Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter Ten: The Capital Asset Pricing Model
Chapter Ten: The Capital Asset Pricing Model
Uploaded by
Lakskmi Priya M COriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter Ten: The Capital Asset Pricing Model
Chapter Ten: The Capital Asset Pricing Model
Uploaded by
Lakskmi Priya M CCopyright:
Available Formats
1
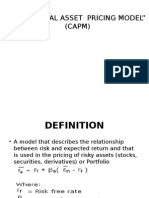
CHAPTER TEN
THE CAPITAL ASSET PRICING
MODEL
2
THE CAPM ASSUMPTIONS
NORMATIVE ASSUMPTIONS
expected returns and standard deviation cover a
one-period investor horizon
nonsatiation
risk averse investors
assets are infinitely divisible
risk free asset exists
no taxes nor transaction costs
3
THE CAPM ASSUMPTIONS
ADDITIONAL ASSUMPTIONS
one period investor horizon for all
risk free rate is the same for all
information is free and instantaneously
available
homogeneous expectations
4
THE CAPITAL MARKET LINE
THE CAPITAL MARKET LINE (CML)
the new efficient frontier that results from risk
free lending and borrowing
both risk and return increase in a linear fashion
along the CML
5
THE CAPITAL MARKET LINE
THE CAPITAL MARKET LINE
M
r
P
o
P
CML
rfr
6
THE CAPITAL MARKET LINE
THE SEPARATION THEOREM
James Tobin identifies:
the division between the investment decision and the
financing decision
7
THE CAPITAL MARKET LINE
THE SEPARATION THEOREM
to be somewhere on the CML, the investor
initially
decides to invest and
based on risk preferences makes a separate
financing decision either
to borrow or
to lend
8
THE MARKET PORTFOLIO
DEFINITION: the portfolio of all risky
assets which contains
complete diversification
a central role in the CAPM theory which is the
tangency portfolio (M) with the CML
9
THE SECURITY MARKET LINE
(SML)
FOR AN INDIVIDUAL RISKY ASSET
the relevant risk measure is its covariance with
the market portfolio (o
i, M
)
DEFINITION: the security market line
expresses the linear relationship between
the expected returns on a risky asset and
its covariance with the market returns
10
THE SECURITY MARKET LINE
(SML)
THE SECURITY MARKET LINE
or
where
m i
m
rf m
rf
r r
r r
,
2
o
o
(
(
+ =
M i rf rf
i
r r r r
, 2
) ( | + =
2
,
,
M
M i
M i
o
o
| =
11
THE SECURITY MARKET LINE
(SML)
THE SECURITY MARKET LINE
THE BETA COEFFICIENT
an alternative way to represent the covariance of a
security
12
THE SECURITY MARKET LINE
(SML)
THE SECURITY MARKET LINE
THE BETA COEFFICIENT
of a portfolio
is the weighted average of the betas of its component
securities
=
=
N
i
M i i M P
X
1
, ,
| |
13
THE SECURITY MARKET LINE
(SML)
THE SECURITY MARKET LINE
SML
|
E(r)
r
rf
r
M
| =1.0
14
THE MARKET MODEL
FROM CHAPTER 7
assumed return on a risky asset was related to
the return on a market index
iI I i iI i
r r c | o + + =
1
15
THE MARKET MODEL
DIFFERENCES WITH THE CAPM
the market model is a single-factor model
the market model is not an equilibrium model
like the CAPM
the market model uses a market index,
the CAPM uses the market portfolio
16
THE MARKET MODEL
MARKET INDICES
the most widely used and known are
S&P 500
NYSE COMPOSITE
AMEX COMPOSITE
RUSSELL 3000
WILSHIRE 5000
DJIA
17
THE MARKET MODEL
MARKET AND NON-MARKET RISK
Recall that a securitys total risk may be
expressed as
2 2 2 2
i i iI i c
o o | o + =
18
THE MARKET MODEL
MARKET AND NON-MARKET RISK
according to the CAPM
the relationship is identical except the market
portfolio is involved instead of the market index
19
THE MARKET MODEL
MARKET AND NON-MARKET RISK
Why partition risk?
market risk
related to the risk of the market portfolio and to the beta of
the risky asset
risky assets with large betas require larger amounts of
market risk
larger betas mean larger returns
20
THE MARKET MODEL
MARKET AND NON-MARKET RISK
Why partition risk?
non-market risk
not related to beta
risky assets with larger amounts of o
cI
will not have
larger E(r)
According to CAPM
investors are rewarded for bearing market risk not non-
market risk
You might also like
- Businessnews Simplified Supply Chains Advanced WorksheetDocument9 pagesBusinessnews Simplified Supply Chains Advanced Worksheetc_a_tabet0% (1)
- Csec Poa January 2014 p2Document13 pagesCsec Poa January 2014 p2Renelle RampersadNo ratings yet
- Risk and Return Theories IIDocument30 pagesRisk and Return Theories IISajid ChishtiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Capital Asset Pricing & Artge PRNG ThryDocument64 pagesChapter 8 Capital Asset Pricing & Artge PRNG ThryAanchalNo ratings yet
- Financial Derivatives: Pricing and Risk ManagementFrom EverandFinancial Derivatives: Pricing and Risk ManagementRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- My Role Model - Sourav Chandidas GangulyDocument18 pagesMy Role Model - Sourav Chandidas Gangulyagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- Summers Report On Indian Cement Industry (Specially Ultra Tech Cement)Document78 pagesSummers Report On Indian Cement Industry (Specially Ultra Tech Cement)kapil60% (5)
- Deployments and Deployment Attempts: Futuregrid, and The More Modern Intergrid and IntragridDocument22 pagesDeployments and Deployment Attempts: Futuregrid, and The More Modern Intergrid and Intragridagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- Soal Tes Accounting PT. KKGSDocument7 pagesSoal Tes Accounting PT. KKGSMora SyahroniNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ten: The Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument20 pagesChapter Ten: The Capital Asset Pricing ModelvishalNo ratings yet
- SAPM Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument27 pagesSAPM Capital Asset Pricing ModelSam RcostaNo ratings yet
- Sessions 7&8Document20 pagesSessions 7&8Bhavya JainNo ratings yet
- Capital Market Theory PPT - 022357Document16 pagesCapital Market Theory PPT - 022357Pira KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument27 pagesUnit 7: Capital Asset Pricing ModelAmish QwertyNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Theory and Asset Pricing ModelsDocument31 pagesPortfolio Theory and Asset Pricing Models2009028818No ratings yet
- Security Market Line: Presented by Ujjayini DasDocument13 pagesSecurity Market Line: Presented by Ujjayini Dasd-fbuser-42356381No ratings yet
- Topic 5: The Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument43 pagesTopic 5: The Capital Asset Pricing ModelHuy PhanNo ratings yet
- 08 Iapm9e PPT - ch08Document42 pages08 Iapm9e PPT - ch08Runalen EncarguesNo ratings yet
- CapitalAssetPricingModel CAPMDocument13 pagesCapitalAssetPricingModel CAPMabaz_zbNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Efficient Markets, Investment Value and Market PriceDocument29 pagesChapter Four: Efficient Markets, Investment Value and Market Pricezulfi007No ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Efficient Markets, Investment Value and Market PriceDocument29 pagesChapter Four: Efficient Markets, Investment Value and Market Priceaqsamumtaz812No ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)Document4 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)Raja Fahd SultanNo ratings yet
- Investment Analysis & Portfolio ManagementDocument33 pagesInvestment Analysis & Portfolio ManagementShuhab KhosoNo ratings yet
- The Standard Capital Asset Pricing ModelsDocument12 pagesThe Standard Capital Asset Pricing ModelsRifat HelalNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing and Arbitrage Pricing Theory: Prof. Karim MimouniDocument22 pagesCapital Asset Pricing and Arbitrage Pricing Theory: Prof. Karim MimouniSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- Managing Continuous Risks - Variable Income AssetsDocument36 pagesManaging Continuous Risks - Variable Income AssetsAbinash BiswalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document16 pagesChapter 8MOHAMAD ZAIM BIN IBRAHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument27 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Modelsumit vishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - CAPM (IPM)Document26 pagesPart 3 - CAPM (IPM)Rakib HasanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Systematic and Unsystematic Risks in CapitalDocument18 pagesAnalysis of Systematic and Unsystematic Risks in CapitalNishant Edwin PaschalNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Risk-Return AnalysisDocument23 pagesA Survey On Risk-Return Analysisberhanabera80No ratings yet
- Investments Analysis and Management Canadian 3rd Edition Cleary Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesInvestments Analysis and Management Canadian 3rd Edition Cleary Solutions Manualcyanineorganize.4p2new100% (20)
- Capital Markets and Pricing of RiskDocument23 pagesCapital Markets and Pricing of RiskAshesh DasNo ratings yet
- CAPM Lecture NotesDocument19 pagesCAPM Lecture NotesNaailah نائلة MaudarunNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Asset Pricing ModelsDocument32 pagesAn Introduction To Asset Pricing ModelsmahrukhNo ratings yet
- SML and CMLDocument16 pagesSML and CMLABHISHEK VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument18 pagesCapital Asset Pricing ModelSonalir RaghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Multifactor Value at RiskDocument44 pagesChapter 5 - Multifactor Value at RiskVishwajit GoudNo ratings yet
- CAPM Index ModelsDocument14 pagesCAPM Index ModelsSalia Tobias MwinenkumaNo ratings yet
- The Standard Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument29 pagesThe Standard Capital Asset Pricing ModelPedro Martín López LiraNo ratings yet
- Investment Analysis - Chapter 5Document28 pagesInvestment Analysis - Chapter 5Linh MaiNo ratings yet
- Sapm Unit 3Document13 pagesSapm Unit 3pm2640047No ratings yet
- FINC 3330 - Notes CH 11Document2 pagesFINC 3330 - Notes CH 11fischeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - An Introduction To Asset Pricing ModelsDocument36 pagesCHAPTER 8 - An Introduction To Asset Pricing ModelsArah Ibrahim-MacakilingNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument16 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Modelisteaq ahamedNo ratings yet
- 4 - Portfolio TheoryDocument22 pages4 - Portfolio TheorySIDDHARTH SNNo ratings yet
- Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Gareth MylesDocument26 pagesInvestment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Gareth MyleshoalongkiemNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8.2 (Capm and Apt)Document30 pagesLecture 8.2 (Capm and Apt)Devyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing Model: Presented By: Kanika Shobhit Jain Vandana AgrawalDocument12 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Model: Presented By: Kanika Shobhit Jain Vandana Agrawaljames651bondNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document22 pagesModule 5AliceJohnNo ratings yet
- 04 CapmDocument25 pages04 CapmDaniel RisticNo ratings yet
- "The Capital Asset Pricing Model" (CAPM)Document55 pages"The Capital Asset Pricing Model" (CAPM)Nayyar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Security Analysis and Portfolio ManagementDocument14 pagesSecurity Analysis and Portfolio ManagementSaptarshi RayNo ratings yet
- "We Are What We Repeatedly Do. Excellence, Then, Is Not An Act But A Habit." - AristotleDocument49 pages"We Are What We Repeatedly Do. Excellence, Then, Is Not An Act But A Habit." - AristotleErick OpiyoNo ratings yet
- 11 - Modern Based Factor ModelsDocument23 pages11 - Modern Based Factor ModelsmuzammalNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument36 pagesCapital Asset Pricing ModelJithesh JanardhananNo ratings yet
- Invt03 AP - Models 0823Document58 pagesInvt03 AP - Models 0823Huang XinNo ratings yet
- 5 CapmDocument11 pages5 Capmquynhnhudang5No ratings yet
- CapmDocument43 pagesCapmVaidyanathan RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - An Introduction To Asset Pricing ModelsDocument28 pagesChapter 8 - An Introduction To Asset Pricing ModelsImejah FaviNo ratings yet
- COMM 371 - Lecture 5 - Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)Document52 pagesCOMM 371 - Lecture 5 - Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)riyaNo ratings yet
- Fi 2023 24 Chapter 5 - HandoutsDocument7 pagesFi 2023 24 Chapter 5 - HandoutsInês Carvalho CostaNo ratings yet
- M 2 CapmDocument27 pagesM 2 CapmNitin DNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing Model SAPMDocument18 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Model SAPMarmailgmNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument18 pagesCapital Asset Pricing ModelSanjeevNo ratings yet
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel: Builder of A Steel Strong IndiaDocument9 pagesSardar Vallabhbhai Patel: Builder of A Steel Strong Indiaagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- Smart GridDocument11 pagesSmart Gridagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- The Great Leader - Sardar Vallabhbhai PatelDocument9 pagesThe Great Leader - Sardar Vallabhbhai Patelagrawalrohit_228384100% (1)
- TelanganaDocument18 pagesTelanganaagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- If I Were Prime Minister of IndiaDocument20 pagesIf I Were Prime Minister of Indiaagrawalrohit_22838450% (2)
- Sardar PatelDocument39 pagesSardar Patelagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- Determining Difference in Net Profit Under Cash BasisDocument5 pagesDetermining Difference in Net Profit Under Cash Basisagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- Final Presentation On MisDocument22 pagesFinal Presentation On Misagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- EnterprenuerDocument10 pagesEnterprenueragrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- Management by Objectives: Presented By: Ashish Prajapati Seema Patil Vaibhav SinghDocument14 pagesManagement by Objectives: Presented By: Ashish Prajapati Seema Patil Vaibhav Singhagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- Wal MartDocument55 pagesWal Martagrawalrohit_228384100% (1)
- First Year of Launch: Market ContextDocument5 pagesFirst Year of Launch: Market Contextagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- PNB BankDocument87 pagesPNB Bankagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- MISDocument10 pagesMISagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- Personality Dev ElopementDocument7 pagesPersonality Dev Elopementagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- Project Report On HDFC Bank LTDDocument48 pagesProject Report On HDFC Bank LTDagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- Future ShockDocument13 pagesFuture Shockagrawalrohit_2283840% (1)
- INFOSYS CASE STUDY - Narayana Murthy and Infosys'Document2 pagesINFOSYS CASE STUDY - Narayana Murthy and Infosys'agrawalrohit_228384100% (1)
- Social Issues of PakDocument8 pagesSocial Issues of PakDilawar MumtazNo ratings yet
- Chap 23Document12 pagesChap 23Sakshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- System Model of IR in India (DUNLOP)Document22 pagesSystem Model of IR in India (DUNLOP)Swastik PattnaikNo ratings yet
- (FIN) 2020552075 - FERYANDA UTAMI - Final DefenseDocument24 pages(FIN) 2020552075 - FERYANDA UTAMI - Final DefenseFeryanda UtamiNo ratings yet
- (I) Statement of Changes in Working Capital (Ii) Fund Flow StatementDocument3 pages(I) Statement of Changes in Working Capital (Ii) Fund Flow StatementShailendrasingh DikitNo ratings yet
- ECON601 - The Impact of AI & ML On Labor Market-10042022Document22 pagesECON601 - The Impact of AI & ML On Labor Market-10042022Rauf JaferiNo ratings yet
- COD of NTPC PLANT PDFDocument5 pagesCOD of NTPC PLANT PDFDurjoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- TERM EXAM 2023 2nd YearDocument5 pagesTERM EXAM 2023 2nd YearSolange CardonaNo ratings yet
- Black MailDocument10 pagesBlack Mailpersonalmail.acc0No ratings yet
- MATHEMATICAL LITERACY 20 FEBRUARY 2018 14 September 2018Document88 pagesMATHEMATICAL LITERACY 20 FEBRUARY 2018 14 September 2018Sultry PapiNo ratings yet
- Akfort Commercial OfferDocument1 pageAkfort Commercial OfferDmitriyNo ratings yet
- Princess Cruise - Southeast Asia 2022 - CDocument2 pagesPrincess Cruise - Southeast Asia 2022 - CHerwanto KwanNo ratings yet
- DI Chapter 1 - TablesDocument10 pagesDI Chapter 1 - TablesOmkar PokaleNo ratings yet
- Political Layers and Geopolitics Political Layer - Power To Control Other States or Nations That Do Not Enjoy Much Power ThatDocument13 pagesPolitical Layers and Geopolitics Political Layer - Power To Control Other States or Nations That Do Not Enjoy Much Power ThatMichael Angelo100% (1)
- FRM 5Document4 pagesFRM 5irfanhaidersewagNo ratings yet
- Financial Stability Report December 2023 Lyst1034Document11 pagesFinancial Stability Report December 2023 Lyst1034Upsc NotesNo ratings yet
- CivPro Case ListDocument7 pagesCivPro Case ListBianca Nerizza A. Infantado IINo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - 3eDocument47 pagesChapter 12 - 3eDJ HoltNo ratings yet
- External Factors Affecting Investment Decisions ofDocument20 pagesExternal Factors Affecting Investment Decisions ofDellNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting and Control Activity 2-Finals (Manufacturing Overhead: Actual and Applied)Document7 pagesCost Accounting and Control Activity 2-Finals (Manufacturing Overhead: Actual and Applied)Saarah KylueNo ratings yet
- Function of Households Reading, Matching, Multiple ChoiceDocument2 pagesFunction of Households Reading, Matching, Multiple ChoiceMikias TewachewNo ratings yet
- 11th Economics EM WWW - Tntextbooks.inDocument288 pages11th Economics EM WWW - Tntextbooks.inBharath KumarNo ratings yet
- SUDAN Investment Prospectus 2021Document59 pagesSUDAN Investment Prospectus 2021Mustafa SaeedNo ratings yet
- Compound Interest MCQSDocument13 pagesCompound Interest MCQSNiranjan BiswalNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Texas Utility Bill PR - 1Document1 pageToaz - Info Texas Utility Bill PR - 1olegdanyleiko2No ratings yet
- Capital InflowsDocument30 pagesCapital InflowsBaigalmaa NyamtserenNo ratings yet
- 06 Annual Worth AnalysisDocument19 pages06 Annual Worth Analysis王泓鈞No ratings yet