Job Name : Demineralization Plant Serial No. : 7434-33-U-2006 Dwg. No. : 7434-33-3A, Rev. 1 Vessel : Deputanizer Reflux Receiver Drum Item No. : 1-D-5 Capacity : 10.152 M3 U. Check for the Anchor Bolts Due to Seismic and Wind Loading 1. For longitudinal forces, Fl
Date : 18.2.2004
Job No. : 7434-33
Client : APRC Type : Horizontal
Figure (11)
Fl Max. moment, Mmax. = Fl . Z Cross-sectional area per anchor bolt, Ab (7/8" M26) No. of anchor bolts per saddle, nb Total cross-sectional area of anchor bolts, A = nb . Ab Shear stress, T = Fl / A Bending stress, Sb = Mmax. / (A . L") Resultant stress, Si = SQRT (Sb2 + 3 T2 ) Allowable stress, S' = 0.5 . Re 2. For transverse forces, Ft
5329.18 377658 0.419 4 1.676 3179.7 1546.88 5720.52 15000
lb. lb-in. INCH2 each INCH2 PSIG PSIG PSIG PSIG
2417.25 Kg 4351.091 Kg-M 270.322 MM2 1081.288 MM2 223.851 108.9005 402.7246 1056 OK Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G
Figure (12)
Ft Max. moment, Mmax. = Ft . Z Cross-sectional area per anchor bolt, Ab (7/8" M26) No. of anchor bolts per saddle, nb Total cross-sectional area of anchor bolts, A = nb . Ab Shear stress, T = Ft / A Bending stress, Sb = 2 Mmax. / (A . Y) Resultant stress, Si = SQRT (T2 + 3 Sb2 ) Allowable stress, S' = 0.5 . Re
2664.59 188829 0.419 4 1.676 1589.85 5723.45 10040 15000
lb. lb-in. INCH2 each INCH2 PSIG PSIG PSIG PSIG
1208.639 Kg 2175.546 Kg-M 270.322 MM2 1081.288 MM2 111.9255 402.9309 706.8149 1056 OK Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G Kg/CM2G
You might also like
- Saddle Dimension CalculationDocument2 pagesSaddle Dimension Calculationrinabiswas50% (2)
- Skirt Bracing Calc For Vertical Pressure VesselsDocument4 pagesSkirt Bracing Calc For Vertical Pressure Vesselsnagtummala100% (1)
- Saddle-Design-Operating - FinalDocument17 pagesSaddle-Design-Operating - FinalSiva baalan75% (4)
- Zick Analysis For Saddle SupportDocument8 pagesZick Analysis For Saddle Supportfuransu777100% (1)
- Saddle Road Transportation Analysis 1Document2 pagesSaddle Road Transportation Analysis 1vpjagannaathNo ratings yet
- Saddle Support Calculation PD 5500,2000 Annex.G)Document26 pagesSaddle Support Calculation PD 5500,2000 Annex.G)Neeraj Kumar33% (3)
- Design of Tooth Locked Quick Open Die Pressure VesselDocument4 pagesDesign of Tooth Locked Quick Open Die Pressure VesselSEP-PublisherNo ratings yet
- FlangeCalc AS1210 v1.5Document28 pagesFlangeCalc AS1210 v1.5Ben100% (2)
- Davit With ElbowDocument2 pagesDavit With ElbowSajal Kulshrestha100% (4)
- Sulfuric Acid Tank - APIDocument4 pagesSulfuric Acid Tank - APISakthi VelNo ratings yet
- Blind Flange Design Calculations - by Abdel Halim GalalaDocument6 pagesBlind Flange Design Calculations - by Abdel Halim GalalaNirmalraj Manoharan67% (3)
- Saddle Design at Operating ConditionDocument17 pagesSaddle Design at Operating ConditionGanesh Bhardwaj100% (2)
- Saddle CalculationDocument7 pagesSaddle CalculationMichael HaiseNo ratings yet
- Saddle CalculationDocument10 pagesSaddle Calculationpharis_chrisNo ratings yet
- Saddle v1-10: Fixed Saddle Sliding SaddleDocument30 pagesSaddle v1-10: Fixed Saddle Sliding SaddleidiazgNo ratings yet
- Saddle Reaction Summary - For Empty CaseDocument12 pagesSaddle Reaction Summary - For Empty CasesridharNo ratings yet
- Saddle 1Document3 pagesSaddle 1RUDHRA DHANASEKARNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Bending Stress: M1 Allowable Limit RemarkDocument16 pagesLongitudinal Bending Stress: M1 Allowable Limit RemarkSandal JepitNo ratings yet
- Tutorial of WRC 107 For Lifting LugsDocument20 pagesTutorial of WRC 107 For Lifting LugsPeterWayNo ratings yet
- Leg CalculationDocument21 pagesLeg CalculationBahtiar Anak LaNangNo ratings yet
- 28 Roark Flat PlatesDocument14 pages28 Roark Flat Platesgutmont0% (1)
- Design and Verification of Lifting LugsDocument3 pagesDesign and Verification of Lifting LugsFabio Okamoto100% (1)
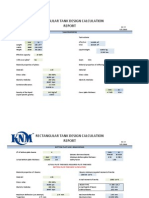
- PPE-STD-CAL-ME-006 Rectangular Tank Thickness CalculationDocument4 pagesPPE-STD-CAL-ME-006 Rectangular Tank Thickness CalculationNadya Askar100% (1)
- Lifting Lug TutorialDocument20 pagesLifting Lug Tutorialmontie3No ratings yet
- Design Calculations For Pressure VesselsDocument54 pagesDesign Calculations For Pressure VesselsEdgar A. Arredondo QuirozNo ratings yet
- Cone Design Tool: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDDocument1 pageCone Design Tool: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDrina2393No ratings yet
- Saddle Calc PD5500Document4 pagesSaddle Calc PD5500rsubramaniNo ratings yet
- Saddle 3Document3 pagesSaddle 3RUDHRA DHANASEKAR100% (1)
- Nozzle Neck CalculationDocument4 pagesNozzle Neck CalculationAkshat JainNo ratings yet
- Saddle CalcDocument26 pagesSaddle CalcVamsi S100% (2)
- Davit Cal 2251B Davit Arm CalculationDocument4 pagesDavit Cal 2251B Davit Arm Calculationnitin400No ratings yet
- How To Calculate Flat Plate Thickness of Flat Bottom Storage TankDocument3 pagesHow To Calculate Flat Plate Thickness of Flat Bottom Storage TankSiva baalan100% (1)
- Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Lifting Trunnion Common Practices PDFDocument4 pagesBoiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Lifting Trunnion Common Practices PDFAlexandru AsmarandeiNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Design CalculationsDocument2 pagesPressure Vessel Design CalculationsMohan VarkeyNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Design Calculations of Pressure Vessel - SampleDocument27 pagesMechanical Design Calculations of Pressure Vessel - SampleSakthi Vel100% (1)
- Rectangular Tank CalculationDocument9 pagesRectangular Tank CalculationFabrício Menegassi75% (4)
- PV Elite Saddle AnalysisDocument4 pagesPV Elite Saddle AnalysismrosNo ratings yet
- Combined Shell-Ring InertiaDocument13 pagesCombined Shell-Ring Inertianeurolepsia3790No ratings yet
- Zick Analysis of SaddlesDocument6 pagesZick Analysis of SaddlesVitor OlivettiNo ratings yet
- Vessel Saddle SupportsDocument5 pagesVessel Saddle SupportsAzwa Onexox75% (4)
- Section VIII CalDocument19 pagesSection VIII CalPradeep Kothapalli100% (1)
- SEISMIC ANALYSIS KazzincDocument14 pagesSEISMIC ANALYSIS KazzincArees KhambattaNo ratings yet
- New - Reinforcement of NozzleDocument31 pagesNew - Reinforcement of NozzleNithin ZsNo ratings yet
- Flat Plate - Roark & YoungDocument15 pagesFlat Plate - Roark & YoungPrasad Pingle0% (1)
- Stresses in Vessel On Two Sad... Ports Using ZICK Analysis PDFDocument8 pagesStresses in Vessel On Two Sad... Ports Using ZICK Analysis PDFanishNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Saddle Dan Lifting LugDocument18 pagesPerhitungan Saddle Dan Lifting LugAhmad FaujiNo ratings yet
- KNM Process Systems Sdn. BHD.: Project Name: Ammonia & Urea Plant Revamp ProjectDocument32 pagesKNM Process Systems Sdn. BHD.: Project Name: Ammonia & Urea Plant Revamp ProjectrichardchiamNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Reinforcing Calculations For A Pressure Vessel Design - by Abdel Halim GalalaDocument5 pagesNozzle Reinforcing Calculations For A Pressure Vessel Design - by Abdel Halim Galalapaary100% (2)
- 12-372 Safety and Relief Valves Sizing CalDocument11 pages12-372 Safety and Relief Valves Sizing CalRavi YadavNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet For Shell and Tube Heat Exchager Design SpecificationDocument5 pagesTechnical Data Sheet For Shell and Tube Heat Exchager Design SpecificationSakthi Vel100% (1)
- KimVic Rectangular-Tank-SizingDocument20 pagesKimVic Rectangular-Tank-SizingAdekimi EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Aeration & Settlement Tank CalculationDocument35 pagesAeration & Settlement Tank Calculationdadz mingiNo ratings yet
- Summary Table For Dimensions and External Loads SSP01NDocument2 pagesSummary Table For Dimensions and External Loads SSP01NJ A S JASNo ratings yet
- 4000 m3 Storage Tank - Data SheetDocument3 pages4000 m3 Storage Tank - Data SheetSakthi Vel100% (1)
- Mechanical Design CalculationsDocument15 pagesMechanical Design CalculationsJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- E0805-220-V-903-120-3A (Latihan)Document65 pagesE0805-220-V-903-120-3A (Latihan)Sabrang LorNo ratings yet
- 11 TrunnionDocument21 pages11 TrunnionMitul PatelNo ratings yet
- Spec He Urea P-4Document144 pagesSpec He Urea P-4M Aditya Regisyah PNo ratings yet
- Lug Calculation 1Document2 pagesLug Calculation 1Sachin5586No ratings yet
- Lifting CalcDocument12 pagesLifting Calcwisnu_bayusaktiNo ratings yet
- 267 Pipe Stress Analysis ReportsDocument11 pages267 Pipe Stress Analysis ReportsRaymond MetselaarNo ratings yet
- SG Holidays 2015Document1 pageSG Holidays 2015Raymond MetselaarNo ratings yet
- 2a Piping Estimate & Summary ExampleDocument15 pages2a Piping Estimate & Summary ExampleRaymond MetselaarNo ratings yet
- Project Start Date End Date Work Days A B CDocument1 pageProject Start Date End Date Work Days A B CRaymond MetselaarNo ratings yet
- Week NumbersDocument4 pagesWeek NumbersRaymond MetselaarNo ratings yet
- TR-107453 Stress Indices For Elbows With Trunnion Attachments TechnicalDocument129 pagesTR-107453 Stress Indices For Elbows With Trunnion Attachments TechnicalLimin ZhangNo ratings yet
- PDMS Equi Guide v02 - English Version - EngDocument84 pagesPDMS Equi Guide v02 - English Version - EngRaymond Metselaar100% (1)
- Public Holidays 2013: Payment For Work Done On A Public HolidayDocument2 pagesPublic Holidays 2013: Payment For Work Done On A Public HolidayRaymond MetselaarNo ratings yet
- 03 - MonoflangesDocument2 pages03 - MonoflangesRaymond MetselaarNo ratings yet
- Bolt Loading NotesDocument7 pagesBolt Loading NotesRaymond MetselaarNo ratings yet
- Pipe and Tube Bursting PressuresDocument2 pagesPipe and Tube Bursting PressuresRaymond MetselaarNo ratings yet
- Boiler and Pressure Vessel CourseDocument2 pagesBoiler and Pressure Vessel CourseAnonymous nfHBPXz178100% (1)
- As 4942-2001 Pressure Equipment - Glossary of TermsDocument5 pagesAs 4942-2001 Pressure Equipment - Glossary of TermsSAI Global - APAC0% (1)
- EMM3302 Group ProjectDocument8 pagesEMM3302 Group ProjectNizar NanoNo ratings yet
- API 650 Tank Construction Sequence PDF - Google SearchDocument3 pagesAPI 650 Tank Construction Sequence PDF - Google SearchSunket Patel100% (1)
- 2600series PRV Catalog 304C R2Document96 pages2600series PRV Catalog 304C R2vikzefgNo ratings yet
- Regulations For Safety Inspection of Hazardous Machines and EquipmentDocument132 pagesRegulations For Safety Inspection of Hazardous Machines and EquipmentclegenceNo ratings yet
- Ab-526 Isi Certification RequirementsDocument17 pagesAb-526 Isi Certification RequirementsJonas RachidNo ratings yet
- ASME Sec VIII Div 1 Flange Stress Calculation - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-TipsDocument4 pagesASME Sec VIII Div 1 Flange Stress Calculation - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-TipsLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Anexo II Da NR 30 in EnglishDocument22 pagesAnexo II Da NR 30 in EnglishVítor Andrade SoaresNo ratings yet
- Plant Inspection OverviewDocument2 pagesPlant Inspection OverviewSiva Kumar100% (1)
- Commissioning & Operation Maintenance GuideDocument786 pagesCommissioning & Operation Maintenance GuideNardo LlanosNo ratings yet
- Saes A 005Document34 pagesSaes A 005Elie AouadNo ratings yet
- P265GHDocument2 pagesP265GHbakkali_bilalNo ratings yet
- 02 Samss 006Document17 pages02 Samss 006inatt101No ratings yet
- Engineering Services by KBR Technical Services, IncDocument23 pagesEngineering Services by KBR Technical Services, IncswatkoolNo ratings yet
- QW-483 (Black) PQR No.: Tme 356Document1 pageQW-483 (Black) PQR No.: Tme 356Sudhir KotkarNo ratings yet
- As 1358-2004 Bursting Discs and Bursting Disc Devices - Application Selection and InstallationDocument7 pagesAs 1358-2004 Bursting Discs and Bursting Disc Devices - Application Selection and InstallationSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel PlateDocument71 pagesPressure Vessel PlateVILLANUEVA_DANIEL2064100% (2)
- Asme N 494-3Document16 pagesAsme N 494-3YESID MAURICIO SILVA GALINDONo ratings yet
- Astm A387 A387m-06Document6 pagesAstm A387 A387m-06Naceur Turki100% (1)
- 2019 RI Brochure With Case StudiesDocument56 pages2019 RI Brochure With Case StudiesJohan ConradieNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Pressure Vessel Skirt Considering Seismic Load As Per Uniform Building Code IJERTCONV4IS10007Document5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Pressure Vessel Skirt Considering Seismic Load As Per Uniform Building Code IJERTCONV4IS10007RSalehNo ratings yet
- 【Catalogue】 Aquafos Pressure Tank (NSF)Document4 pages【Catalogue】 Aquafos Pressure Tank (NSF)cmpuckNo ratings yet
- Dgms All Circular 2003Document23 pagesDgms All Circular 2003imaduddinshaNo ratings yet
- Technical Report: Mechanical Integrity Assessment of Cpi Separator Tank A-4301 at KPD, KunnarDocument18 pagesTechnical Report: Mechanical Integrity Assessment of Cpi Separator Tank A-4301 at KPD, KunnarR A BismilNo ratings yet
- Design of Pressure Vessel - CADEMDocument88 pagesDesign of Pressure Vessel - CADEMgkdora574No ratings yet
- Pressure VesselDocument40 pagesPressure VesselPrt00789% (18)
- Clad - Rolled BookDocument43 pagesClad - Rolled BookpunitdubeyNo ratings yet
- Asme Sec Ix - Short NotesDocument20 pagesAsme Sec Ix - Short NotesParvee K NakwalNo ratings yet
- A03 - Kangrim Company Introduction (Package Boilers)Document48 pagesA03 - Kangrim Company Introduction (Package Boilers)metreus30No ratings yet